Organisms and Population Chapter Notes | Biology Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is an Organism? |

|
| Population |

|
| Population Growth |

|
| Population Interaction |

|
What is an Organism?
An organism is the fundamental unit of life, exhibiting growth, reproduction, and responsiveness to its environment. Comprised of cells working in concert, organisms possess specialized structures and organs essential for survival. Interacting within ecosystems, they form intricate food chains and ecological bonds, capable of adaptation and evolutionary change to enhance their survival prospects.
Population
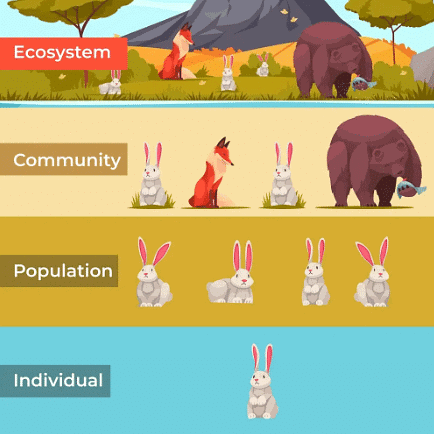
Populations, comprising individuals of the same species sharing resources and residing within a defined geographic area, possess the capacity for interbreeding. Subject to dynamic shifts influenced by birth, death, immigration, and emigration, populations exhibit species-specific traits and behaviors shaped by genetic diversity and environmental factors. Evolutionary processes, chiefly driven by natural selection, operate at the population level.
Key attributes distinguish populations from individuals:
- Death and Birth Rates: Population-level metrics indicating the number of deaths and births per thousand individuals within a specific area and timeframe.
- Sex Ratio: The proportion of females to males within a population, typically expressed as the number of females per 1000 males, reflecting gender distribution.
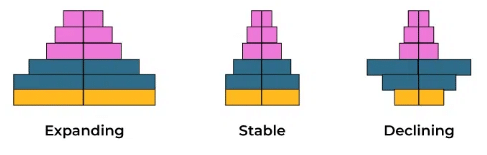
- Age Pyramid: Graphical representation of population age distribution, illustrating the percentage of individuals across various age groups. The shape of the pyramid indicates the population's growth trajectory—whether increasing, stable, or declining.
Size of a Population
It indicates the status of the population in the habitat. It is measured in the form of population density, that is the number of individuals per square unit of the area. Its evaluation helps in, for example, investigating the impact of a predator in a habitat or the effect of a pesticide application in an area.
Population Growth
Population size for a particular species fluctuates over time due to various factors such as food availability, predation pressure, and adverse weather conditions. These fluctuations indicate whether the population is experiencing growth or decline. Four key processes influence population density within a given habitat:
- Natality: The rate of live births within a specific population over a defined period.
- Mortality: The rate of deaths within a specific population over a defined period.
- Immigration: The influx of individuals from outside the habitat into the population during the specified timeframe.
- Emigration: The departure of individuals from the population to other habitats during the specified timeframe.
Populations grow through births and immigration and decline through deaths and emigration. Population density is mainly impacted by births and deaths, while the other two factors(immigration and emigration) become significant only in specific circumstances.
Population Growth Models
These are used to analyze and predict the growth of organisms, populations, and biological systems over time. Helps to understand the dynamics of growth, the underlying factors that drive it, and how it changes over time. The two growth models explained here are:
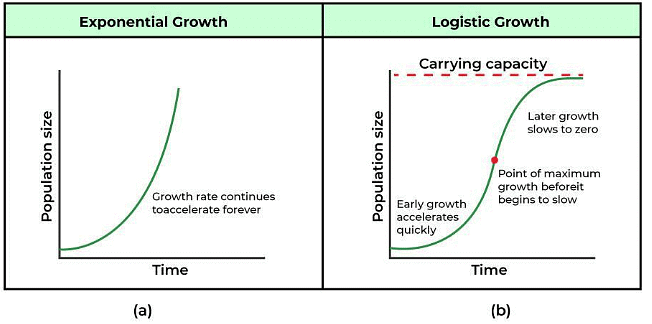
Exponential Growth Models
Assumes that there are no limiting factors and that resources are unlimited. The size of the population increases at a rate that is proportional to the current size of the population, leading to a steady increase in population size over time. Graphically, represented as ‘J’ shaped.
If in a population of size N, the birth rates are represented as b and death rates as d, then the increase or decrease in N during a unit time period t (dN/dt) will be
- dN/dt = (b – d) × N
Let (b–d) = r, then dN/dt = rN
