Nature’s Treasures Chapter Notes | Chapter Notes For Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Air |

|
| Water |

|
| Energy from the Sun |

|
| Fossil Fuels |

|
Introduction
One day, Riya and Aman were walking through a beautiful forest when they met an old wise man sitting under a big tree. He smiled and asked, "Do you know the greatest treasures in the world?"
Riya quickly said, "Gold and diamonds!" Aman added, "Maybe money?"
The wise man laughed and pointed around them. "The real treasures are all around you! The air you breathe, the water in the rivers, the sunlight that warms you, the trees that give fruits, and the soil that grows food. Without these, life wouldn’t exist!"
Riya and Aman looked around in wonder. They realized that nature had been giving them these gifts every day, yet they never thought of them as treasures!
Natural treasures are the elements and resources that nature provides, crucial for the survival of all living beings and improving our quality of life. These treasures include air, water, sunlight, soil, plants, animals, and minerals. Each of these resources plays a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance and supporting life on Earth.
This chapter will help us discover these natural treasures and learn why we must protect them for a better future.
Air
What is Air?
The invisible gas we call air is a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, water vapour, and other gases. It may also contain some dust particles.
- Oxygen is essential for combustion and is vital for living organisms.
- Air is colourless and can be seen through; it is transparent.
- Air takes up space and exists in both water and soil.
- The layer of air surrounding the Earth is referred to as the atmosphere.
- The atmosphere is essential for life on our planet.
- Aquatic animals breathe by using dissolved air in water.
- Plants and animals depend on one another to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide from the air.
- The largest component of air, which does not support combustion, is nitrogen. The remaining 1% consists of carbon dioxide, a few other gases, and water vapour.
What happens if we hold our breathe for too long?
If we hold our breath for too long, our body doesn’t get enough oxygen, which makes it hard to function. This is why we need oxygen to stay alive.

- The air we breathe contains oxygen.
- Our body requires oxygen to work properly.
- If we hold our breathe for too long, we don't get enough oxygen, affecting our ability to function. Thus, oxygen is essential for our survival.
- Similarly, most living things also depend on oxygen to live.
Do you know?
- We can live without food or water for several days, but we cannot survive without oxygen for more than a few minutes.
Composition of Air
Air is a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, water vapour, and a few other gases. The layer of air around the Earth is called the atmosphere, which is essential for life. Air is colourless and transparent, meaning we can see through it. It occupies space and can also be present in water and soil.
- Nitrogen (78%): This is the most common gas in the atmosphere, and it does not support burning.
- Oxygen (21%): This gas is essential for breathing and burning.
- Other Gases (1%): This includes argon, carbon dioxide, neon, helium, methane, and a few others.
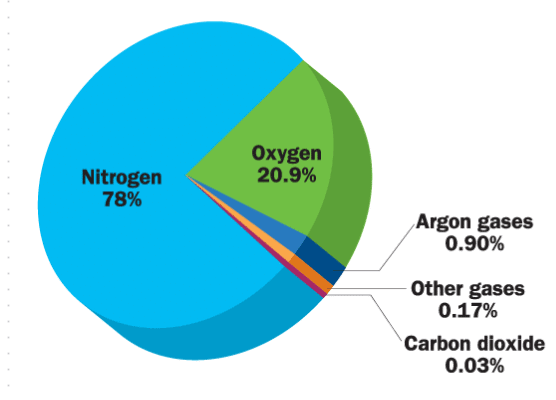
The term percentage indicates parts out of 100, symbolised by '%'.
Characteristics of Air
Air is invisible, but its presence can be observed through its effects. For example:
- Wind: Moving air, which can vary from gentle breezes to strong storms.
- Physical Effects: Rustling leaves, fluttering pages of a book, or swaying clothes on a clothesline.
Do you know?
Some of the top windmill farms in India include the Muppandal Wind Farm in Tamil Nadu, the Jaisalmer Wind Park in Rajasthan, and the Brahmanvel Wind Farm in Maharashtra.
Water
It is common knowledge that water is important on our Earth and without water, life as we know it would cease to exist. While Earth has an abundant reservoir of water, covering three-fourths of its surface, freshwater is a mere 2.6% of the total water. Water is said to be a renewable resource but the rate at which humans and animals are using water, fresh water might be a scarce resource in the recent future. Our body is also made up of 70% water and we use water for a number of reasons from cooking to cleaning and of course drinking it.

