Rickettsia, Chlamydia and Mycoplasma Chapter Notes | Microbiology - NEET PG PDF Download
Rickettsia
General Properties
- Members of Rickettsiae share several key traits:
- They are obligate intracellular organisms, meaning they must live inside host cells to survive.
- They cannot grow on artificial media, but they can be cultured using living cells, eggs, or mice (with the exception of Bartonella).
- They are usually spread by arthropod vectors, except for Coxiella, which is transmitted through inhalation.
- The order Rickettsiales includes genera like Rickettsia, Orientia, and Ehrlichia.
- Former members such as Coxiella and Bartonella are no longer part of this family.
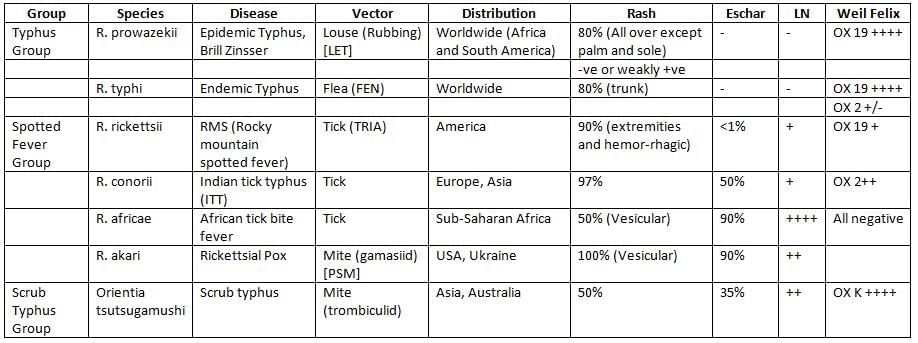
Clinical Manifestation
- Most severe form with systemic involvement: Rocky Mountain spotted fever
- Mildest form: R.pox
- Eschars are observed in:
- Rickettsial Pox
- African Tick Bite Fever
- Indian Tick Typhus (ITT)
- Scrub Typhus
- Distribution of Rash:
- Epidemic Typhus: Present all over the body, except for the palms and soles
- Endemic Typhus: Starts on the trunk and then spreads to the extremities
- Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever and Indian Tick Typhus (ITT): Rash on palms and soles
- Vesicular/Varicelliform Rash: Seen in Rickettsial Pox and African Tick Bite Fever
- No Rash: Characteristic of Q fever
- Q Fever:
- Acute Q Fever: Symptoms include fever, lung issues, and hepatitis
- Chronic Q Fever: Can lead to endocarditis
- CNS Involvement: Can cause mental confusion and coma, seen in both epidemic and endemic typhus
- Recrudescent Illness: Known as Brill-Zinsser disease, caused by R.prowazekii
- Transmission of ticks and mites:
- Bite from the infected insect.
- Transovarial transmission (from mother to offspring).
- Louse and flea-borne rickettsiae transmission:
- Autoinoculation (getting infected by rubbing the insect).
- Aerosol (inhaling dried feces of lice or fleas, which can occur in labs or during bioterrorism).
Scrub Typhus
- Agent: Orientia tsutsugamushi. It is different from Rickettsia both genetically and because it lacks Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) in its cell wall.
- Vector: Trombiculid mites, especially the genus Leptotrombidium (like L. akamushi in Japan and L. deliensis in India). The larval stage, known as chiggers, is the only stage that feeds on humans, which is why scrub typhus is sometimes called chiggerosis.
- Clinical manifestations: The typical symptoms include a triad of an eschar (a sore at the bite site), swollen lymph nodes in the region, and a maculopapular rash. However, this classic triad is only seen in 40-50% of cases.
- Antigenic diversity: Three main antigenic types have been identified: Karp, Gilliam, and Kato. Due to this significant antigenic diversity, immunity can decrease after 1-3 years.
- Zoonotic tetrad: Four key elements are necessary to sustain O. tsutsugamushi in nature:
- Trombiculid mites.
- Small mammals (like field mice, rats, and shrews).
- Secondary scrub vegetation or forests (which is why it's called scrub typhus).
- Wet season (when mites reproduce).
- Global scenario: Scrub typhus is found in several regions including Japan, China, the Philippines, Southeast Asia, India, Pakistan, Afghanistan, tropical Australia, New Guinea, and the Pacific Islands.
