Shapes and Angles Class 5 Notes Maths Chapter 2
| Table of contents |

|
| What is a Shape? |

|
| Types of 2-D Shapes |

|
| What are Polygons? |

|
| Solved Examples: Shapes |

|
| Angles |

|
| Types of Angles |

|
| Angles in 2-D Shapes |

|
| Solved Examples: Angles |

|
From the wheels of a car to the windows of a building—is made up of different shapes and from observing a door moves through different angles as you open it or you see people doing yoga, you will see how these shapes and angles come together.
 Once you understand it, you’ll start noticing patterns and designs everywhere. So get ready to swing open the door to a fun adventure with shapes and angles.
Once you understand it, you’ll start noticing patterns and designs everywhere. So get ready to swing open the door to a fun adventure with shapes and angles.

What is a Shape?
- A Shape is the outline of an object.
- It tells us what an object looks like, whether it's round, square, or any other form.
- They help us describe and identify the objects around us.
For Example, a ball has a round shape, a book has a rectangular shape as shown below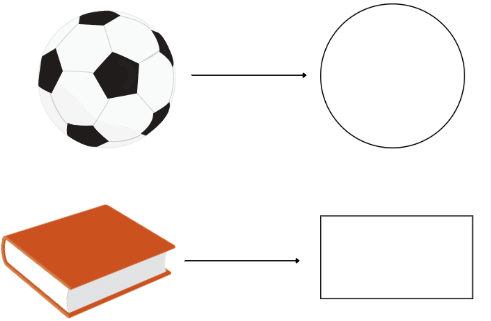
Types of 2-D Shapes
There are basically two types of 2-D shapes as shown below.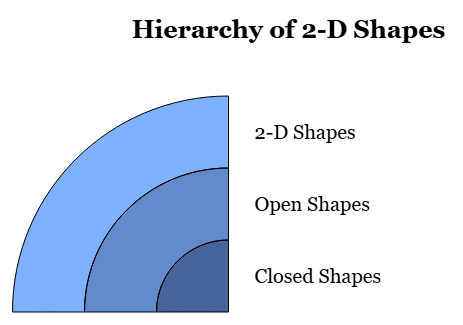
Now, let us discuss Open Shapes and Closed Shapes in detail.
1. Open Shapes
- An Open Shape is like a drawing where the lines don't connect.
- They don't start and finish at the same spot.
- It's like a shape with some parts left open or with lines that don't meet.
- Following are the Examples of Open Shapes
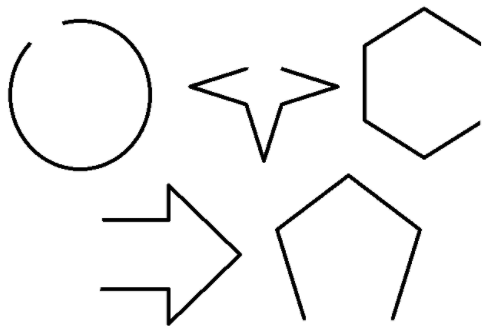
2. Closed Shapes
- A closed shape is like a drawing where you begin and finish at the same spot and there are no open ends.
- It's a complete shape with no gaps or loose ends.
- In regular shapes, rectangles, triangles, circles, etc., can be referred to as closed figures.
- Following are the Examples of Closed Shapes
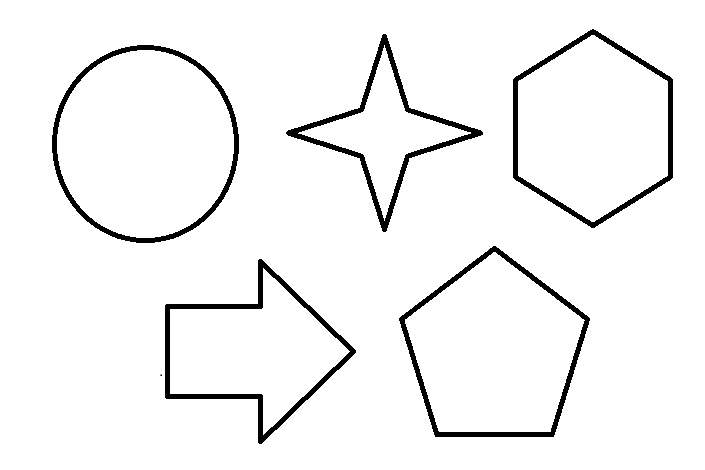
Now, Imagine a 2-D shape made of straight lines and closed boundaries. This includes shapes like squares, triangles, and hexagons.
These are called Polygons.
What are Polygons?
- In geometry, a Polygon is any closed figure made up of a series of lines (sides).
- A Polygon must have a minimum of three lines.
- Triangles (three sides), Quadrilaterals (four sides), and Pentagons(five sides) etc. are the some examples of polygons.
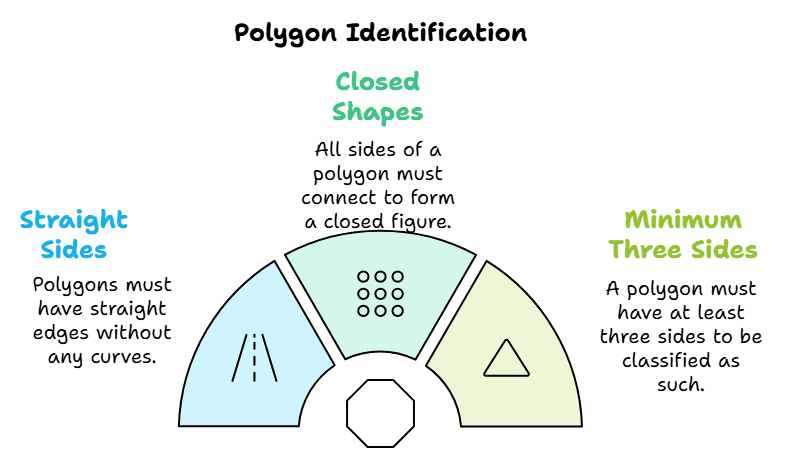
Tips to identify a Polygon
- They have straight sides (no curves).
- They are closed shapes (all sides connect).
- They have at least three sides (like a triangle) and can have many more.
Solved Examples: Shapes
Example 1: Identify whether the following shapes are Open or Closed shapes.
1.