Uses of Water in Daily Life
- Drinking: Water is important for staying hydrated and healthy.
- Cooking: Water is used for making meals and drinks.
- Bathing: Water is important for personal hygiene.
- Washing: Water cleans clothes, dishes, and household items.
- Cleansing: Water helps clean different surfaces in the home.
- Agriculture: Water is essential for growing crops and supporting agricultural activities.
- Industrial Purposes: Water is used in many industrial processes and manufacturing.
It's important to save water and use it wisely. Water is valuable, so we should encourage others to use it carefully.
Sources of Water
- Rivers: Flowing freshwater that is important for drinking, irrigation, and industry.
- Lakes: Large inland freshwater bodies used for various needs.
- Ponds: Smaller freshwater areas for irrigation and local requirements.
- Wells: Deep holes in the ground to reach underground freshwater.
Understanding Water Pollution and Conservation
- Water pollution happens when we throw rubbish and waste into freshwater sources like rivers, lakes, and ponds. Water that is polluted is unsafe for living beings to drink. As freshwater sources are limited, many areas in India experience a water shortage. Access to water is not equal for everyone, making it crucial to conserve water and use it wisely. We should also keep water clean and prevent pollution to ensure it remains safe for all. Rainwater harvesting is one of the methods for conserving water.
Rainwater Harvesting
Harvesting is a method to collect rainwater and store the rainwater. The purpose of harvesting rainwater is that two-thirds of the earth is covered with water. Ocean and seawater contain many dissolved salts and cannot be used for drinking, agriculture and domestic purposes. So constant use of groundwater results in scarcity of groundwater. So rain harvesting clears the problem of depleting the groundwater.
Technique involved in Rainwater Harvesting
First, collect the rainwater at the rooftop and then allow the rainwater to travels through the pipes or drains and then attach a wire mesh to the mouth pipe which filters large fragments such as leaves etc. This water is transported to the water tanks. These tanks contain layers of sand, gravel, charcoal that will filter the dirt and other impurities from rainwater.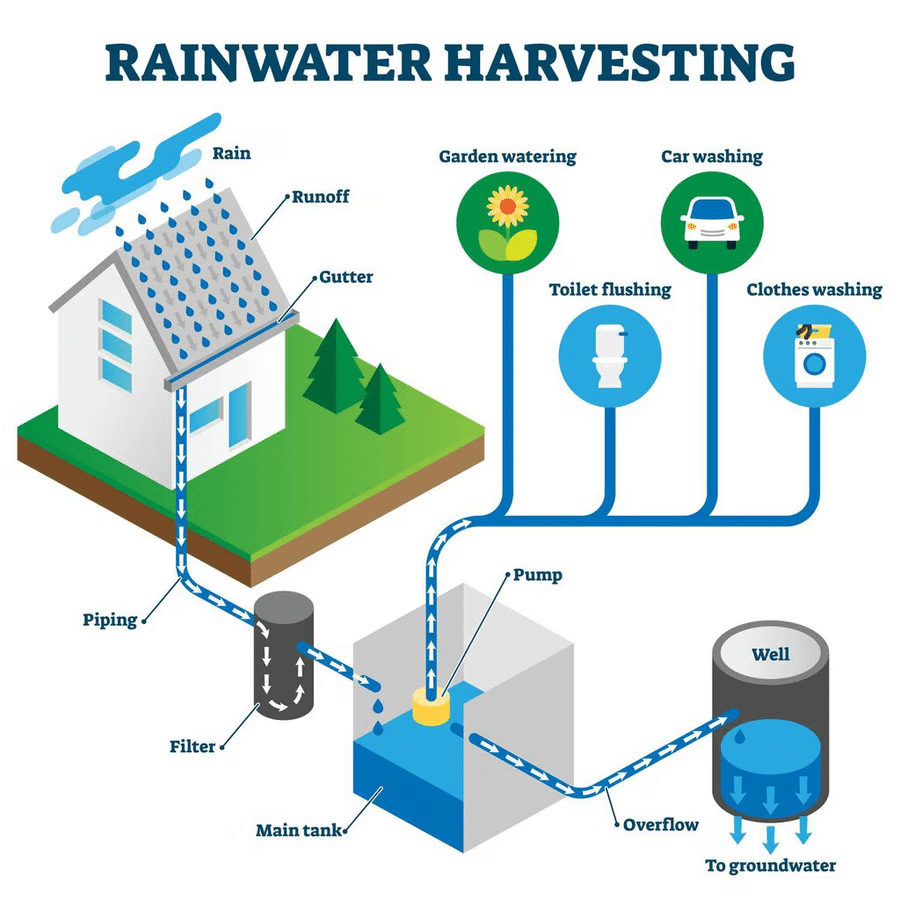
