Grade 10 Exam > Grade 10 Notes > Preparation for EmSAT Grade 10 > Chapter Notes: Prenatal diagnosis and genetics
Prenatal diagnosis and genetics Chapter Notes | Preparation for EmSAT Grade 10 PDF Download
Introduction
- Main goal of any test done before birth for screening or diagnosing is to first find fetuses that have high chance of having serious problems in structure, genes, metabolism, or blood issues.
- After finding such fetuses, a test to confirm the diagnosis is used.
- Screening tests are different from diagnostic tests because screening tests are made to find most cases but they might also show positive results when there is no problem.
- Diagnostic tests are very correct and doctors use them to make decisions about care.
- Screening tests are safe and can be used for everyone or for people with low chance of problem.
- Diagnostic tests might need procedures that go inside the body and are used only for people with high chance or those who had positive screening result.
- Now it is possible to find many conditions before birth that earlier could be found only after birth.
- This helps parents to make better choices about the pregnancy with more knowledge.
- Parents have many reasons for wanting tests before birth.
- In some cases, it is because they had a child with problem before or there is family history of serious gene condition.
- In other cases, a high chance shown by screening test makes them want a sure result.
- No matter the reason, for most conditions, test before birth needs a sample from fetus and this carries chance of losing the fetus.
- This chapter focuses on some new developments and methods available now for diagnosis before birth and what they mean for medical practice.
Advances in Molecular Genetics
- There are three ways to find genes that add to complex diseases.
- These ways are screening candidate genes, mapping linkage, and studies of association which are case-control studies.
- In screening candidate genes, possible genes that cause disease are chosen, like genes that cause inherited types of disease.
- Then these genes are sequenced in patients who have complex diseases.
- In linkage mapping, parts of chromosomes marked by random gene differences are followed in families with complex diseases.
- This is to search for parts that go together with the disease feature.
- In case-control association studies, differences in how often common gene differences happen are looked for between people with same ethnic background who have the disease and those who do not.
- This is to find differences that are strongly linked to the disease.
- Final goal of each way is to find if there are sure changes that strongly cause the disease or changeable forms that have weak cause link to the disease.
- Very wide range of methods is available now for finding gene disorders.
- Review of these methods is outside the scope of this chapter.
- Human Genome Project showed that current genome sequence has about 2.5 billion building blocks broken by only 341 gaps.
- It seems to code for only 20,000 to 25,000 genes that make proteins.
- Only 3 percent of these genes have meaning for diagnosis.
- About 1200 tests based on genes should become available.
- Bigger labs will be able to offer wide range of these testing needs.
- Close working with a unit for clinical genes is very important to make sure samples go to right lab.
Invasive Fetal Tests
- In most cases, amniocentesis and sampling of chorionic villus are done to get a sample from fetus for study.
- It is guessed that around 5 percent of women who are pregnant, which is about 30,000 women each year in the UK, could be given choice of tests before birth that go inside.
- Amniocentesis is most common procedure done before birth for diagnosis that goes inside in the United Kingdom.
- Most are done to get fluid from around fetus for checking chromosomes.
- Majority are done from 15 full weeks of pregnancy onward.
- Amniocentesis before 15 full weeks of pregnancy is usually done between 10 and 13 weeks of pregnancy.
- It involves taking in tissue from placenta instead of fluid from around fetus.
- Sampling of chorionic villus can be done either through belly or through cervix.
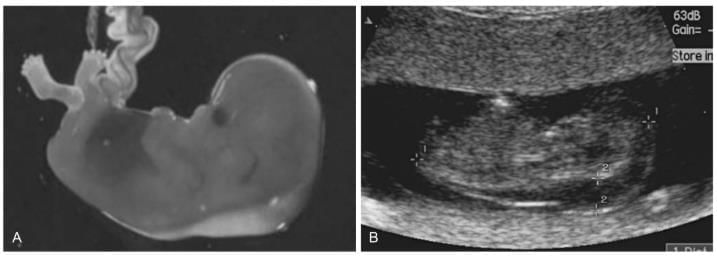
1st Trimester Feats with Increased Nuchal Edema
- Picture shows fetus in first three months with more nuchal swelling.
- Nuchal translucency check which finds fetus with chance for Down syndrome.
- Best guess of chance of losing pregnancy linked to amniocentesis comes from study by Tabor and others in 1986.
- This study put 4606 women with low chance randomly into groups.
- It showed that group with amniocentesis had loss rate 1 percent more than control group.
- This 1 percent is often said in talk before test.
- Several procedure linked loss rates of around 0.5 percent can be reached.
- There are no studies that compare sampling of chorionic villus with no testing.