- Indian scenario: Scrub typhus is the most common rickettsial disease in India.
- Diagnosis: It can be diagnosed using the Weil-Felix test (higher OXK titer).
Ehrlichiosis
This infection belongs to the family Anaplasmataceae and includes four types of organisms that must live inside cells: Ehrlichia, Wolbachia, Anaplasma, and Neorickettsia.
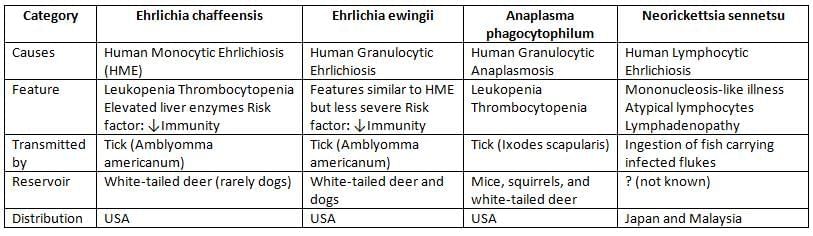
Common to all three Species
- Intracellular parasite: This type of organism lives inside the cells of its host.
- Cannot grow: It is unable to be grown in artificial laboratory conditions or media.
- Growth pattern: It develops in clusters within a compartment of the immune cells known as the phagosome, forming structures that resemble mulberries. These structures are referred to as MORULA.
- Medication: The recommended treatment is Doxycycline.
Laboratory Diagnosis of Rickettsiosis
Weil Felix Test
The Weil Felix test is a diagnostic method used to detect antibodies against rickettsial infections. It relies on the agglutination of specific strains of Proteus bacteria (OX 19, OX 2, and OX K) that share a stable antigenic similarity with rickettsial antigens.
Procedure: The test is performed through a tube agglutination method. This involves treating serial dilutions of the patient's serum with non-motile strains of P. vulgaris OX 19, OX 2, and P. mirabilis OX K.
Results Interpretation:
- Epidemic and Endemic Typhus: Sera primarily agglutinate with OX 19 and sometimes with OX 2.
- Tickborne Spotted Fever: Elevated antibodies to both OX 19 and OX 2.
- Scrub Typhus: Elevated antibodies to OX K.
- Negative Results: The test shows negative results for rickettsial pox, Q fever, ehrlichiosis, and bartonellosis.
- False Positive:. false positive result may occur due to an underlying Proteus infection. Therefore, a fourfold increase in antibody titer in paired sera is more significant than a single high titer.
- False Negative: False negative results can happen if there are excessive antibodies in the patient's sera, known as the prozone phenomenon. This can be mitigated by testing with serial dilutions.
- Specificity: Since the Weil Felix test is nonspecific, it is crucial to confirm results with specific tests for rickettsial infections.
Tests for Detecting Specific Antibodies
- Indirect Immunofluorescence Assay: This test is the most commonly used blood test to confirm a diagnosis.
- Complement Fixation Test (CFT): While this method is specific, it is not as sensitive.
- IgM Capture ELISA: This test is useful for early diagnosis, especially within the first week, and has excellent sensitivity.
- Latex Agglutination Test: This is another method used for diagnosis.
Other Diagnostic Methods
- Histological Examination:. biopsy from a rash can be examined even during the acute phase of the illness to aid in diagnosis.
- Isolation of Rickettsiae: Since Rickettsiae cannot grow in cell-free media, they can be isolated using cell lines (such as Vero, primary chick embryo, WI-38, HeLa), egg inoculation (such as yolk sac inoculation), or animal inoculation (for example, guinea pigs).
- Neil Mooser Reaction: This involves injecting specimens into male guinea pigs and observing changes over 3–4 weeks, which differ among rickettsial species.
- R. rickettsii: Causes scrotal necrosis, a rare complication.
- R. prowazekii: Causes fever without testicular inflammation.
- R. conori, R. akari, and R. typhi (code-CAT): Cause fever and a positive tunica reaction, indicating testicular inflammation.
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Tests: These tests target the 16S rRNA gene or outer membrane protein (OMP) genes of Rickettsiae for diagnosis.
Treatment of Rickettsiosis
- Doxycycline: This antibiotic is the preferred treatment for most rickettsial infections.
- Chloramphenicol: This antibiotic is an alternative option for treatment.