Some regions use traditional methods, like stepwells (Bawadi in Rajasthan and Vav in Gujarat), to gather rainwater and water from nearby lakes, ponds, and rivers.
Trenches, which are deep holes dug in the ground, have their walls lined with stones to allow water seepage.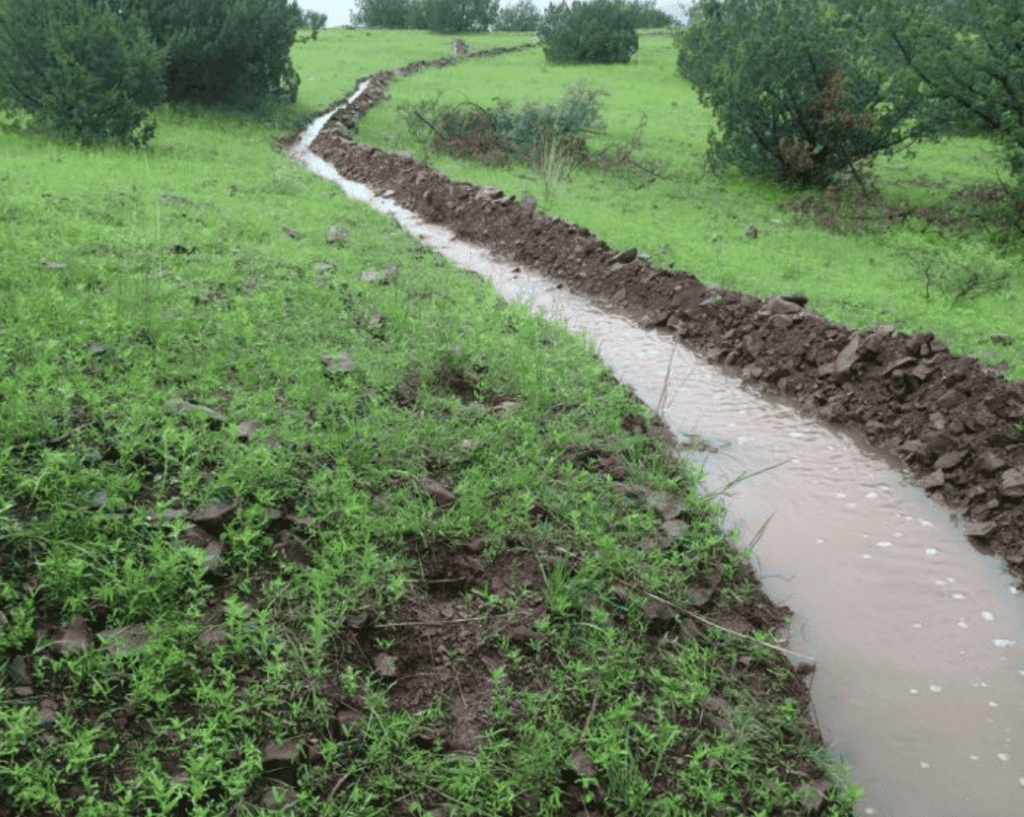
World Water Day
World Water Day is celebrated on 22nd March each year. It highlights the need to conserve water and avoid pollution, ensuring it remains safe for all living beings. How can you conserve water?
Energy from the Sun
What are some ways we can use the Sun's energy directly?
We can use the Sun's energy directly for cooking in a solar cooker and for heating water in a solar water heater.
The importance of sunlight as the main source of energy:
- Sunlight helps plants make their food. The Sun provides warmth and light to all living things. Life on Earth relies on the Sun.
- Solar panels collect the Sun's energy to create electricity.
- We can also use energy from the Sun directly for cooking in a solar cooker or for heating water in a solar water heater.
- The Sun is essential for life. Plants use the Sun's energy to produce food, which animals consume. This cycle relies on the Sun, making it our main energy source.
- The Sun plays an important role in the water cycle by causing water to evaporate.
Forests
Forests are one of the most important natural treasures on Earth. They are large areas covered with trees, plants, animals, and birds. Forests provide us with fresh air, wood, medicines, and food. They also help in keeping the environment clean and protecting wildlife. Forests are called the "lungs of the Earth" because they give us oxygen and absorb carbon dioxide. Many animals like tigers, elephants, deer, and monkeys live in forests, making them their home. However, over the years, the forest cover has been decreasing mainly due to human activities like large-scale cutting of trees. It takes many years to restore lost forests. Therefore, we must preserve and use forests responsibly.

