Our Sky Class 4 Notes EVS Chapter 10 Free PDF
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Pictures of the Sky |

|
| The Shadows |

|
| Play with Shadows |

|
| Night Sky |

|
| India’s Chandrayaan Mission |

|
| Points to Remember |

|
| Difficult Words |

|
Introduction
Have you ever looked up at the sky? The sky looks different at different times of the day — in the morning, afternoon, and night. The colour of the sky changes throughout the day. The Sun’s colour also seems to change during the day. The Moon looks different too — its size and shape change over time. Birds, animals, trees, and people all do different activities at different times of the day.
Let’s explore more about how the sky changes and how living things behave during the day and night!
Pictures of the Sky
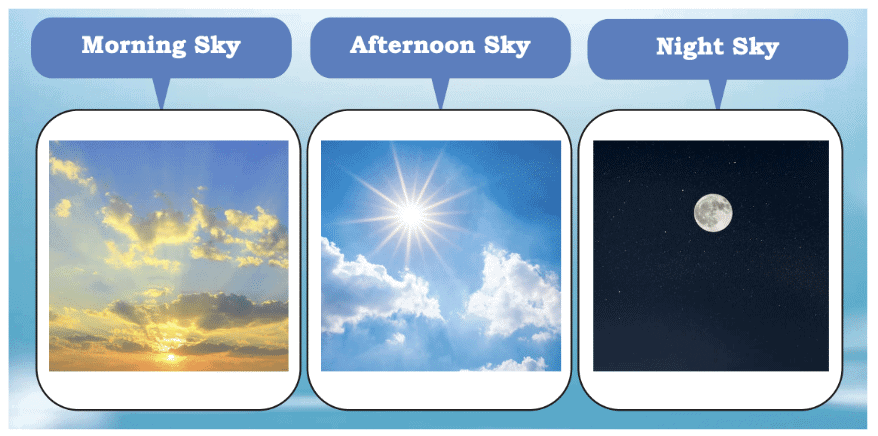
The sky changes appearance throughout the day:
- In the morning, it is orange and bright.
- In the afternoon, it is blue and clear.
- At night, it is dark with twinkling stars.
The Sun also changes colour:
- It appears reddish in the morning and evening.
- It looks bright yellow at noon.
The shape of the Moon varies:
- On some nights, it appears as a complete circle, known as Poornima or the full Moon.
- On other nights, it looks like the letter 'C', and on some occasions, it is not visible at all, called Amavasya or the new Moon.
Sky during sunrise and sunset:
- Sunrise: The sky turns orange and pink, birds chirp, animals wake up, and people start their day.
- Sunset: The sky becomes red or purple, birds return to their nests, animals rest, and people relax at home.
The Shadows
Shadows are dark shapes formed when an object blocks light. This section explains how shadows change throughout the day because of the Sun’s movement:
- Morning: Shadows are long and extend towards the west.
- Noon: Shadows are short as the Sun is directly overhead.
- Evening: Shadows become long again but now point towards the east.
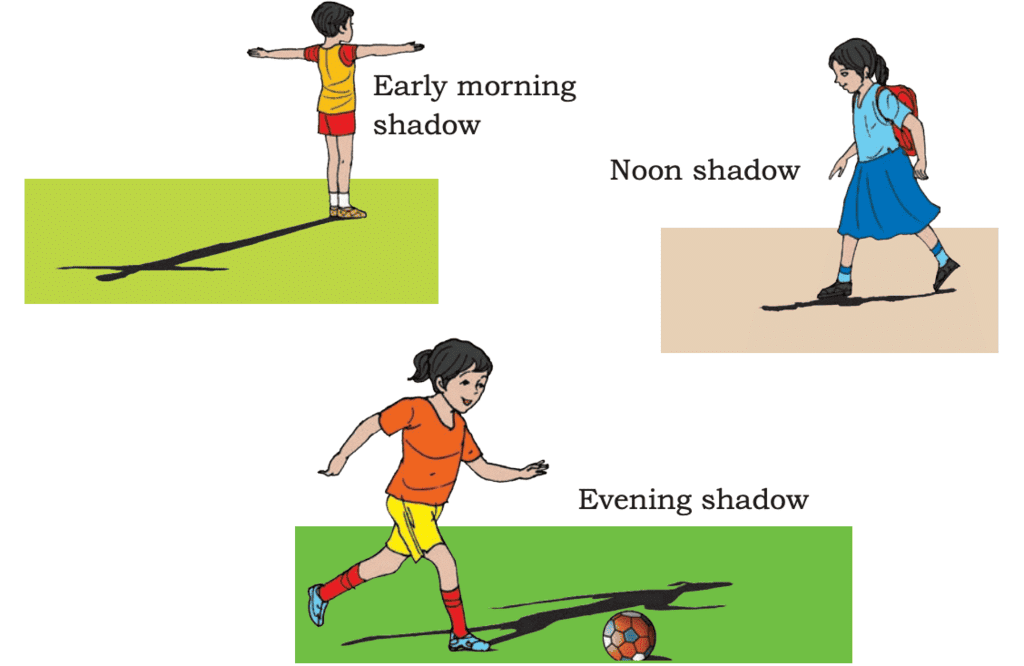 In the pictures above, the shadows are different at various times of the day. In the morning, the shadows are long, they are short at noon, and they become long again in the evening. However, the evening shadows appear in the opposite direction of the morning shadows.
In the pictures above, the shadows are different at various times of the day. In the morning, the shadows are long, they are short at noon, and they become long again in the evening. However, the evening shadows appear in the opposite direction of the morning shadows.
Creating Shadows
We can make shadows by blocking light with an object.
Let's perform an activity:
To explore shadows, take a torch and a stick.
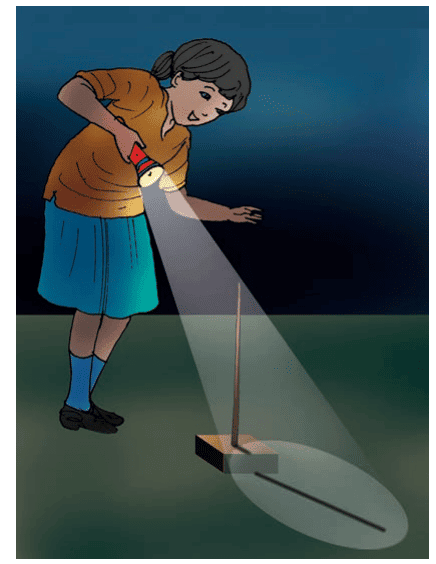