Sol: The shapes shown above are Open Shapes.
This is because they start and end at different points. The lines donot connect.
2.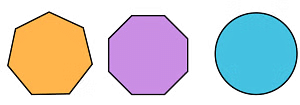
Sol: The shapes shown above are Closed Shapes.
These are closed shapes because all the lines or the curves are connected, and the start and end point are the same.
Example 2: Matthew came across these objects while going to school. Can you help him identify these objects as open or closed shapes?
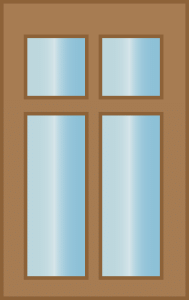
Sol: Sorting these things depends on their shapes.
The first object resembles a twisted rope with ends that do not touch, making it an Open Shape.
The second thing is a paper clip with two ends that don't connect, making it an Open shape.
The third thing is a window, and its sides are connected, so it is a closed shape.
Example 3: Is the shape in the following image open or closed?
Sol: The picture shows a shape where all the sides are connected, and it starts and finishes at the same point.
So, it's a Closed shape.
Example 4: A circle is a closed shape. So, Is it a polygon?
Ans: No, a Circle is not a Polygon.
Sol: According to the definition of Polygon ,
It should have atleast 3 straight lines joined to form a closed shape.
As Circle doesnot have any straight lines,
Therefore it is not a Polygon.
Angles
- An Angle is made when two lines meet at one point.
- Imagine a slice of Pizza, Each slice has an angle at the pointy end as shown below
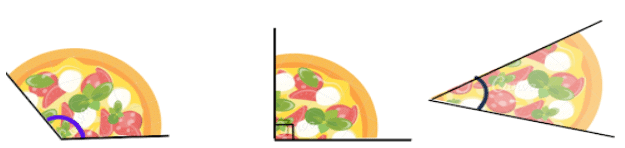
Measuring Angles
- An angle measure in geometry is the measurement of the angle created when two lines meet at one common point.
- The unit of measurement of an angle is degree.
- The sign '°' represents a degree.
- Angles with varying degrees include 30 degrees, 45 degrees, 90 degrees, and so on. And is written as 30 degrees, 45 degrees, 90 degrees, and so on.
- Angles are measured using a simple geometric instrument such as a Protractor.
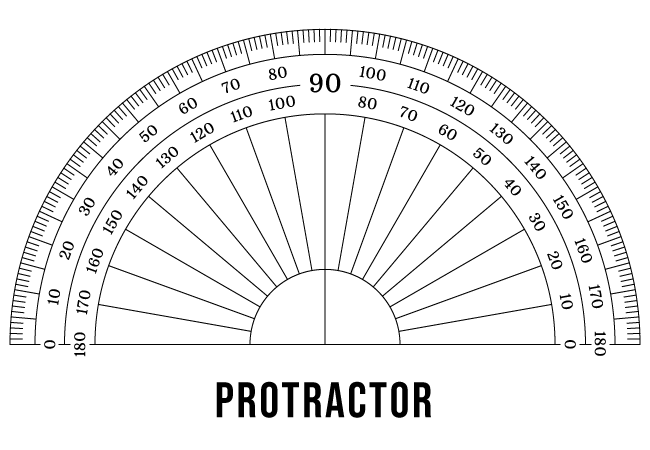
Types of Angles
Angles are basically classified into three categories.
- Angles less than 90 degrees are called Acute Angles.
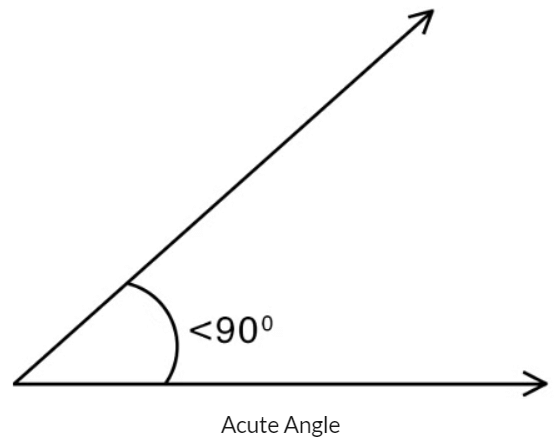
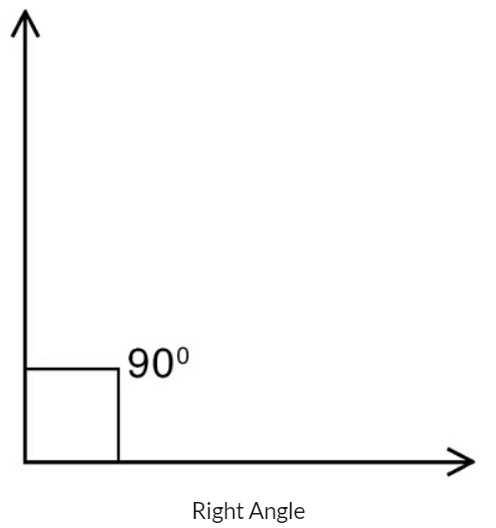
- Angles equal to 90 degrees are called Right Angle.
- Angles greater than 90 degrees but lesser than 180 degrees are called Obtuse Angles.

