Class 6 Exam > Class 6 Notes > Year 6 Science IGCSE (Cambridge) > Chapter Notes: Materials: Properties and Changes
Materials: Properties and Changes Chapter Notes | Year 6 Science IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Properties of Substances |

|
| Thermal and Electrical Conductors |

|
| Reversible Changes |

|
| Chemical Reactions |

|
Properties of Substances
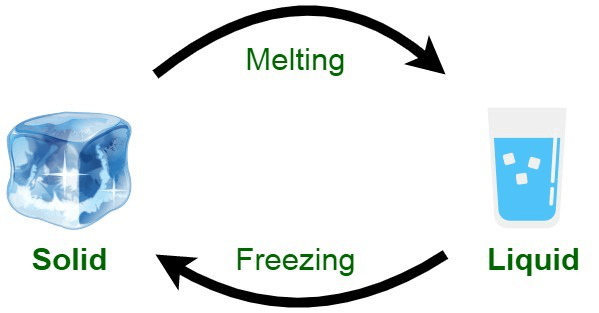
Change of State
- Substances can change their state when they are heated or cooled to certain temperatures. For instance, when ice is heated, it melts and turns into liquid water. Ice melts at a temperature of 0 °C.
- The temperature at which a solid becomes a liquid is known as the melting point. Different substances have different melting points. For example, gold, which is also a solid, has a melting point of 1064 °C.
- Melting point is a characteristic of a substance and helps to distinguish it from other substances. Each substance has its own specific melting point.
- Boiling point is another property of a substance. It is the temperature at which particles throughout a liquid have enough energy to change into a gas.
- Different substances have different boiling points. For example, pure water boils at 100 °C, vinegar boils at 118 °C, and liquid gold boils at 2856 °C.
Boiling and Evaporation
Liquids transform into gases through the processes of boiling and evaporation. However, there are key differences between these two processes.
- Boiling occurs when all the particles in a liquid have enough energy to change into a gas. This process typically requires heating the liquid.
- Evaporation, on the other hand, happens when particles at the surface of a liquid gain enough energy to become gas, and it can occur at any temperature.
Properties of Gases
- Air is composed of a mixture of gases, and gas is one of the fundamental states of matter.
- All matter, including gases, possesses the following properties:
- It occupies space.
- It has mass.
Thermal and Electrical Conductors
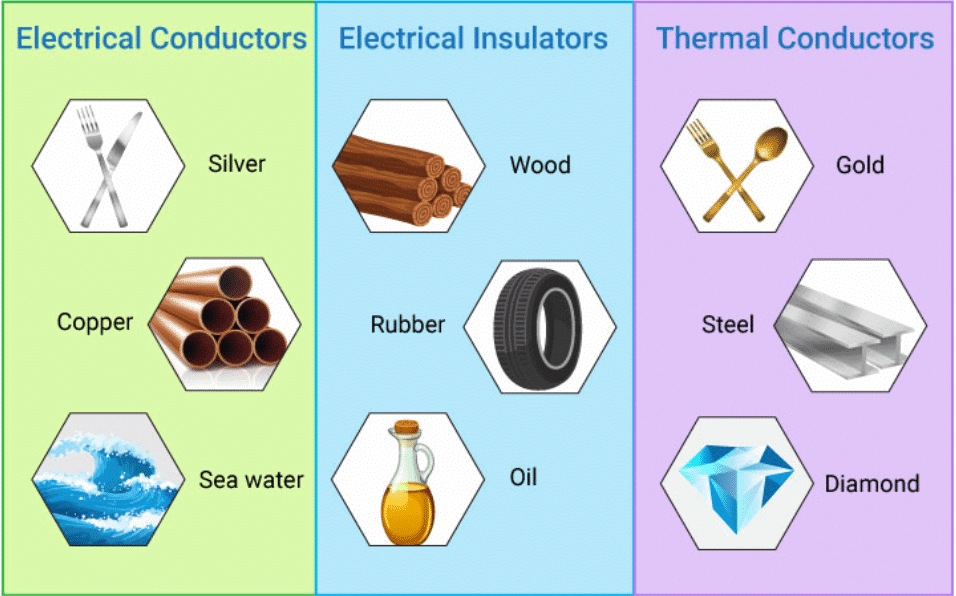
Substances Can Conduct Heat
- Heat can be transferred from one object to another through a process called conduction. Substances and materials that transfer heat effectively are known as thermal conductors.
- Different materials have varying abilities to conduct heat, which is a characteristic property of the substance. Metals, for instance, are excellent conductors of heat, with silver being the best conductor. In contrast, non-metals like glass and plastic are not good at conducting heat.
Substances That Can Conduct Electricity
- Some materials have the ability to conduct electricity, and these are known as electrical conductors.
- Conductivity is a property that certain materials possess, and as you may already know, metals are prime examples of substances that can conduct electricity.
Reversible Changes