Bartonellosis
Bartonella species are fastidious, intracellular, gram-negative bacteria that have ability to invade RBCs. They differ from other rickettsiae being capable of growing on blood agar.

Treatment of Bartonella Infections
- Typical Cat scratch diseases: Azithromycin
- Atypical Cat scratch diseases: Doxycycline
- Trench fever: Gentamicin + Doxycycline
- Bacillary angiomatosis peliosis: Erythromycin
- Oroya fever: Chloramphenicol or Ciprofloxacin
- Verruga peruana: Rifampin or Streptomycin.
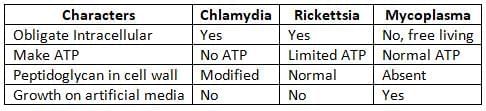
Chlamydia
General Properties
- Obligate intracellular gram-negative bacteria: These bacteria must live inside the cells of a host.
- Growth conditions: They cannot grow on artificial growth media but can multiply when introduced into cell lines, eggs, or mice.
- Filterable nature: These bacteria can be filtered and produce structures called inclusion bodies, similar to viruses.
- Genetic material: Unlike viruses, they contain both RNA and DNA.
- Cell wall composition: They have modified forms of peptidoglycans in their cell walls.
- Energy dependency: They cannot produce their own ATP (energy currency) and are known as energy parasites because they rely on the ATP from the host cell.
- Tropism: These bacteria show a preference for squamous epithelium and lymph nodes.
- Life cycle: They exist in two different forms:
- Elementary body (EB)
- Reticulate body
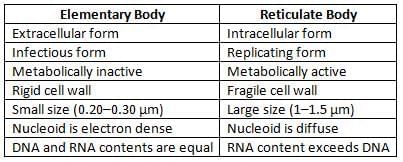
Chlamydia Trachomatis
C. trachomatis is the most common cause of:
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs), nongonococcal urethritis (NGU), and post-gonococcal urethritis (PGU)
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) and acute epididymitis
- Inclusion conjunctivitis: Swimming pool conjunctivitis (adults) and ophthalmic neonatorum or inclusion blennorrhea (neonates)
Complications:
- Reiter syndrome is marked by:
- CUP: This includes conjunctivitis, urethritis, and polyarthritis, along with mucocutaneous lesions.
- It is often seen in individuals with HLAB27 antigen.
- It is the most common cause of peripheral inflammatory arthritis in young men, primarily affecting the large joints of the legs.
- Fitz Hugh Curtis syndrome: This condition involves perihepatitis and is typically found in sexually active women.
- Urethral Syndrome in women includes symptoms such as:
- dysuria (painful urination)
- frequency of urination
- urethritis (inflammation of the urethra)
- pyuria (presence of pus in urine)
- No bacteriuria (absence of bacteria in urine).

Trachoma
- Chronic conjunctivitis is characterized by follicular hypertrophy (enlargement of lymph follicles), papillary hyperplasia (overgrowth of papillae), pannus (vascularized corneal tissue), and cicatrization (scarring).
- The stages of chronic conjunctivitis include: Trachoma dubium, Protrachoma, Established trachoma stages I to IV.
- Inclusion bodies, known as HP (Halberstaedter - Prowazek) bodies, are observed only in the established stages of trachoma (I to IV).
LGV (Lymphogranuloma Venereum)
- LGV is a type of sexually transmitted disease (STD) that is caused by the bacterium C.trachomatis, specifically the serovars L1, L2, and L3.
- The most common serotype is L2, which is more prevalent than L1 and L3.
- LGV serovars tend to be more invasive compared to other types of serovars.
- The occurrence of LGV is decreasing, with a ratio of 3.4 males for every 1 female affected.
- Clinical features of LGV include:
- Painless ulcers on the skin.
- Painful lymph nodes that become swollen, known as buboes.
- Esthiomone, which refers to swelling of the vulva (also called elephantiasis).
- Rectal stricture and proctitis can occur as well.
- A skin test can be positive, which is known as the Frie test.
Laboratory Diagnosis of Chlamydial Infection
- Microscopy: Gram staining often reveals sterile pyuria, characterized by an increased number of neutrophils without the presence of organisms, as they are poorly gram-negative.
- Other stains, like Castaneda, Machiavelli, and Gimenez, are more effective methods for identifying chlamydiae in samples.