In a dark room, shine the torch on the stick and watch the shadow it makes.
If the stick is moved closer to the light, the shadow becomes larger.
If the stick is moved farther from the light, the shadow becomes smaller.
When the direction of the light changes, the shadow also moves or changes direction.
This is why shadows look different in the morning and evening because the Sun’s position changes in the sky.
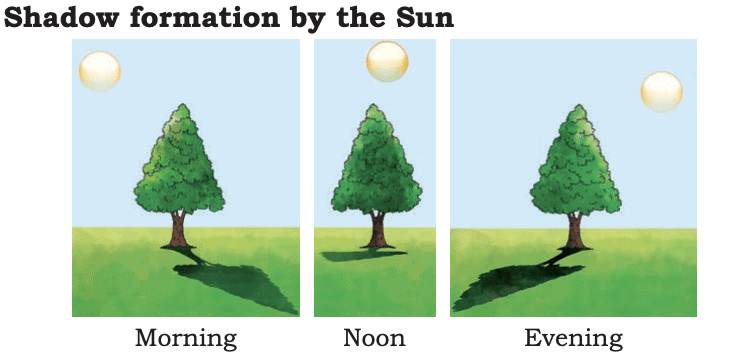
Movement of the Sun and Shadows
The Sun looks like it moves from the East in the morning to directly overhead at noon.
After noon, it slowly moves towards the West in the afternoon.
Because the Sun moves, the direction of shadows also changes during the day.
Did you know?
We can tell the time by looking at shadows. Ancient people noticed this and created a device called a sundial to tell time.
Raja Jai Singh of Jaipur built Jantar Mantar in Jaipur, Ujjain, Delhi, Varanasi, and Mathura. It has a sundial called Samrat Yantra, which can tell time accurately based on the shadow.
Play with Shadows
It is fun to make different shapes with shadows. Try it with your friends!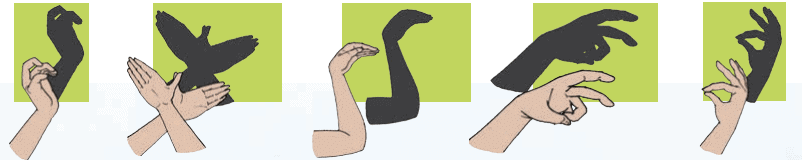
Shadow puppetry has been practiced in India for a long time.
Night Sky
After the Sun sets, the sky fills with thousands of twinkling stars. Stars often form patterns called constellations. You can try drawing a pattern you see in the night sky.

