Reaching the Age of Adolescence Class 8 Notes Science Chapter 7
What is Adolescence?
Adolescence is a developmental phase that marks the transition from childhood to adulthood. It is characterized by physical, psychological, and social changes that prepare individuals for adult roles and responsibilities.
The period of life, when the body changes, leading to reproductive maturity.
- Adolescence begins around 11 and lasts up to 18 or 19 years of age.
- Adolescents are called teenagers as this period covers the teens (13-19 years of age).
- For females, adolescence begins a year or two earlier than boys. The period of adolescence varies from person to person.
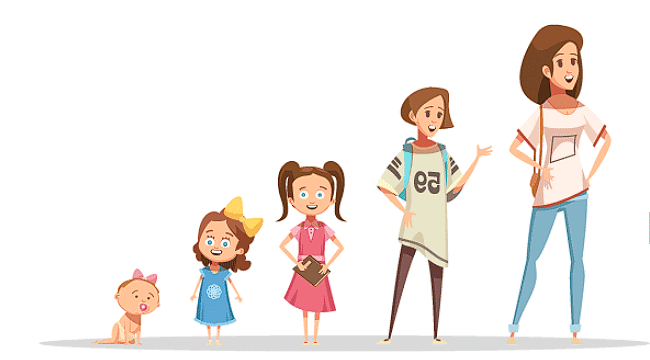 Reaching the Age of Adolescence
Reaching the Age of Adolescence
What is Puberty?
Puberty is the phase of development during which a child's body undergoes various changes to become sexually mature. It marks the beginning of adolescence and is driven by hormonal changes.
 Puberty
Puberty
Let's Revise: How is puberty related to adolescence?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Puberty marks the beginning of adolescence and brings about hormonal changes that lead to physical and reproductive maturity.
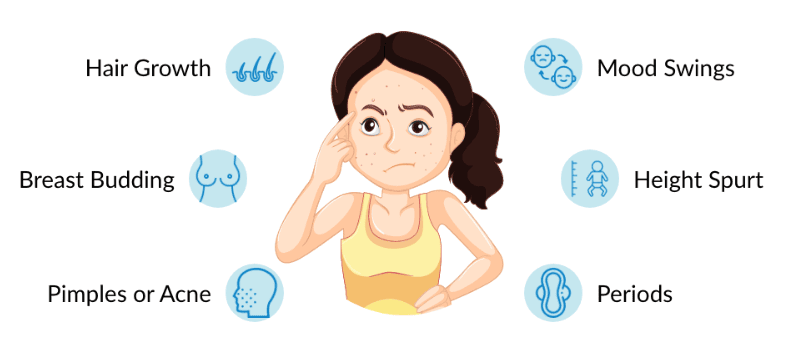
Changes during Puberty
1. Increase in Height:
- There is a sudden increase in height of a person during puberty due to the elongation of the bones of the arms and legs.
- Even though the height of a person depends on an inherited gene, eating habits, and exercise during adolescence also decide height.
- Initially, girls grow faster than boys.
- Both reach maximum height by the age of about 18 years.
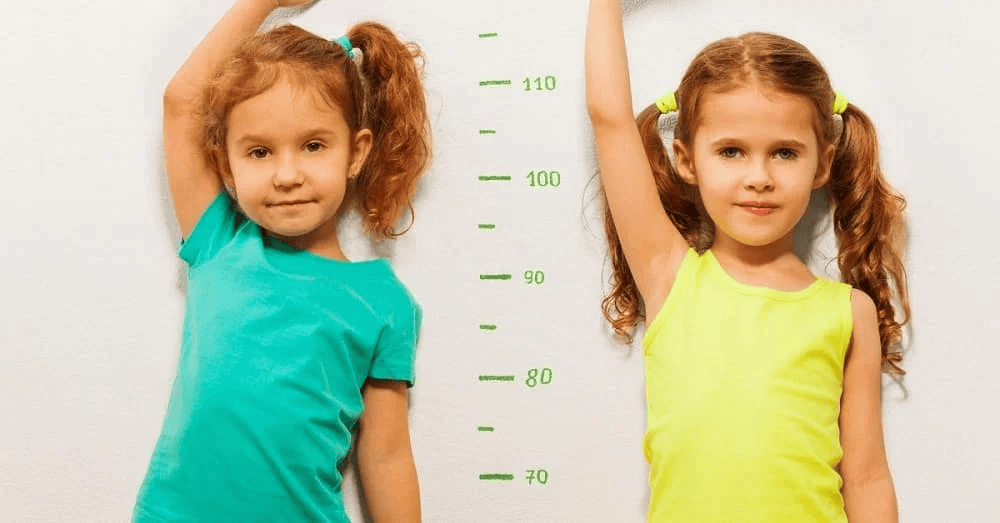

Increase in Height
2. Changes in Body Shape
- In boys, the shoulders broaden and muscles of the body grow more prominently than in girls.