Importance of Forests for Wildlife
- Forests provide a natural habitat for many wild animals, birds, and insects, offering them food and shelter.
- The variety of life in forests ensures that all creatures have enough food. For instance, plants yield fruits, seeds, and leaves, while other animals may supply decaying flesh or prey.
- Forests are essential for maintaining nature's balance, as every animal relies on other living beings for survival.
Forest Conservation
Threats to Forest Cover
- The area of forest cover has been shrinking over the years, largely due to human actions such as extensive tree felling for agriculture, urban expansion, and logging.
- Growing a new forest or restoring lost ones takes a long time. Thus, it’s essential to conserve and responsibly use forests to give them a chance to regenerate.
Van Mahotsav: A Festival for Forests

- Van Mahotsav is a week-long celebration held in July throughout the country to support forest conservation.
- During this event, new plants and trees are planted, and awareness about the importance of respecting forests is raised.
- The goal is to enhance green cover and encourage communities to participate in efforts to conserve forests.
Do you know?
Since ancient times, India has respected and protected forests. This includes the idea of sacred groves, which you have learned about in the chapter 'Diversity in the Living World'. Many people have worked hard to stop tree cutting and save forests. A notable example is the Chipko movement, which began in the early 1970s in Uttarakhand (formerly part of Uttar Pradesh). Local women participated by hugging trees to shield them from being cut down.
Forests are crucial for our ecosystem, and it is important to protect and use them responsibly to allow time for regeneration. The rising demand for trees for industry and housing has resulted in widespread deforestation, which can severely harm the environment.
Soil, Rocks, and Minerals
Soil

- Soil contains various elements such as sand, insects, and worms, along with many tiny organisms that are invisible to the naked eye.
- When plants and animals die, they decompose and enrich the soil, contributing to its makeup.
- Soil samples from different areas can differ in colour due to the variety of materials present.
- Soil is created through the gradual breakdown of rocks by the Sun, water, and living organisms over thousands of years.
- Different types of soil are suitable for specific uses; some are great for growing certain plants, while others are ideal for making bricks for construction.
- Forests host a diverse range of soils.
Rocks
- Rocks are commonly seen around us and are used in the building of houses, buildings, roads, and other structures.
- Some rocks, like slate, are used for roofing, while laterite can be made into bricks.
- Notable rocks include granite, sandstone, and marble.
- For thousands of years, humans have relied on rocks to create tools like hand axes and arrowheads.

Minerals
- Rocks are composed of minerals, from which essential metals like aluminium, gold, copper, and iron are extracted.
- Minerals are crucial for manufacturing items such as airplanes, cars, jewellery, cosmetics, and electrical equipment.
- For instance, basic mobile phones contain around a dozen minerals, including gold, silver, copper, and cobalt.
- The formation of rocks takes thousands to millions of years, making it important to use and conserve them wisely.
Fossil Fuels
- Fossil fuels are created from the remains of small organisms and plants buried deep within the Earth.
- Over millions of years, these remains become petroleum, natural gas, and coal.
- Petroleum, natural gas, and coal are collectively known as fossil fuels.
- Fossil fuels exist in limited amounts; if we keep using them as we do now, they will run out soon.
- To prevent this, we need to look for alternative energy sources.
Common Types of Fuels
- Petrol and diesel are the most commonly used fuels for vehicles.
- Petrol, diesel, and kerosene come from petroleum.
- Natural gas is used for cooking and generating electricity; it is now also used as Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) for vehicles. It is a cleaner option than petrol or diesel.
- Coal is primarily used for electricity generation and is found in several regions of India.

