Local Government in Rural Areas Chapter Notes | Chapter Notes For Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| How Does Local Governance Work in India's Villages? |

|
| Panchayati Raj System |

|
| Gram Panchayat |

|
| Child-Friendly Panchayat Initiative |

|
| Panchayat Samiti and Zila Parishad |

|
How Does Local Governance Work in India's Villages?
India is a diverse country with around 600,000 villages, 8,000 towns, and over 4,000 cities. Two-thirds of the population lives in rural areas. For example, Lakshmanpur, a small village in the Himalayas, has around 200 houses and 700 people, mainly farmers. Some villagers serve in the armed forces, while others move to cities for better jobs.
India's Panchayati Raj system ensures local governance, allowing people to participate actively in their development. Let’s explore how this system works in Lakshmanpur.

Panchayati Raj System
- In every Indian village, there is a local government system called the 'Panchayat.' This system acts like a village council that assists in governing the village.
- The Panchayat system, also referred to as Panchayati Raj, enables community members to take part in decision-making and manage their own affairs. Democracy in this system functions through both the direct involvement of the people and their elected representatives.
- The Panchayati Raj system operates on three levels: the village, the block, and the district, forming a three-tier system. These institutions cover nearly all aspects of life in the district, including agriculture, housing, road maintenance, water resource management, education, health care, social welfare, and cultural activities.
- At all three levels, special regulations have been established to ensure that disadvantaged groups can voice their needs and issues. There is also a provision to reserve one-third of the seats for women.
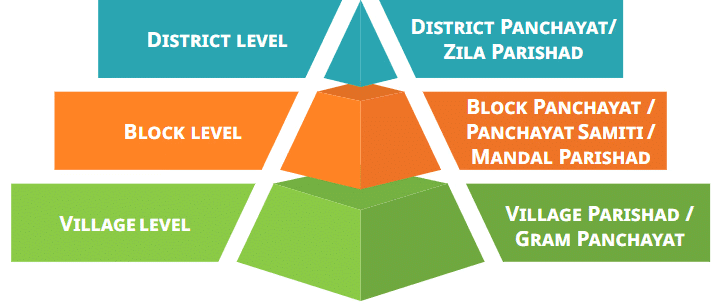
Responsibilities of Panchayati Raj
The Panchayati Raj system operates at three levels, which are the village, the block, and the district, known as a 'three-tier system'. These institutions are responsible for many aspects of life in the district, including:
- Agriculture: Supporting farmers with their work.
- Housing: Ensuring access to housing and necessary infrastructure.
- Road Maintenance: Keeping roads in good repair.
- Water Supply: Guaranteeing sufficient water for everyone.
- Education: Overseeing local schools and educational initiatives.
- Healthcare: Providing access to medical services.
- Social Welfare: Assisting with community support programs.
- Cultural Activities: Promoting and facilitating cultural events.
Active participation from the community and their elected representatives is crucial in the Panchayati Raj system. This allows villagers to address their issues and collaborate on development plans. The Gram Panchayat is chosen directly by the Gram Sabha, which is made up of adults from the village or nearby villages.
Participation and Development
- The Panchayati Raj system encourages active participation from villagers in decision-making and development processes.
- It ensures that the benefits of government schemes reach everyone at the grassroots level, promoting equity and development across the district.
Gram Panchayat
- The Gram Panchayat is the basic unit of local government in villages.
- It is the nearest government body to the people in rural areas.
- Members of the Gram Panchayat are elected directly by the Gram Sabha.
- The Gram Sabha is made up of adults from a village or a group of nearby villages who are enrolled as voters.
- In the Gram Sabha, both women and men discuss local issues and make decisions together.
- Each Gram Panchayat elects a head or president, known as the Sarpanch or Pradhan.
- In recent years, there has been an increase in the number of women becoming Sarpanchs, reflecting greater gender equality in local leadership roles.
Role of Panchayat Secretary
- The Panchayat Secretary assists the Gram Panchayat by performing various administrative functions.
- Their duties include organizing meetings, maintaining records, and ensuring the smooth functioning of the Panchayat.
Role of Patwari
Many Gram Panchayats are supported by an officer known as Patwari. In various regions of India, the Patwari is responsible for maintaining land records for villagers. In some instances, they even preserve old maps that have been passed down through generations!
Exemplary Sarpanchs
The Sarpanch plays a vital role in promoting development and resolving community issues. Here are a few remarkable examples:
- Dnyaneshwar Kamble, a transgender individual, became the Sarpanch of Tarangfal village in Maharashtra's Solapur district in 2017. His motto, "Seva to the village is seva to the public," illustrates his dedication to serving the community. Kamble won the election against six other candidates.
- Vandana Bahadur Maida, a member of the Bhil community from Khankhandvi village in Madhya Pradesh, broke through patriarchal norms to become her village's first female Sarpanch. She motivated local women to engage in Sabha meetings and addressed important matters like education and sanitation, earning significant recognition. Vandana's story shows how women can lead the way in transforming rural India.
- Hiware Bazar, located in Ahmednagar district, Maharashtra, faced severe drought and low agricultural output. Under the guidance of Popatrao Baguji Pawar as Sarpanch, the village implemented Anna Hazare's model for rainwater harvesting, watershed management, and extensive tree planting. These initiatives greatly improved groundwater levels and turned Hiware Bazar into a thriving green village within a few years. In 2020, Shri Popatrao Pawar was awarded the Padma Shri for his contributions.
Child-Friendly Panchayat Initiative
- Panchayats are meant to listen to everyone, including children. The Child-Friendly Panchayat Initiative helps children share their thoughts on things that matter to them.
- In many States, efforts are being made to involve children in Bal Sabhas and Bal Panchayats regularly. Village elders work to address the issues raised by children.
- For Example, Maharashtra has seen Bal Panchayats tackling problems like child labour and child marriage. These groups encourage parents to send their kids back to school and delay marriages for girls who should be studying.
- Some Gram Panchayats have been recognized for their child-friendly efforts . For example, Sikkim's Sangkhu Radhu Khandu Gram Panchayat has focused on children's needs by building compound walls around schools for safety and constructing kitchens to provide hygienic midday meals .