- Inclusion bodies can also be found in the cytoplasm and have different names:
- LCL body (Levinthal-Cole-Lillie body): related to Psittacosis
- Miyagawa corpuscle: linked to LGV
- HP body (Halberstaedter-Prowazek body): associated with trachoma
- Lugol’s I2: used exclusively for C. trachomatis (this stains the glycogen inclusion body).
- Direct immunofluorescence test (DIF): used to directly detect inclusion bodies in clinical samples.
- Antigen detection:
- Enzyme Immunoassays identify chlamydial group-specific antigens (LPS).
- Culture methods:
- Mice inoculation: effective only for C. psittaci and LGV biovars.
- Yolk sac inoculation
- Cell culture inoculation:
- McCoy Cells and HeLa
- HEp2 for C. pneumoniae
- Serology tests:
- Micro-IF test: the preferred test for detecting specific antibodies using outer membrane protein (OMP) antigen.
- CFT (genus-specific): detects genus-specific antibodies using LPS antigen.
- High antibody levels are seen in cases of LGV, infant pneumonia, and salpingitis.
- Nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs), such as PCR: the best diagnosis method, offering high sensitivity and specificity, and is almost replacing the traditional culture method.
Treatment of Chlamydial Infections
- C. trachomatis: Azithromycin (1 gram single dose) is the overall drug of choice, except for:
- Complicated genital infections: Doxycycline or erythromycin are the drugs of choice.
- Neonatal infections: Erythromycin is the drug of choice for ophthalmic neonatorum and infant pneumonia.
- C. psittaci: Tetracycline is preferred over erythromycin for 7–14 days.
- C. pneumoniae: Tetracycline or erythromycin is used for 14 days.
Non Gonococcal Urethritis (NGU): Refer to chapter 3.3 for specific treatment guidelines.
Mycoplasma
Mycoplasma are the smallest free-living organisms known.General Properties
- They are filterable, which is why they are also known as Eaton’s agent.
- Previously referred to as PPLO - Pleuropneumonia-like organism.
- They do not have a rigid cell wall; instead of a peptidoglycan layer, they have cholesterol.
- This makes them resistant to antibiotics that target cell walls, like beta-lactams.
Clinical Features
- Incubation period is 2–4 weeks. they spread from person to person through respiratory droplets.
- The most common symptom is upper respiratory illness.
- They are the leading cause of community-acquired atypical pneumonia in adults.
- Pneumonia is known as primary atypical pneumonia (PAP), walking pneumonia, or Eaton agent pneumonia.
- Extrapulmonary symptoms include issues with the nervous system, skin, heart, joints, and blood.
Note: Ureaplasma urealyticum causes non-gonococcal urethritis, epididymitis, vaginitis, and cervicitis.
Laboratory Diagnosis
- They are poorly gram-negative, show pleomorphism, and resemble L forms.
- When stained with Dienes stain, a block of agar with Mycoplasma colony, added to methylene blue, is observed under a microscope.
- They exhibit gliding mobility but lack flagella and pili.
- Culture medium includes PPLO broth and PPLO agar.
- They form fried egg colonies.
- Antigen detection is done using a direct immunofluorescence test.
- PCR is more sensitive, while culture is more specific.a
- Detection of Antibodies:
- Heterophile antibody:
- The cold agglutination test detects Mycoplasma antibodies using human ‘O’ red blood cell antigen.
- The Streptococcus MG test detects Mycoplasma antibodies using Streptococcus MG antigen.
- Specific antibody:
- CFT (complement fixation test).
- ELISA for IgM, IgG, and IgA detection.
- Heterophile antibody:
- The combination of PCR for respiratory tract secretions and serological testing is the most sensitive and rapid method for diagnosing M. pneumoniae infection.
Treatment
- For Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Ureaplasma. DOC— Azithromycin.
- For M. hominis. DOC— Doxycycline.
|
75 docs|5 tests
|
FAQs on Rickettsia, Chlamydia and Mycoplasma Chapter Notes - Microbiology - NEET PG
| 1. What are Rickettsia and how do they affect human health? |  |
| 2. What is Anaplasma phagocytophilum and what disease does it cause? |  |
| 3. How does Neorickettsia sennetsu differ from other Rickettsia species? |  |
| 4. What are the characteristics of Chlamydia and how does it infect humans? |  |
| 5. What role does Mycoplasma play in human disease? |  |