- But random trials comparing sampling of chorionic villus by any way with amniocentesis in second three months showed extra pregnancy loss rate of 3 percent.
- Other ways of testing fetus that go inside include taking blood from fetus, skin from fetus, and muscle biopsy from fetus.
- Chance of problem in taking blood from fetus without issues is between 1 and 3 percent.
- However, if fetus has too much fluid, chance may be as high as 20 percent.
- Once sample from fetus is got, testing for chromosomes or not for chromosomes can start.
Cytogenetics
- Checking full set of chromosomes stays the best standard for studying chromosomes.
- It is still the method used most often in diagnosis before birth.
- Most important progress in study of cell genes has been making of technology for fluorescent in situ hybridization.
- Also quantitative fluorescent polymerase chain reaction methods.
- Full check of chromosomes takes about two weeks from fluid around fetus or villi from chorion.
- Samples are grown until enough cells that are dividing are collected.
- Then chromosomes in stage of division are spread on slides for microscope.
- These chromosomes are then made to have bands by breaking with enzyme.
- Finally looked at under microscope.
- Besides finding number problems in chromosomes like extra or missing, this method also finds changes in structure and problems where size of change is more than 3 million bases.
- Similar method is used for blood from fetus but much faster result can be got within 48 hours.
- Because grown white blood cells divide much faster than cells from fluid around fetus.
Fluorescent in situ Hybridization (FISH)
- FISH method is based on finding that marked RNA for ribosomes joins to chromosomes that have short arm.
- These are chromosomes with center not in middle so arms not equal.
- It involves DNA piece marked with fluorescent being joined to gene DNA sequences.
- It can be used to study certain spot on chromosome.
- These certain pieces can be joined not only to chromosomes in division stage but also put directly on fixed nuclei in between divisions of cells that are not dividing.
- Four main kinds of FISH pieces are available now.
- These are pieces for repeated sequences, pieces for whole gene DNA, pieces for certain spot, and pieces for painting certain chromosome.
- FISH signals are seen by microscope for fluorescence using light source that lights up the marked samples.
- Usual high detail chromosome banding methods can result in up to 1000 bands for each set of genes.
- However, even at such high detail, deletions, copies, or moves are hard to find.
- FISH however can be used to find where marker chromosomes come from and to confirm number and structure problems.
- FISH can also find areas as small as 0.5 thousand bases on chromosomes in division stage.
- In contrast to only much bigger areas of 5 to 10 million bases using usual banding.
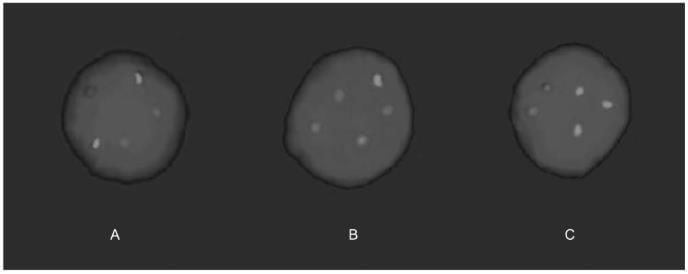
Aneuploidy Screening Using Fish
Chorionic villi Obtained after CVS
Quantitative Fluorescent Polymerase Chain Reaction (QF-PCR)
- Polymerase chain reaction is fast and trusted method for finding number of copies of chromosome by making more of highly changeable chromosome certain short repeated parts.
- Fluorescent color put into products of making more allows seeing and measuring using automatic DNA scanner.
- Two fluorescence tops with ratio of 1 to 1 will be made for each chromosome certain short repeat from normal fetuses with right number.
- Samples from fetuses with three copies will usually show either three tops with ratio of 1 to 1 to 1 which is three copies three different.
- Or two tops with ratio of 2 to 1 which is three copies two different.
- Good thing of QF-PCR over FISH is it costs less especially when big numbers are done.
- Also, less stuff is needed, samples with blood can be studied well.
- It is less time taking and less work heavy.
- Bringing in of fast testing of all samples before birth has raised issue of need for full check of chromosomes and reporting these samples.
- Most women who have testing that goes inside do so because they were found as high chance by certain screening method.
- Full check of chromosomes may find problems of unknown meaning like marker chromosomes.
- These may not be passed from parents and so of small or no meaning.
- These findings often cause hard talks for guidance and raise right and wrong issues for patients both in how to understand and choose between ending pregnancy or continuing worry for rest of pregnancy.
- Overall, around 0.07 to 0.14 percent of pregnancies checked for chromosomes will have important chromosome problem that would not be found by fast testing.
- This needs to be thought by those doing testing before birth in their talk before test with patients.