- For girls, there is a widening of the region below the waist and less growth of muscle.
3. Voice Change
- During puberty, it is noticed that the voice of boys starts cracking and their voice box or larynx starts to grow.
- Adam’s Apple: The increase in the size of the voice box in boys is seen as a prominent protrusion in the neck. This protrusion is called Adam’s apple.
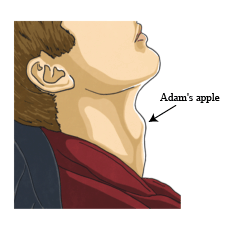 Adam's Apple
Adam's Apple
4. Increased Activity of Sweat and Sebaceous Glands
- During puberty, there is an increase in the secretion of sweat glands and sebaceous glands (oil glands) which may lead to the appearance of acne and pimples.
5. Development of Sex Organs
- At puberty, male sex organs like the testis and penis develop completely and begin to produce sperm.
- In girls, the ovaries enlarge and start releasing eggs/ova.
6. Reaching Mental, Intellectual, and Emotional Maturity
- Adolescents are more independent and self-conscious than earlier. They tend to think more. Feeling insecure while trying to adjust to the changes in mind and body is prominent.
- During adolescence, a person’s brain has the greatest capacity for learning.
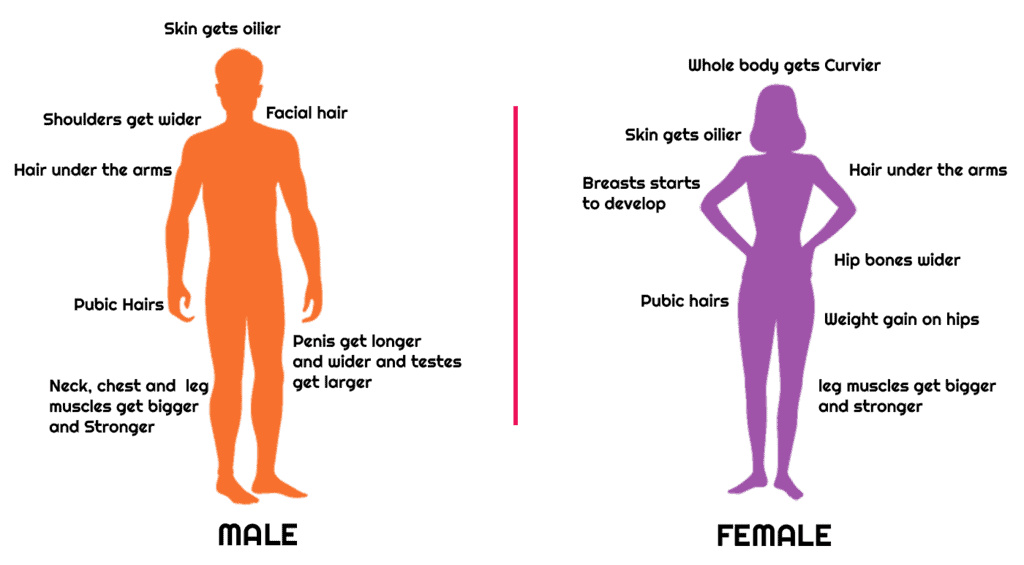 Changes at Puberty
Changes at Puberty
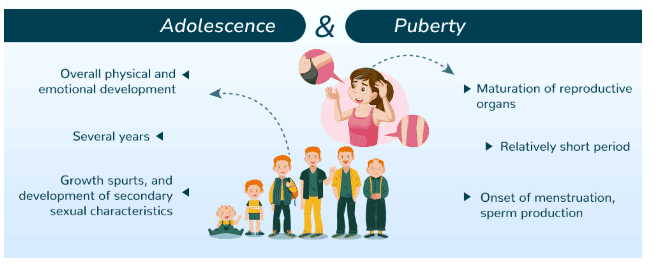
Difference between Adolescence and Puberty
Secondary Sexual Characters
Characters that develop prominently during adolescence which helps to distinguish between male and female are known as secondary sexual characters.