Changes to Substances
- When solid ice is placed in a warm environment, it melts and transforms into liquid water. This process is known as a change of state and is classified as a physical change.
- A physical change involves altering the appearance or texture of a substance without creating a new one. The substance remains the same; only its form changes.
- For instance, when water is put back in the freezer, it solidifies again into ice. This phenomenon is called a reversible change because we can switch solid ice to liquid water and vice versa.
- Heating causes ice to melt into liquid water, and when water loses heat and cools down, it becomes solid once more.
- The transformation between ice and water can be represented in writing as follows:
Liquid Water Heating Cooling ⇌ Solid Ice
Irreversible Changes to Substances
- When a match is burned, it undergoes an irreversible change. The wood in the match transforms into a black substance called carbon, indicating a chemical change.
- Unlike reversible changes, where a substance can return to its original state, irreversible changes result in the formation of a new substance.
Dissolving of Substances
- Some substances have the ability to dissolve in water or other liquids. For instance, seawater is salty because it contains dissolved salt.
- It is important to understand that the substance that dissolves is called the solute, while the substance in which the solute dissolves is called the solvent. Together, the solute and solvent form a solution.
- When a solute dissolves, its particles move between the particles of the solvent and spread out evenly. This is why you cannot see the solute in a solution after it has dissolved. A solution has a uniform appearance, meaning it looks the same throughout.
Can We Speed Up the Dissolving of Solids?
- Stirring: When Marcus stirs his coffee, he helps the sugar dissolve faster. Stirring spreads out the sugar particles into the spaces between the water particles more quickly. This is because stirring increases the rate at which a solute, like sugar, dissolves. The rate refers to how fast something happens.
- Temperature: Have you ever wondered why we use hot water to make coffee instead of cold water? The particles in all matter are constantly moving. When we heat a substance, we add energy to its particles, making them move faster and spread out more. In a heated solvent, like hot water, the particles of the solute (sugar, in this case) also gain energy and move faster than they would in cooler water. This extra energy allows the sugar particles to spread through the water more easily, so they dissolve faster.
Chemical Reactions

Reactants and Products
A chemical reaction occurs when certain substances are mixed together and undergo a change to form a new substance. In this process, the substances that are mixed together are called reactants, while the new substances that are produced as a result of the reaction are known as products.
Evidence for Chemical Reactions
There are various ways to determine if a chemical reaction has taken place. One way is by observing the formation of a product, such as when vinegar and bicarbonate of soda react to produce a visible gas. This gas serves as evidence of the reaction occurring.
The document Materials: Properties and Changes Chapter Notes | Year 6 Science IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 6 is a part of the Class 6 Course Year 6 Science IGCSE (Cambridge).
All you need of Class 6 at this link: Class 6
|
29 docs|6 tests
|
FAQs on Materials: Properties and Changes Chapter Notes - Year 6 Science IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 6
| 1. What are thermal conductors and why are they important? |  |
Ans.Thermal conductors are materials that allow heat to pass through them easily. They are important because they are used in applications where heat transfer is essential, such as in cooking utensils, heat exchangers, and electrical components that need efficient cooling.
| 2. What are electrical conductors and how do they differ from insulators? |  |
Ans.Electrical conductors are materials that allow electric current to flow through them easily, while insulators resist the flow of electric current. Conductors, such as copper and aluminum, are commonly used in wiring and electronic devices, whereas insulators, like rubber and glass, are used to protect and separate conductors.
| 3. What are reversible changes in materials? |  |
Ans.Reversible changes are alterations in a substance that can be undone, returning the material to its original state. Examples include melting ice into water and then freezing it back to ice. These changes do not alter the chemical composition of the material.
| 4. What is a chemical reaction and how can it be identified? |  |
Ans.A chemical reaction is a process in which substances (reactants) change into new substances (products) with different properties. Indicators of a chemical reaction can include color change, gas production, temperature change, and the formation of a precipitate.
| 5. How do properties of materials influence their use in real-world applications? |  |
Ans.The properties of materials, such as conductivity, malleability, and reactivity, determine how and where they can be used. For example, metals with high thermal conductivity are used in cookware, while materials that are resistant to corrosion are chosen for outdoor construction to ensure durability.
Related Searches




