Non-invasive Prenatal Diagnosis: Fetal Cells and Cell-free Fetal DNA
- This stays the best goal of diagnosis before birth.
- Because testing before birth that goes inside carries chances to both mother and fetus.
- Other ways that do not go inside are being looked for actively.
- It is now fully clear that whole fetal cells and DNA from fetus without cells are present in blood of mother.
- These are perfect targets for diagnosis.
- One way is taking out whole fetal cells from blood of mother.
- Several kinds of cells have been taken out like red blood cells with nucleus, cells positive for CD34 which are starters for blood, and cells from trophoblast.
- Though these kinds of cells have been shown without doubt to be in blood of mother, each has big bad point.
- This makes their use in medical testing now very problematic.
- Red blood cells with nucleus cannot be grown more in culture.
- The ruling out study of chromosomes in division stage which is important part of diagnosis before birth.
- Cells positive for CD34 do have chance for growing more in lab.
- However, they have been found to stay in blood of mother maybe from earlier pregnancies.
- This makes diagnosis in next pregnancies hard.
- Cells from trophoblast are not always found in blood of mother.
- Moreover, because of lack of sure fetal cell mark and trusted way of sorting, steady and trusted finding of any of these kinds of cells is at present time hard.
- Once fetal cells are taken out from blood of mother, there are sensitive new methods that can be used for gene study.
- Main limit in using these methods in medical way, besides certain problems said before, is usually low number of fetal cells found in blood of mother.
- It is about one fetal cell for each ml of blood from mother.
- How well aneuploidy is found through study of whole fetal cells in blood of mother gets to 75 percent in some reports.
- With false positive rate guessed between 0.6 and 4.1 percent.
- In 1997, Lo and others showed presence of large amounts of DNA from fetus without cells in liquid part and clear part of blood from pregnant women.
- This same group also showed fast clearing of this DNA levels after birth.
- Very low or not found levels of moving DNA two hours after birth.
- Always more DNA from fetus is present in liquid part of blood from mother than in cell part of blood from mother.
- Main source of DNA from fetus in circulation of mother seems to be placenta.
- Levels of DNA from fetus go up with pregnancy with big rise in last 8 weeks of pregnancy.
- Unlike fetal cells with nucleus in blood of mother which usually needs use of advanced ways to make more cells.
- Study of DNA from fetus has good point of being trusted processed and easily done for large number of samples.
- Main problem stopping its more wide use at present seems to be lack of available gene sequences only from fetus that find and or measure presence of DNA from fetus in both male and female fetuses.
- In general, medical uses of measuring DNA from fetus in liquid part and clear part of blood from mother have focused on measuring sequences of DNA from fetus.
- And finding presence or no of gene sequences only from fetus.
Gender Detection
- In one study, gender of fetus was rightly guessed by DNA from fetus from samples of liquid part of blood from mother taken between 10 and 13 weeks with 100 percent how well it finds.
- Finding male DNA sequences from fetus is quite easy.
- One possible use for finding without going inside of male fetuses at chance for disorders linked to X.
- Field of finding gender is very useful in early pregnancy so could be first step to find fetuses at chance.
- These would need testing that goes inside for sure finding of diagnosis.
- Or in cases where sex of fetus changes medical care like in use of steroid therapy in born with adrenal overgrowth in those carrying female but not male fetuses.
Non-invasive Diagnosis of Aneuploidy
- Using real time PCR, one group showed 2 times more in levels of DNA from fetus for three copies of 21.
- Compared with cases with right number.
- Later studies have supported these views on sure three copies of 21 but not on three copies of 18.
- Saying that different growth of fetus and problems in placenta result in different levels of DNA from fetus.
- Study of stored samples from mother serum has also shown 1.6 times more in amount of DNA from fetus levels in pregnancies with three copies positive as compared with matched for pregnancy age controls.
- Taken together, these findings say possible use of DNA from fetus as extra screening thing to study.
- Another new use of study of DNA from fetus is in looking at pregnancies at chance for wrong number due to balanced move in parent.
Pre-eclampsia
- In pre-eclampsia, there is almost five times more DNA from fetus in blood of mother compared with controls.
- In women who will get pre-eclampsia, levels become wrong two weeks before signs.
- Raised levels of DNA from fetus were found as early as 17 weeks pregnancy followed by second rise about 3 weeks before start of signs.
- This may allow both screening for disease as well as showing coming pre-eclampsia.
- However, this test is not yet in usual medical practice as it needs more checking.
Monogenic Disorders
- Maybe one of most important use of DNA from fetus in liquid part of blood from mother is typing genes of fetus without going inside in pregnancies made hard by red cell alloimmunisation.
- Typing Rh-D of fetus without going inside was first said in 1998.