What are Hormones?
The changes at adolescence are influenced by hormones. The transformations during adolescence are guided by hormones.
- Secretions from endocrine glands are special fluids.
- The male hormone, testosterone, starts being released by the testes during puberty.
- This leads to changes in boys, such as the growth of facial hair.
- When girls reach puberty, their ovaries start making the female hormone, estrogen.
- Estrogen helps in the growth of breasts and the development of milk-secreting glands inside them.
- The production of these hormones is controlled by another hormone from the pituitary gland.
Some of these characters are listed below: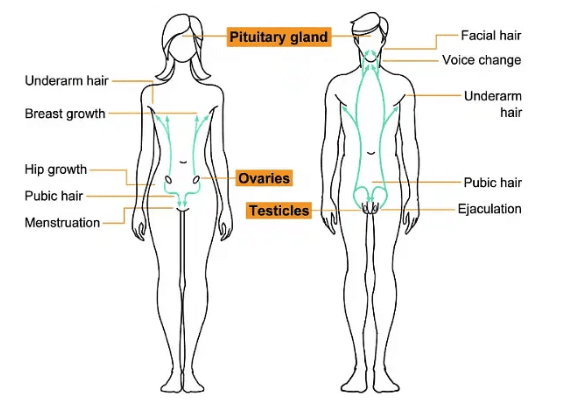 Secondary Sexual Characters
Secondary Sexual Characters
Role of Hormones in Initiating Reproductive Function
Endocrine glands release hormones into the bloodstream. The hormones travel to specific body parts known as target sites. Examples include the testes and ovaries, which are ductless glands producing sex hormones for the development of secondary sexual characteristics. The pituitary gland plays a crucial role by releasing hormones that influence the production and regulation of sex hormones, stimulating egg maturation in ovaries and sperm formation in testes.
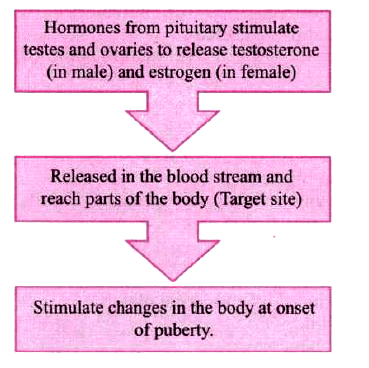 The onset of puberty is controlled by hormones
The onset of puberty is controlled by hormones
Reproductive Phase of Life in Humans
Adolescents become capable of reproduction when their testes (in males) and ovaries (in females) start producing gametes. However, In humans, females are born with all their eggs and have a finite number, while males produce sperm continuously throughout their life after puberty.
Female Reproductive Phase
- In females, the reproductive phase begins around puberty (10 to 12 years old) and typically continues until approximately 45 to 50 years of age. During puberty, the ovaries start maturing ova, with one ovum released every 28 to 30 days.
- The uterus lining thickens to support a potential fertilized egg, leading to pregnancy. If fertilization doesn't occur, the released egg and the thickened uterine lining, along with blood vessels, are shed, resulting in menstruation.
- Menstruation happens approximately every 28 to 30 days, with the first menstrual flow at puberty known as menarche.
- Menstruation stops around 45 to 50 years of age, known as menopause.
- The menstrual cycle is governed by hormones and includes various important processes.
- The egg matures and is released.
- The uterine wall thickens.
- If pregnancy doesn't occur, the wall breaks down.
- If the egg is fertilized, it divides and attaches to the uterus for further growth.
 Female Reproductive PhaseLet's Revise: What is the difference between menarche and menopause?
Female Reproductive PhaseLet's Revise: What is the difference between menarche and menopause?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Menarche is the first occurrence of menstruation, marking the start of the reproductive phase in females, while menopause is the end of menstruation, signaling the end of the reproductive phase, usually around 45–50 years of age.
How is the Sex of the Baby Determined?
What are chromosomes?
Inside a fertilized egg, or zygote, are instructions that determine the baby's sex. These instructions are found in thread-like structures called chromosomes.
The sex of a baby is determined by the combination of sex chromosomes (a type of chromosome involved in sex determination) inherited during conception. In the fertilized egg, instructions for sex are encoded in chromosomes located within the cell nucleus. Humans possess 23 pairs of chromosomes in their cells, including two sex chromosomes named X and Y.