Do you know?
- Traditional Cooking Fuels: Historically, people used coal, wood, and dung cakes for cooking. These were common but not environmentally friendly.
- Modern Cooking Fuels: Today, many households have switched to natural gas and Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG). These options are cleaner and more efficient, making them better for the environment and cooking.
Environmental Impact
- Burning fossil fuels produces smoke and carbon dioxide, which pollutes the air.
- Heavy reliance on fossil fuels for transport and home use has led to significant air pollution.
Conserving Fossil Fuels
- Fossil fuels exist in limited amounts, and if we continue to use them the way we do now, they will soon be exhausted.
- To prevent this, we must look for alternative energy sources.
- Moreover, burning fossil fuels releases smoke and carbon dioxide, which adds to air pollution.
- Heavy reliance on fossil fuels for transport and home energy has led to significant air pollution.
- It’s important to know the difference between renewable and non-renewable resources. Fossil fuels are non-renewable, while sources like solar and wind energy are renewable.
Natural Resources: Renewable and Non-renewable
Natural resources help us create many useful items that improve our daily lives, including electric bulbs, furniture, solar panels, and bicycles.
The importance of natural resources:
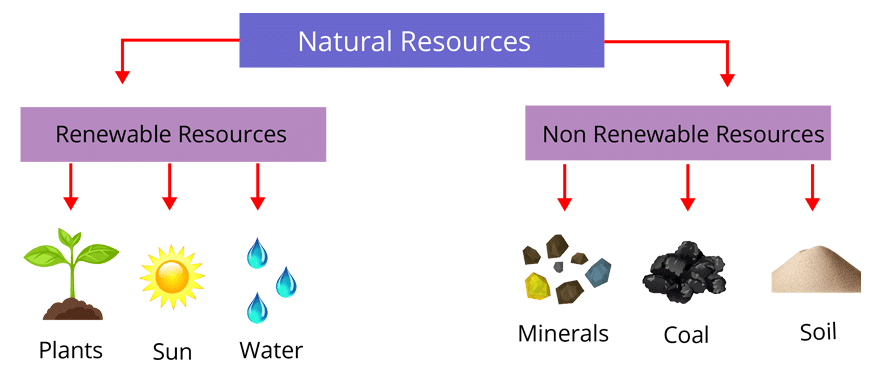
- Natural resources are materials provided by nature, essential for sustaining all life on Earth.
- For instance, we get heat and light from the Sun, water from rivers, and food from plants and animals, all crucial for our survival.
Types of Natural Resources
Resources essential for our existence come from nature, known as natural resources. They can be divided into two categories: renewable and non-renewable resources, based on how quickly they can be replenished.
- Renewable Resources: These resources can be naturally renewed or restored over time. Examples include air, water, and forests. Since all living beings, including humans, depend on these resources, we should use them wisely.
- Non-Renewable Resources: These resources exist in finite amounts and cannot be replenished quickly once used. Examples include minerals, soil, rocks, coal, petroleum, and natural gas.
Resources created by humans to satisfy their needs are referred to as human-made resources.
Resources We Use

- Natural resources such as air, water, soil, plants, and animals are vital for our everyday lives. They help fulfil our needs and support all life on Earth.
- Key natural resources include air, water, sunlight, forests, soil, rocks, minerals, and fossil fuels, which we use to create useful items like electric bulbs, furniture, solar panels, and bicycles.
- We get all the resources from nature. Therefore, we must conserve our natural resources and use them responsibly withouot wasting them. This way, we can continue to fulfill our present needs while also saving for the future without harming the environment.
Key Points
- Natural resources are divided into renewable and non-renewable types. Renewable resources can naturally replenish over time, while non-renewable resources are limited and cannot be easily replaced.
- Human-made resources are created by people to satisfy their needs.
- Air is crucial for breathing and life, made up of nitrogen, oxygen, and other gases.
- Water is essential for life, serving many purposes, and must be conserved and kept clean.
- The Sun provides energy for various life processes and human activities.
- Forests are vital for biodiversity, soil preservation, and climate control.
- Soil comes from weathered rocks and is necessary for plant growth.
- Rocks and minerals are used in building and manufacturing.
- Fossil fuels are energy sources derived from ancient living things, but they can harm the environment.
- Conserving natural resources is crucial for sustainability and future generations. All living beings, including humans, rely on these resources, so we should use them wisely.
FAQs on Nature’s Treasures Chapter Notes - Chapter Notes For Class 6
| 1. What are the main categories of natural resources? |  |
| 2. How does rainwater harvesting work and why is it important? |  |
| 3. What role do forests play in the environment? |  |
| 4. What are fossil fuels and why are they considered non-renewable resources? |  |
| 5. How does solar energy contribute to sustainable living? |  |






