- Since 2001, lab for international blood group reference in Bristol has offered typing Rh-D of fetus using DNA from fetus without cells in blood of mother to doctors caring for women with alloimmunised.
- This has much lowered number of procedures that go inside done in UK for typing Rh-D of fetus.
- More lately, same lab has also started offering typing Rh-c and Kell of fetus using same technology.
- Other gene disorders like myotonic muscle problem, short limb disorder, and cystic fibrosis have all been found using DNA from fetus in blood of mother.
- Also, workers in Hong Kong using DNA from fetus to leave out or sure the presence of changed gene passed from father in major beta blood disorder have been able to find fetuses at chance who then need testing that goes inside.
Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis
- First reports of genetic diagnosis before putting in were printed almost 35 years ago.
- Main purpose of PGD is to do genetic testing before pregnancy and to avoid ending pregnancy which is big limit of usual diagnosis before birth.
- To now more than 7000 PGD have been done with birth of almost 1000 healthy children.
- List of disorders for which PGD has been used now more than 100 with most often ones being cystic fibrosis and blood disorders.
- See review by Kuliev and Verlinsky.
- PGD is nice choice for couples carrying moves because of their bad results in having children.
- There is four times less sudden losses in women doing PGD compared those not doing PGD.
- PGD is now done either by testing egg cells for gene problems from mother or by gene study of single cells taken from before putting in growing babies.
- So only not affected growing babies may be put back to womb making sure start of not affected pregnancy.
- Each of these ways has good and bad points and is used depending on medical situation.
- Taking piece from growing baby is done as early as stage with 6 to 8 cells or at blastocyst stage.
- Allowing testing for both from mother and from father gene problems.
- Even with lowering in cell number of growing baby which may change how well growing baby lives, taking piece from growing baby is way of choice for problems from father that rule or for couples at chance for problems that are hidden where both parents carry.
- Typing for HLA.
- In contrast, testing egg cell is used for gene problems from mother and is done by taking away first and second polar bodies from egg cells.
- These show the extra products of division one and division two.
- While testing egg cell does not give info on gender or changes from father.
- It may be way of choice for PGD of hidden disorders and changes from mother that rule and moves.
- Because over 90 percent of errors in chromosomes come from division in mother.
- This way is of special worth for wrong numbers linked to age and complex wrong numbers and choice of egg cells free of wrong numbers for making pregnant.
The document Prenatal diagnosis and genetics Chapter Notes | Preparation for EmSAT Grade 10 is a part of the Grade 10 Course Preparation for EmSAT Grade 10.
All you need of Grade 10 at this link: Grade 10
|
29 videos|255 docs|56 tests
|
FAQs on Prenatal diagnosis and genetics Chapter Notes - Preparation for EmSAT Grade 10
| 1. What is prenatal diagnosis and why is it important? |  |
Ans. Prenatal diagnosis refers to the medical procedures used to determine the health and development of a fetus during pregnancy. It is important because it can identify potential genetic disorders, congenital anomalies, and other complications early on, allowing for informed decision-making by parents and healthcare providers. Early diagnosis can also facilitate planning for necessary interventions and support.
| 2. What are the common methods used for prenatal genetic testing? |  |
Ans. Common methods for prenatal genetic testing include non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT), chorionic villus sampling (CVS), amniocentesis, and ultrasound. NIPT analyzes fetal DNA in the mother's blood, while CVS and amniocentesis involve collecting samples from the placenta or amniotic fluid, respectively, to test for specific genetic conditions. Ultrasound can help detect physical anomalies and assess fetal growth.
| 3. What are the risks associated with invasive prenatal testing methods? |  |
Ans. Invasive prenatal testing methods such as chorionic villus sampling (CVS) and amniocentesis carry some risks, including miscarriage, infection, and injury to the fetus. While these risks are generally low, they are important considerations for parents when deciding whether to undergo these procedures. Non-invasive methods, like NIPT, present fewer risks but may not provide definitive results.
| 4. How do genetic disorders get inherited, and what should parents know? |  |
Ans. Genetic disorders can be inherited in various ways, including autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, X-linked, and multifactorial inheritance patterns. Parents should be aware of their family health history, as this can influence the likelihood of passing on genetic conditions. Genetic counseling can help parents understand their risks and the implications of genetic testing.
| 5. What role does genetic counseling play in prenatal diagnosis? |  |
Ans. Genetic counseling provides information and support to expecting parents regarding the risks, benefits, and limitations of prenatal genetic testing. Counselors help interpret test results, discuss potential outcomes, and explore options available if a genetic condition is detected. This process helps parents make informed choices based on their values and circumstances.
Related Searches