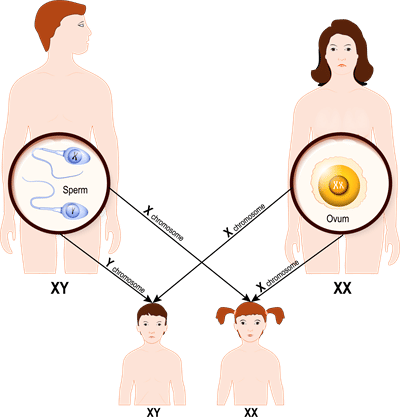 Sex Determination
Sex Determination
- Females have two X chromosomes (XX), while males have one X and one Y chromosome (XY). Each parent contributes one set of chromosomes through their gametes (egg and sperm).
- An unfertilized egg always carries one X chromosome, and sperm come in two types, one with an X chromosome and the other with a Y chromosome.
- The sex of the unborn baby is determined by which type of sperm fertilizes the egg. If an X-chromosome sperm fertilizes the egg, the baby will be female (XX).
- On the other hand, if a Y chromosome sperm fertilizes the egg, the baby will be male (XY). It's important to note that the sex chromosomes from the father ultimately decide the sex of the baby.
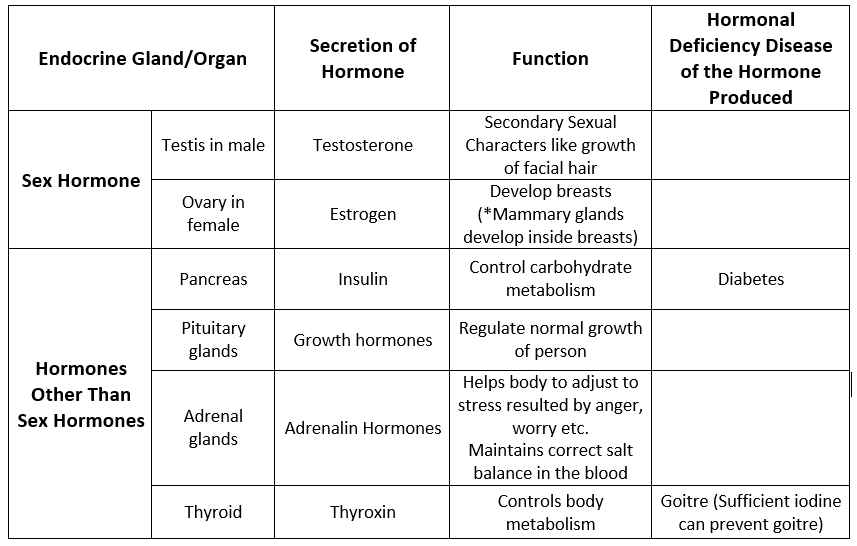
Hormones other than Sex Hormones
- Hormones control the changes during adolescence.
- The pituitary gland (found attached to the brain) secretes hormones which in turn control the production of hormones from other endocrine glands.
- Some endocrine glands, their secretion, and effects are given in the table below:
Role of Hormones in Completing the Life History of Insects and Frogs
- Frogs go through a big change as they grow up, transforming from tadpoles to adult frogs. This transformation is called metamorphosis, and it's similar to how insects change.
- In frogs, a hormone called thyroxine, produced by the thyroid, is in charge of this process.
- To make thyroxine, the tadpoles need iodine, which they get from the water they live in.
- If there isn't enough iodine in the water, the tadpoles won't be able to become adult frogs. So, having the right amount of iodine in their environment is crucial for their development.
