Ratios and Rates Chapter Notes | Preparation for EmSAT Grade 8 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| What is Ratio? |

|
| What are equivalent ratios? |

|
| What is a rate? |

|
| Unit rates |

|
| Converting customary units |

|
Introduction
Understanding ratios, rates, and unit conversions is essential for comparing quantities and making informed decisions in everyday scenarios. A ratio compares two quantities of the same unit, while a rate compares quantities with different units, often expressed as a unit rate when the second quantity is 1. Equivalent ratios maintain the same proportional relationship, and unit rates help identify the best value, like comparing prices. Converting between customary units, such as feet to inches or gallons to quarts, involves multiplying or dividing based on unit relationships. This guide explores these concepts with clear examples to simplify their application.
What is Ratio?
A ratio is a method of comparing two quantities. It shows how much of one item there is in relation to another.
How do you write a ratio?
- You can write ratios in a few different ways:
- Using words: 3 to 4
- Using a colon: 3 : 4
- As a fraction: 3/4
- For Example: The picture below shows 2 circles and 5 triangles.
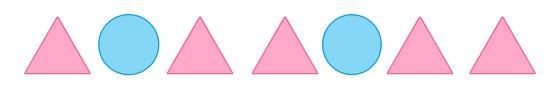 Here are three ways to write the ratio of circles to triangles: 2 to 5, 2 : 5, 2/5
Here are three ways to write the ratio of circles to triangles: 2 to 5, 2 : 5, 2/5
What are equivalent ratios?
- Equivalent ratios represent the same relationship. You can identify them by expressing the ratios as equivalent fractions.
- For example, the ratios 2 : 3 and 4 : 6 are equivalent ratios. You can write them as equivalent fractions.
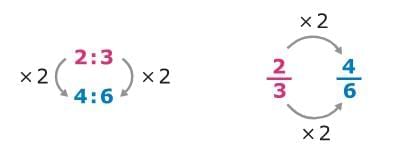
How do you find equivalent ratios?
- Finding equivalent ratios is like finding equivalent fractions:
- First, write the ratio as a fraction.
- Then, multiply or divide the numerator and the denominator by the same number.
- For Example: Ratio 10 : 15.
Write 10 : 15 as the fraction 10/15. Divide the top and bottom by 5.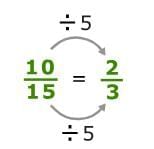 So, the ratios 10 : 15 and 2 : 3 are equivalent ratios.
So, the ratios 10 : 15 and 2 : 3 are equivalent ratios.
What is a rate?
- Ratios and rates both show comparison, but they do so in different ways:
- A ratio compares quantities that have the same unit.
- A rate compares quantities that have different units.
- For Example: There are 10 pizzas at a party. There are 3 veggie pizzas and 7 combo pizzas. Each pizza cost $10.
You can use a ratio to show the proportion of veggie pizzas to combo pizzas. That ratio is 3 : 7.
You can use a rate to look at the cost. The rate is $10 per pizza. Because the second amount in that rate is 1, this rate is called a unit rate.
Unit rates
- A rate is a comparison of two quantities that have different units, such as 100 miles every 2 hours.
- A unit rate is a special type of rate where the second amount is 1, such as 50 miles every 1 hour. When you have a unit rate, you can use the word per.
- For example, you can also say 50 miles every 1 hour as 50 miles per hour.
- Here are some other examples of unit rates:
- $3.29 per pound
- 25 students per class
- 12 eggs per carton
How can you find a unit rate?
- To find a unit rate, you can divide.
- For Example: Sam typed 60 words in 3 minutes. How many words did he type per minute?
Divide the number of words by the number of minutes to find the unit rate.
60 ÷ 3 = 20
So, the unit rate is 20 words per minute.
Using unit rates to make the best purchase
- To compare two prices, you can use unit rates to determine which is the better deal. A unit rate shows the cost of one unit of each item.
- For Example: Giovanni's Grocery Store charges $15 for 5 pounds of peanuts. Groceries-to-Go charges $9 for 2 pounds of peanuts. Which store has a lower price per pound?
Calculate each unit rate to find the better purchase.
Giovanni's Grocery Store: 15 ÷ 5 = 3
So, the unit rate at Giovanni's Grocery Store is $3 per pound of peanuts.
Groceries-to-Go: 9 ÷ 2 = 4.5
So, the unit rate at Groceries-to-Go is $4.50 per pound of peanuts.
Giovanni's Grocery Store has the lower unit rate, so Giovanni's Grocery Store has the better buy.
Converting customary units
Here are some relationships between customary units of length, weight, and capacity (volume) that can help with unit conversions:
- Length:
- 1 foot (ft.) = 12 inches (in.)
- 1 yard (yd.) = 3 ft.
- 1 mile (mi.) = 1,760 yd.
- 1 mi. = 5,280ft.
- Weight:
- 1 pound (lb.) = 16 ounces (oz.)
- 1 ton = 2,000 lb.
- Capacity:
- 1 cup (c.) = 8 fluid ounces (fl. oz.)
- 1 pint (pt.) = 2 c.
- 1 quart (qt.) = 2 pt.
- 1 gallon (gal.) = 4 qt.
How do you convert between customary units?
- To convert between customary units, follow these rules:
- To convert from a larger unit to a smaller unit, multiply.
- To convert from a smaller unit to a larger unit, divide.
- For Example: Convert 6 yards to feet. You are going from a larger unit to a smaller unit.
Multiply by the number of feet in a yard: 3
6 × 3 = 18
So, 6 yards = 18 feet.
Now, let's convert 80 ounces to pounds. You are going from a smaller unit to a larger unit.
Divide by the number of ounces in a pound: 16
80 ÷ 16 = 5
So, 80 ounces = 5 pounds.
Converting customary units with fractions
- If your units contain fractions, you can still follow the same steps.
- For Example: Convert 1/2 gallon to quarts. You are going from a larger unit to a smaller unit.
Multiply by the number of quarts in a gallon: 4
Remember to write your answer in simplest form.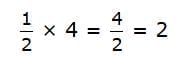 So, 1/2 gallon = 2 quarts.
So, 1/2 gallon = 2 quarts.
Converting mixed customary units
- Sometimes when you divide to convert customary measurements, you get a remainder. You can use the remainder to write the answer.
- For Example: Convert 30 inches to feet. You are going from a smaller unit to a larger unit.
Divide by the number of inches in a foot: 12.
30 ÷ 12 = 2R6
Look at the quotient. The 2 tells the number of feet. The R6 tells the number of extra inches.
So, 30 inches = 2 feet 6 inches.
|
435 docs|98 tests
|
FAQs on Ratios and Rates Chapter Notes - Preparation for EmSAT Grade 8
| 1. What is the definition of a ratio? |  |
| 2. How is a rate different from a ratio? |  |
| 3. Can ratios be simplified like fractions? |  |
| 4. How can ratios be used in real life? |  |
| 5. What are some examples of rates we encounter daily? |  |