The r in this equation is called the ‘intrinsic rate of natural increase’, it assesses the impact of biotic and abiotic factors on population growth.
Logistics Growth Models
Describes the population in an area having limited resources(called as nature’s carrying capacity), initially it exhibits a lag phase, followed by phases of acceleration and deceleration, finally when the population density attains the carrying capacity, it reaches an asymptote. Defines the concept of ‘survival of the fittest’.
Graphically, represented as a sigmoid curve. This type of population growth is called Verhulst – Pearl Logistic Growth. Described by the following equation:
dN/dt = rN{K-N}/K
- N = Population density at time t
- r = Intrinsic rate of natural increase
- K = Carrying capacity
Life History Variation
Population in a habitat evolves to maximize their reproductive fitness, also known as Darwinian fitness(high “r” value). Through a specific set of selection pressures, organisms adapt to achieve the most efficient reproductive strategy. The biotic and abiotic factors of habitat influence the evolution of organisms.
Population Interaction
Two different species of population interact with each other to form interspecific interactions, that could be beneficial, detrimental, or neutral to one of the species or both. Interaction between the two species can be classified as:
- Competition (both species suffer),
- Predation and Parasitism (one benefits and the other suffers),
- Commensalism (one benefits and the other is unaffected),
- Amensalism (one is harmed, other unaffected) and
- Mutualism (both species benefit).
 |
Download the notes
Chapter Notes: Organisms and Population
|
Download as PDF |
Predation
Predation serves as a natural mechanism for transferring energy from plants to higher trophic levels in ecosystems while regulating prey populations. This phenomenon is utilized in biological pest control methods in agriculture to manage pest populations and contribute to species diversity by reducing prey competition.
Predators exhibit strategic behavior, prompting prey species to develop various defense mechanisms to minimize predation effects. Examples include the Monarch butterfly's distastefulness and insect camouflage.
Plants employ diverse defense mechanisms, including mechanical structures like cactus thorns and chemical compounds, to deter herbivores and protect themselves.
Competition
Competition occurs when one species significantly impacts the fitness of another due to resource limitations. Competitive exclusion, illustrated by Gause's Principle, results in the elimination of less competitive species when closely related species compete for the same resources.
Parasites detrimentally affect host survival and reproduction, often with complex life cycles involving intermediate hosts or vectors. Parasites exhibit adaptations such as adhesive organs and high reproductive rates, and many are host-specific.
Parasitism
Types of Parasitism include ectoparasites (e.g., ticks), endoparasites (e.g., liver flukes), and brood parasitism in birds (e.g., cuckoos laying eggs in other bird species' nests).
Commensalism
Commensalism describes interactions where one species benefits while the other remains unaffected. Examples include cattle egrets benefiting from foraging near cattle without harming them.
Mutualism benefits both interacting species, as seen in relationships like lichens (fungi and algae) and mycorrhizal associations between fungi and plant roots. Plant-animal mutualisms involve co-evolution, such as the symbiotic relationship between fig trees and wasps aiding in pollination and food dispersal.
|
78 videos|280 docs|174 tests
|
FAQs on Organisms and Population Chapter Notes - Biology Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is an organism? |  |
| 2. What is population growth? |  |
| 3. How do populations interact with each other? |  |
| 4. What are some examples of population interactions? |  |
| 5. How does understanding organisms and populations help in ecological studies? |  |