Class 7 Civics Chapter 1 Notes - On Equality
What is Equality and Equal Voting Rights?
Equality is a fundamental condition where everyone is given equal opportunities, regardless of their background. It's a cornerstone of democracy, ensuring that every individual's dignity is recognized and respected.
- Universal Adult Franchise: In India, this principle is closely tied to the Universal Adult Franchise, which grants all adults the right to vote, irrespective of religion, caste, education, or wealth.
- Kanta's Experience (in the chapter) highlights the essence of equality. Kanta, a domestic worker, feels a sense of equality when she votes because everyone, rich or poor, has only one vote. However, her daily struggles, such as poor living conditions and the inability to afford medical care, reveal the gaps between theoretical equality and real-life inequalities.
Forms of Inequality in India
Despite constitutional safeguards, various forms of inequality, such as caste and religious discrimination, continue to impact people's lives and dignity. Here are the different forms of Inequality in India.
 Inequality in India
Inequality in India
- Caste-Based Inequality: The caste system still influences people's lives in both rural and urban areas. For example, Dalit writer Omprakash Valmiki faced severe discrimination in school, where he was forced to sit separately and clean the school grounds, violating his dignity.
- Religious Inequality: The Ansaris' Story exemplifies religious discrimination. Despite having the means to rent an apartment, Mr. and Mrs. Ansari were repeatedly turned away due to their Muslim faith, showing how deeply ingrained prejudices can be.
- Recognizing Dignity and Equality: When individuals are treated unequally based on their caste, religion, or economic status, their dignity is violated. Omprakash's father insisted on his son's right to education, and the Ansaris refused to hide their religion to avoid discrimination, both standing up for their rights and dignity.
Equality in Indian Democracy
Indian democracy upholds the principle of equality, recognizing all individuals as equals regardless of gender, caste, religion, tribe, education, or economic background. The Constitution of India has special rules to make sure everyone is equal:
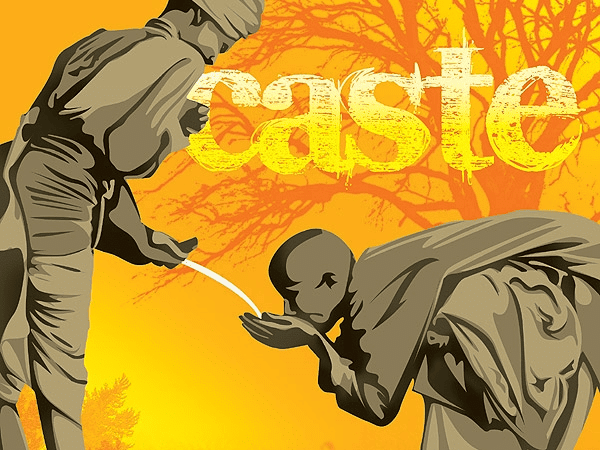 Untouchability
Untouchability
- Equality Before the Law: Every person, from the President to an ordinary citizen, must follow the same laws.
- Non-Discrimination: No one can be discriminated against based on religion, race, caste, gender, or place of birth.
- Access to Public Places: All individuals have the right to access public spaces like parks, hotels, and shops.
- Abolition of Untouchability: The Constitution abolishes untouchability, ensuring equal treatment for everyone.
Government Efforts to Promote Equality
The Indian government enforces equality through laws and schemes designed to protect citizens' rights and uplift disadvantaged communities.
- The government promotes equality through laws and programmes aimed at helping disadvantaged communities.
- There are various laws in India that safeguard everyone's right to be treated equally.
- In addition to these laws, the government has implemented numerous schemes designed to uplift communities and individuals who have faced inequality for centuries.
- These schemes aim to provide greater opportunities for people who have been historically marginalized and denied such opportunities.
 Mid-Day Meal Schemes
Mid-Day Meal Schemes
Midday Meal Scheme: The midday meal scheme is a government initiative aimed at providing cooked lunches to children in all government elementary schools. This program was first introduced in Tamil Nadu, and in 2001, the Supreme Court directed all state governments to implement it within six months. 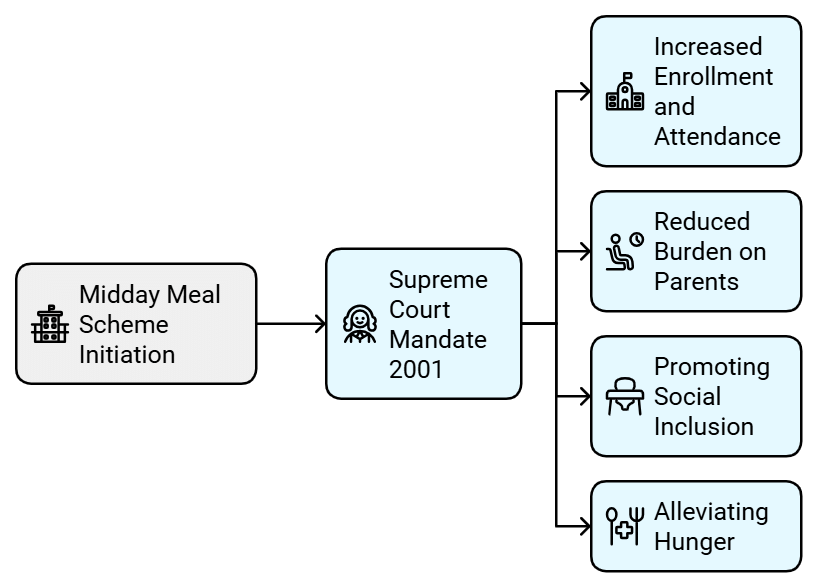
Impact:
- Increased Enrollment and Attendance: The scheme has led to more poor children enrolling in and regularly attending school. Previously, many children would go home for lunch and not return, but the provision of midday meals has improved attendance.