Did You Know
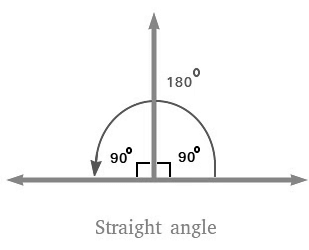
- If the angle is equal to 180 degrees, it is called as Straight Angle.
- It is called straight angle because it measures 180 degrees, forming a straight line without any bends or curves.
Angles in 2-D Shapes
1. Triangle
1. Triangle
- A Triangle is a three-sided geometrical figure with three angles.
- The sum of angles of a triangle is 180 degrees.

2. Quadrilateral
- A Quadrilateral is a four-sided geometrical figure with four angles.
- The sum of angles of a Quadrilateral is 360 degrees.
- Example of Quadrilaterals are given below,
Where each of them have the sum of all the angles equal to 360 degrees.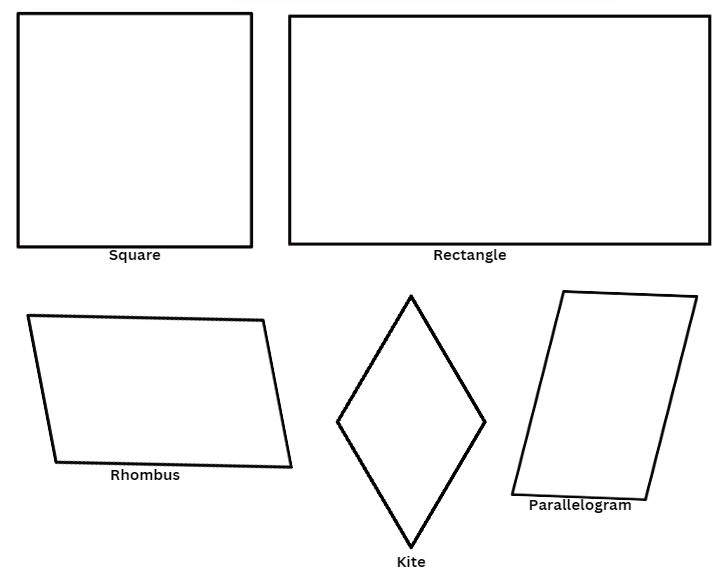
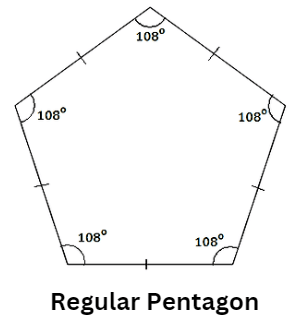
3. Pentagon
- A Pentagon is a five-sided geometrical figure with five angles.
- The sum of angles of a pentagon is 540 degrees.
- A Regular Pentagon has all angles equal to 108 degrees.
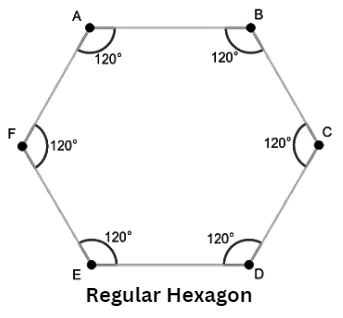
4. Hexagon
- A Hexagon is a six-sided geometrical figure with six angles.
- The sum of angles of a hexagon is 720 degrees.
- A Regular Hexagon has all angles equal to 120 degrees.
Angles Made by Clock at Different Time