The Moon and Its Changing Shapes
The Moon looks like the biggest object in the night sky. Its shape changes on different nights:
Sometimes it is a full circle — called Poornima or full Moon.
Sometimes it looks like the letter ‘C’.
Sometimes it appears cut in half.
On some nights, the Moon is not visible at all — this is called Amavasya or new Moon.

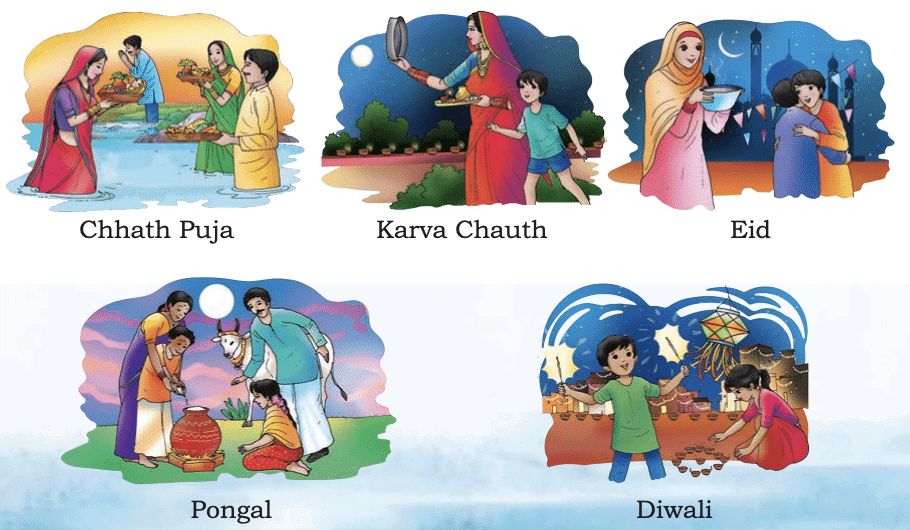
Ancient people used the shapes of the Moon to track days and create calendars. Many festivals are based on the Moon:
- Diwali: Celebrated on the New Moon (no Moon).
- Rakshabandhan, Guru Poornima, Buddha Poornima: Celebrated on the Full Moon.
- Eid: Eid is celebrated on the first night after the New Moon when the Moon becomes visible.
- Other festivals like Chhath Puja and Karva Chauth are also connected to the Moon.
India’s Chandrayaan Mission
India’s Chandrayaan mission focuses on exploring the Moon. On 23 August 2023, the Vikram Lander successfully touched down on the Moon and gathered data about its surface. This marked a significant achievement for India, and students might have learned about it in their Grade 3 textbooks.
Points to Remember
- The Moon’s shape varies nightly, transitioning from Full Moon to New Moon, which is useful for calendars and festivals.
- Festivals like Diwali, Eid, and Rakshabandhan are linked to the Moon’s visibility. Diwali is celebrated when there is no Moon, while Eid occurs on the first night the Moon is seen after a New Moon.
- India’s Vikram Lander landed on the Moon in 2023 to examine its surface.
- Studying the sky helps us understand nature and track time.
Difficult Words
 Celestial transitions
Celestial transitions
- Sunrise: When the Sun comes up in the morning.
- Sunset: When the Sun goes down in the evening.
- Shadow: A dark shape created when something blocks light.
- Sundial: A tool that tells time by using shadows.
- Saptarshi: A famous group of stars in Indian astronomy, known as the Seven Sages.
- Poornima: The night when the Moon is completely full.
- Amavasya: The night when the Moon cannot be seen.
- Chandrayaan: India's mission to explore the Moon. On 23 August 2023, India's Vikram Lander successfully landed on the Moon and gathered data about the Moon's surface.
- Vikram Lander: The part of Chandrayaan that touched down on the Moon.
|
21 videos|111 docs|10 tests
|
FAQs on Our Sky Class 4 Notes EVS Chapter 10 Free PDF
| 1. What are the main topics covered in the chapter "Our Sky"? |  |
| 2. Why is it important to learn about the sky? |  |
| 3. What are some interesting facts about the sky mentioned in the chapter? |  |
| 4. How does the chapter explain the concept of weather? |  |
| 5. What activities can help students learn more about the sky? |  |
