- Reduced Burden on Parents: Mothers no longer need to interrupt their work to feed their children at home during the day, as the meals are provided at school.
- Promoting Social Inclusion: The program has helped reduce caste prejudices by having children of all castes eat the same meal together. In some areas, Dalit women are employed to cook the meals, promoting social inclusion.
- Alleviating Hunger: The midday meal helps alleviate hunger for poor students who often come to school with empty stomachs, allowing them to concentrate better on their studies.
Government programs have made progress in promoting equality of opportunity, but significant challenges remain. For instance:
- The midday meal program has successfully increased enrollment and attendance of underprivileged children in schools.
- However, there are still stark disparities between schools attended by the wealthy and those attended by the poor.
- Discrimination against Dalit children persists in some schools, where they are treated unequally and their dignity is not respected.
- This ongoing discrimination is partly due to the slow change in attitudes. Despite awareness that discrimination is illegal, many people continue to treat individuals unequally based on caste,religion,disability,economic status, and gender.
- Real change will occur only when society collectively believes that everyone is equal and deserves to be treated with dignity.
- Establishing equality in a democratic society is an ongoing struggle, with contributions from individuals and various communities in India.
Need for Ongoing Efforts: Continuous action is required to address these challenges and fully realize the principle of equality in society.
Issues of Equality in other Democracies
The struggle for equality is not just an issue in India. Other democracies also face similar challenges:
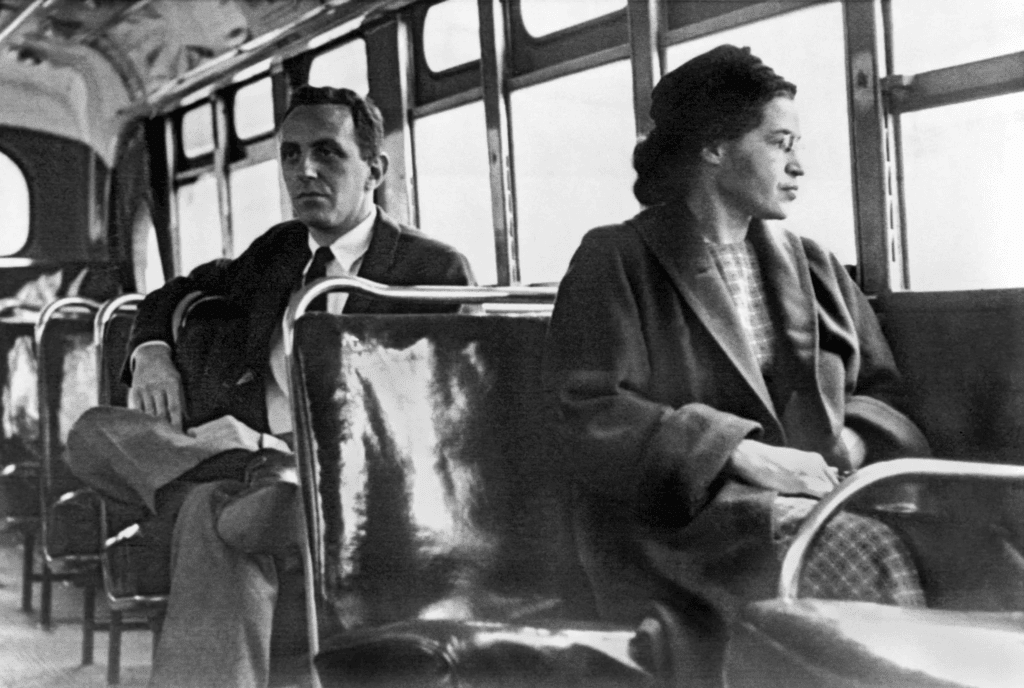 Rosa Parks, an African–American woman, changed the course of American history with one defiant act.
Rosa Parks, an African–American woman, changed the course of American history with one defiant act.
- Many democratic countries face challenges related to equality, similar to India.
- United States Example: In the U.S., African Americans, whose ancestors were slaves, still experience significant inequality despite efforts for equal rights.
- Historically, African Americans faced severe discrimination, such as being forced to give up their bus seats for white passengers.
- Rosa Parks: In 1955, Rosa Parks, an African American woman, refused to give up her bus seat to a white man, sparking the Civil Rights Movement.
- Civil Rights Act of 1964: This law aimed to eliminate discrimination based on race, religion, or national origin, ensuring African American children could attend the same schools as white children.
- Ongoing Struggles: Despite these legal advancements, many African Americans still face poverty and attend underfunded government schools with fewer resources compared to white students, who often have access to better-funded private schools or high-quality public schools.
Challenge of Democracy
Democracy is an ongoing process that constantly needs improvement.
- No country is perfectly democratic.
- People and communities continue to work towards making democratic principles stronger.
- One of the biggest challenges is ensuring everyone is treated equally and with respect.
Excerpt from Article 15 of the Indian Constitution
Article 15 of the Indian Constitution prohibits discrimination based on religion, race, caste, sex, or place of birth.
- The government cannot discriminate against any citizen based on religion, race, caste, gender, or birthplace.
- No one can be denied entry to public places like shops, hotels, or places of entertainment based on these factors.
- Everyone has the right to use public facilities like wells, tanks, roads, and parks without discrimination.
|
63 videos|371 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Civics Chapter 1 Notes - On Equality
| 1. What does Article 15 of the Indian Constitution state about equality? |  |
| 2. How does equality in Indian democracy manifest in voting rights? |  |
| 3. What are some forms of inequality present in India? |  |
| 4. What challenges does democracy face in ensuring equality? |  |
| 5. How are issues of equality addressed in other democracies around the world? |  |

