- On a clock, we may see various angles based on their amplitude: acute, straight, obtuse, flat angles, and even complete angles.
- The full circumference of the clock is 360 degrees.
- The distance between each number on the clock is similar to 30 degrees .
- For Example, the Angle created between 1 o’clock and 2 o’clock is 30 degrees.
Solved Examples: Angles
Example 1: Look at the following pictures and answer the questions given below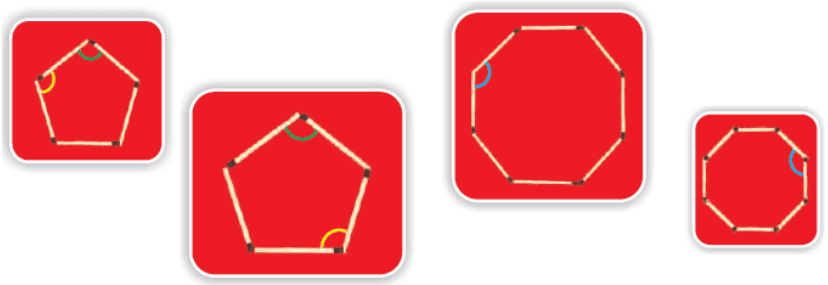
a) Are the angles marked in yellow equal and why?
b) Are the angles marked in green equal and why?
c) Are the angles marked in blue equal and why?
Ans: a) Yes, the angles marked in yellow are equal
Sol: As both the Yellow angles are of a Regular Pentagon(A shape having 5 sides),
Therefore, all angles will be equal to 108 degrees
Hence , the angles are equal.
b) Yes, the angles marked in green are equal
Sol: As both the green angles are of a Regular Pentagon(A shape having 5 sides),
Therefore, all angles will be equal to 108 degrees
Hence , the angles are equal.
c) Yes, the angles marked in blue are equal
Sol: As both the blue angles are of a Regular Octagon(A shape having 8 sides),