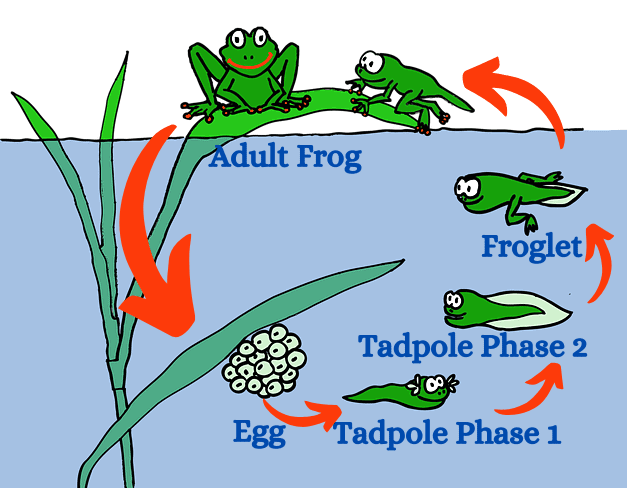 Life Cycle of FrogThe life span of insects can be categorized into four stages:
Life Cycle of FrogThe life span of insects can be categorized into four stages: 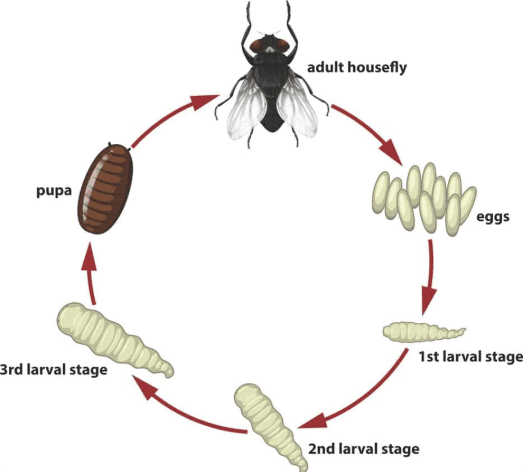 Life Cycle of a Housefly
Life Cycle of a Housefly - Metamorphosis: It is the change of an insect from a larva to an adult.
- Hormones in insects control metamorphosis under the action of ecdysone (molting hormone) and juvenile hormone, produced by endocrine glands such as the prothoracic glands and corpora allata. Ecdysone triggers molting, while juvenile hormone determines the type of molt (larval or adult).
Reproductive Health
The physical and mental well-being of an individual is regarded as healthy. To keep the body healthy, every human being at any age needs to have a balanced diet, observe personal hygiene, and undertake adequate physical exercise.
1. Nutritional Needs of the Adolescents
- Adolescence is a stage of rapid growth and development. So a balanced diet comprising proteins, carbohydrates, fats, minerals, and vitamins in requisite quantity is essential.
- Iron builds blood. Iron-rich food such as leafy vegetables, jaggery, meat, citrus, and Indian gooseberry is good for adolescents.
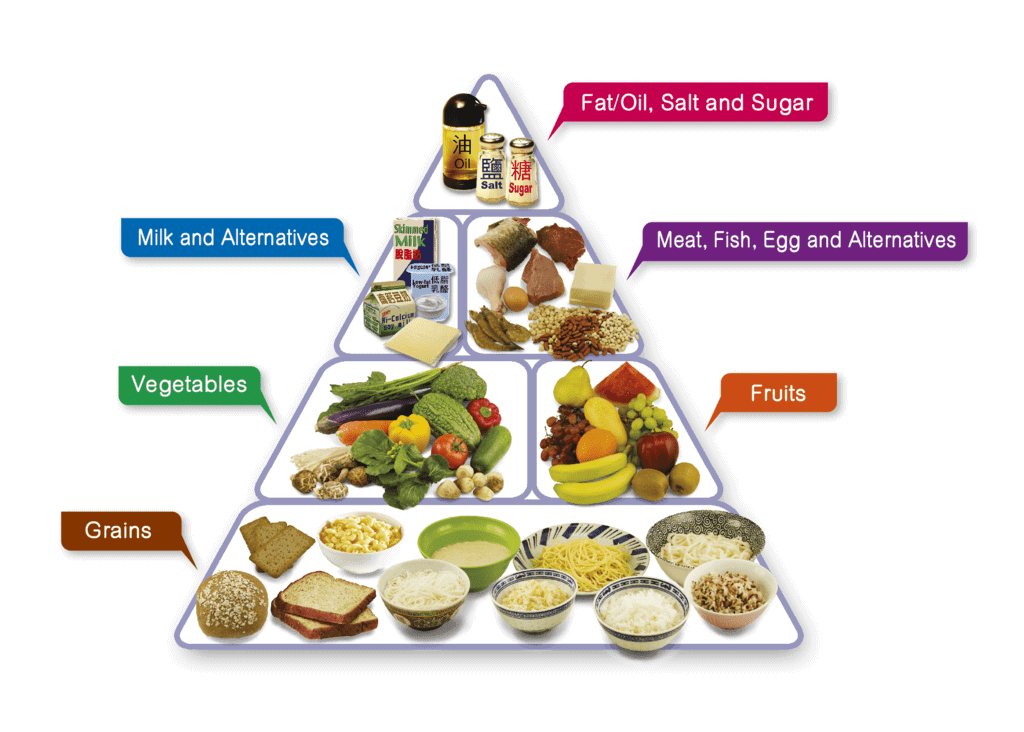 Balanced Diet
Balanced Diet
2. Personal Hygiene
Take a bath once a day. It is more necessary for adolescents due to the increased activity of sweat glands which may lead to a smelly body. All parts of the body should be washed and cleaned every day.