- In Rajasthan, the 'Children's Parliament' initiative, part of Bunker Roy's 'Barefoot College' program, empowers disadvantaged children through education and democratic participation. Children aged 8 to 14 engage in governance, learning about democracy and social responsibility. The initiative includes night schools and parliament-like elections , where children form a Cabinet to oversee school management and address community needs.
- The Children's Parliament has received several awards, including the World's Children's Honorary Award in 2001, for its contribution to community development and social awareness.

Panchayat Samiti and Zila Parishad
Does the Panchayat Samiti function at the block level?
Yes, the Panchayat Samiti operates at the block level, acting as a bridge between the Gram Panchayat at the village level and the Zila Parishad at the district level. It aids in coordinating development programmes and policies across various villages within a block.
- Panchayat Samiti and Zila Parishad are similar organisations located at the block and district levels, respectively, which oversee areas above the village level.
- The Panchayat Samiti links the Gram Panchayat to the Zila Parishad.
- Members of these bodies are elected by local citizens, but may also include members such as Sarpanchs from surrounding villages and local representatives from the State Legislative Assembly.
- The structure of Panchayat Samitis varies by state, yet their role in enhancing local community participation remains constant.

- They coordinate activities across Gram Panchayats, for example, by gathering development plans from all Gram Panchayats and compiling them for presentation at the District or State levels.
- This process is essential for obtaining funding for development projects and government schemes, such as the Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana, which facilitates the construction of all-weather roads in rural areas.
- At all three tiers, specific regulations exist to ensure that the voices and issues of disadvantaged groups are acknowledged.
- These institutions also reserve one-third of the seats for women.
- While the structure and functions of Panchayati Raj institutions might vary slightly among states, their objectives remain aligned.
- The primary goal is to enable villagers to actively engage in the management and development of their villages and local communities.
The Arthashästra: Ancient Wisdom on Governance
- The Arthashästra is a very old book about how to govern a country, written by a wise man named Kautilya, also known as Chänakya, around 2,300 years ago.
- This book talks about many important things, like how to organize and run a state, make the economy strong and prosperous, what a ruler should do, and how to plan for war.
- Kautilya was very knowledgeable about how to manage a state. He wrote about how to set up a system of administration from the village level all the way to the regional capital.
- In the Arthashästra, Kautilya describes how to organize the administration of a state based on the number of villages:
- Sangrahana: For every 10 villages, there should be a sub-district headquarters.
- Kärvatika: For every 100 villages, there should be a district headquarters.
- Dronamukha: For every 400 villages, there should be an administrative unit.
- Sthännya: For every 800 villages, there should be a provincial headquarters.
FAQs on Local Government in Rural Areas Chapter Notes - Chapter Notes For Class 6
| 1. What is the Panchayati Raj System and its significance in rural governance? |  |
| 2. What are the main functions of a Gram Panchayat? |  |
| 3. What is the Child-Friendly Panchayat Initiative? |  |
| 4. How do Panchayat Samiti and Zila Parishad function in the Panchayati Raj System? |  |
| 5. What challenges does the Panchayati Raj System face in its implementation? |  |
