Therefore, all angles will be equal to 135 degrees
Hence , the angles are equal.
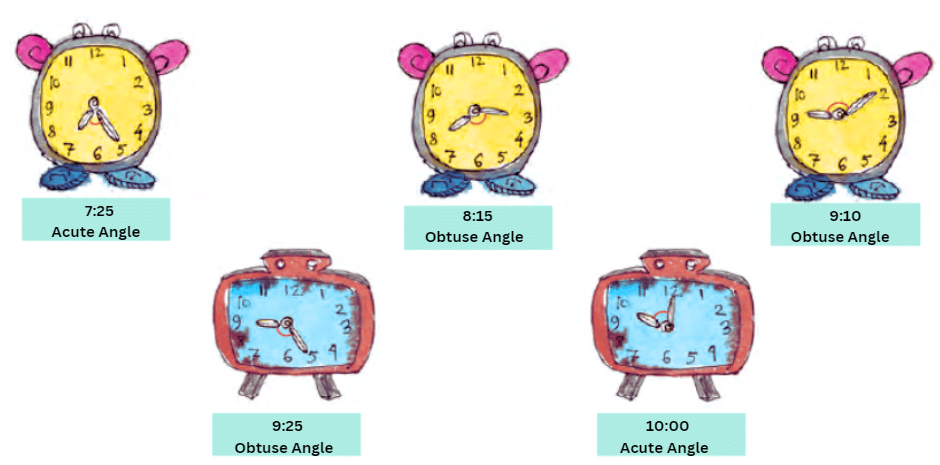
Example 2: What kind of angles are made by the hands of the clock given below
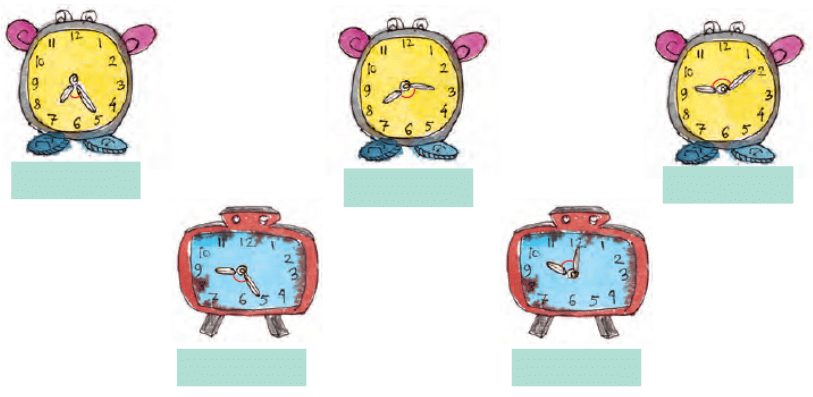
Sol:
Example 3: What kind of angles are made by the given yogic poses below
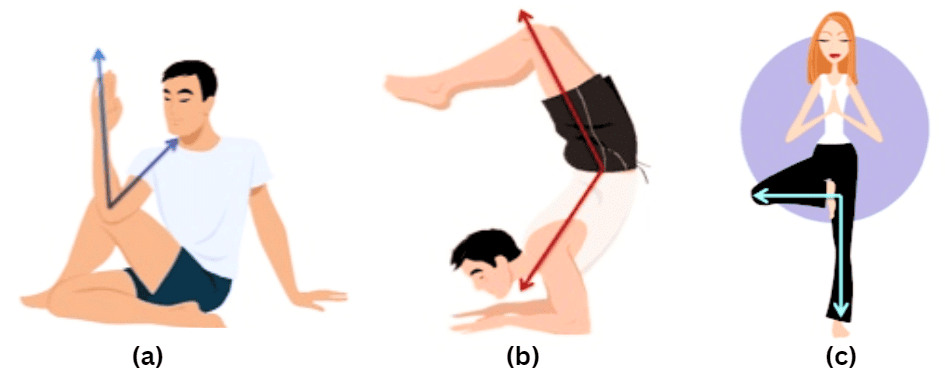
Sol: In figure (a), the angle made by the arm is Acute Angle.
In figure (b), the angle shown is Obtuse Angle.
In figure (b), the angle shown is Right Angle.
Example 4: Find out how many angles are made by joining the following match sticks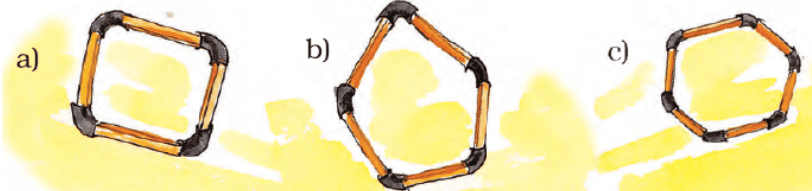
- Sol: In fig(a) ,we can make 4 angles .
- In fig(b), We can make 5 angles.
- In fig(c), We can make 6 angles.
|
31 videos|192 docs|41 tests
|
FAQs on Shapes and Angles Class 5 Notes Maths Chapter 2
| 1. What are the different types of 2-D shapes? |  |
| 2. How do you classify angles? |  |
| 3. Can you provide examples of solved problems related to shapes? |  |
| 4. What is the importance of learning about shapes and angles in Class 5? |  |
| 5. How can I identify different types of angles in real life? |  |