3. Physical Exercise
Adolescents should take walks, exercise, and play outdoor games in fresh air to keep them fit and healthy.
4. Say No to Drugs
During teenage, anyone might get affected by the negative energies surrounding him. At such times, falling for drugs can ruin your life.
 No to Drugs
No to Drugs
- If someone suggests that drugs can make you feel better, always say "No" unless prescribed by a doctor.
- Drugs can be addictive, meaning once you try them, you may want to keep using them, which is harmful.
- Using drugs can damage your body and ruin your health and happiness in the long run.
Do you Know?
HIV is the virus causing AIDS, and it is important to emphasize that HIV transmission occurs through specific activities, not all drug use.HIV can be transmitted from an infected person to a healthy person by sharing needles used for injecting drugs.It can also be passed from an infected mother to her baby through breastfeeding.HIV can also be transmitted through sexual contact with an infected person.It's important to stay away from drugs to protect yourself from harmful diseases like AIDS and to maintain good health.
Let's Revise
Q: What role does iron play in an adolescent’s diet, and what are some iron-rich foods?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Iron helps build blood and prevent anemia. Iron-rich foods include leafy vegetables, jaggery, meat, citrus fruits, and Indian gooseberry.
Q: How can HIV be transmitted, and how can adolescents protect themselves from it?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: HIV can be transmitted through sharing infected needles, sexual contact with an infected person, and from mother to child during breastfeeding.
Keywords from NCERT
Adam's Apple: This is a small bump in the throat that is more noticeable in boys during puberty. It is part of the voice box (larynx) and grows larger as the voice deepens.
Adolescence: This is the time in life when a child becomes an adult. It is a period of big physical, emotional, and social changes.
Adrenaline: This is a hormone released by the adrenal glands when we feel stressed or excited. It helps the body get ready for action by making the heart beat faster and increasing energy.
Balanced Diet: A balanced diet means eating different types of food that provide the right nutrients. It includes fruits, vegetables, grains, proteins, and dairy for growth and health.
Endocrine Glands: These are special glands in the body that make and release hormones directly into the blood to control body functions.
Estrogen: This is a female hormone that helps in the growth of breasts and the start of the menstrual cycle in girls.
Hormones: These are chemicals made by glands that travel through the blood and control growth, mood, energy, and reproduction.
Insulin: A hormone made by the pancreas. It helps control blood sugar by helping cells use the sugar from food for energy.
Larynx: Also called the voice box, it is part of the throat that holds the vocal cords and helps make sound when we speak.
Pituitary Gland: This is a small gland in the brain that controls many other glands in the body and helps with growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
Puberty: Puberty is when a child’s body goes through changes to become sexually mature, meaning they can have babies. This includes developing secondary sexual characteristics like body hair or breast growth.
Reproductive Health: This refers to being healthy in your reproductive system, which includes the ability to have safe sex, take care of any sexual health problems, and make choices about having babies.
Secondary Sexual Characteristics: These are changes in the body that happen during puberty. For girls, it may mean breast growth and wider hips. For boys, it might mean a deeper voice and more facial hair.
Sex Chromosome: These are special chromosomes that decide whether someone is a boy or a girl. Girls have two X chromosomes (XX), and boys have one X and one Y chromosome (XY).
Target Site: This is a part of the body that is affected by a hormone. Hormones travel through the blood and act on specific target sites to cause changes.
Testosterone: This is the main male hormone. It helps develop male body parts and secondary sexual characteristics like muscle growth and sperm production.
Thyroxine: A hormone made by the thyroid gland that helps control the body’s metabolism, growth, and overall development.
Voice Box: Also called the larynx, it is part of the throat that makes sound and helps us speak.
|
90 videos|415 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Reaching the Age of Adolescence Class 8 Notes Science Chapter 7
| 1. What is adolescence and what changes occur during this phase? |  |
| 2. What are secondary sexual characteristics and when do they develop? |  |
| 3. How do hormones initiate reproductive functions in humans? |  |
| 4. How is the sex of the baby determined during conception? |  |
| 5. What is reproductive health and why is it important? |  |

















