Shapes Around Us Chapter Notes | Mathematics for Class 2 (Joyful-Mathematics) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| 2D Shapes |

|
| What are 3D shapes? |

|
| What are some Different 3D shapes? |

|
| Odd One Out |

|
| What are the Properties of Different 3D shapes? |

|
| Corners |

|
Look at the picture and observe different musical instruments:

- Everything we see in the world around us has a shape.
- If we look at musical instruments, we can see how they all are similar to a shape.
- Students, let us help Maria match the musical instruments in the music room of her school to the shapes they match.

- The clarinet resembles a cone.
- Harmonium matches the shapes of a cuboid.
- Dholak resembles the shape of a cylinder.
- The tambourine matches the shape of a circle.

Musical instruments are tools we use to make music. Just like tools in a toolbox, each instrument has its own job and sound.
For example, a guitar has strings that we strum to make music, while a drum lets us tap out beats with sticks.
There are different types of instruments. Some you blow into, like a flute or a trumpet, and they make sound when air passes through them. Others you hit or shake, like drums or maracas, to make different sounds.
Each instrument has its own unique shape, size, and sound. Some are big and loud, like a piano, while others are small and delicate, like a violin.
Let us now revise the concept of 2D Shapes
2D Shapes
2D shapes can be defined as plane figures that can be drawn on a flat (or plane) surface or a piece of paper.
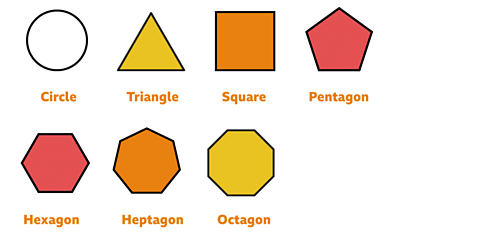
- Circle: A circle is a round shape on a flat surface. It's like a big loop that goes around and around. Imagine there's a special point right in the middle of the circle, called the "center." Every point on the circle is the same distance away from this center point.
- Triangle: A triangle is a three-sided polygon (2D Shape) which has three edges and three vertices. The sum of all the three angles of a triangle is equal to 180°.
- Square: A square is a four-sided polygon (2D Shape), whose four sides are equal in length and all the angles are equal to 90°.
- Rectangle: A rectangle is a 2D shape which has four sides, where the opposite sides are equal and parallel to each other.
- Pentagon: A pentagon is a shape with five sides, like a house on paper. It can look the same on all sides (regular) or different (irregular). When it's regular, each corner inside the shape is 108 degrees, and each corner outside the shape is 72 degrees.
- Octagon: An octagon is an eight-sided polygon which can be either regular or irregular. It is a 2d shape which has eight angles. The sum of all the interior angles of an octagon is 1080°.
What are 3D shapes?
- Imagine you have special shapes that aren't flat like paper.
- These shapes take up space all around, and we call them 3D shapes because they have three dimensions: length, height, and width.
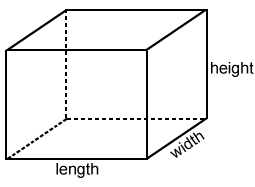
- It's similar to holding a toy or a block that you can touch and feel from all sides.
- Now, you might know about 2D shapes, such as squares and circles, which are flat, like drawings on paper.
- Well, 3D shapes are different because they're not flat. Instead, they're real objects that you can hold because they occupy space in three different ways.
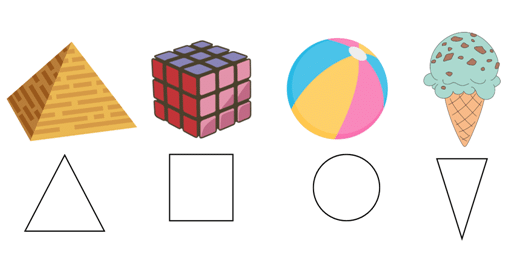
- Some examples of 3D shapes include cubes (similar to dice), pyramids (like the top of a triangle tower), spheres (like a ball), and cones (like an ice cream cone). You can find these shapes all around you—in toys, buildings, and even in your snacks, such as cookies and fruits!
- Look at the shapes given below and see how they match the shapes.
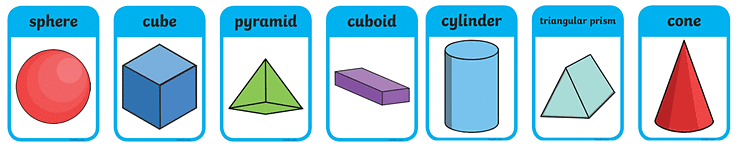
What are some Different 3D shapes?
Here are some common examples of different 3D shapes that you should know about. Take a look at the image below to see what they look like:
- Sphere (3D circle)
- Cube (3D square)
- Square Pyramid (3D triangle with a square base)
- Cuboid (3D Rectangle)
- Cylinder (3D shape with a circular base)
- Triangular Prism (3D shape with identical triangle bases)
- Cone (3D triangle with a circular base)
Odd One Out
Let us play a game.Given below are images of a few objects. Can you identify which is the odd one out?
"Odd one out" means finding the one thing that is different or doesn't belong in a group. It's like playing a game of "spot the difference" where you look at a group of things and find the one that doesn't fit with the others.
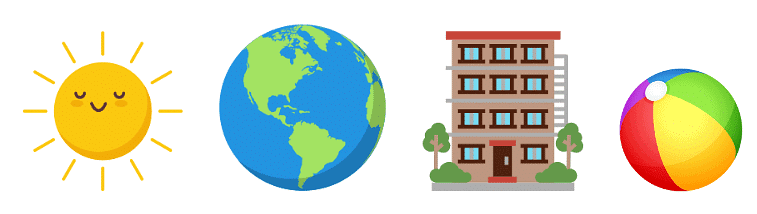
First is the sun, then a globe, a building and a ball.
Now, we can see that the sun, globe and ball, all match the shape of a circle. The building is not circular in shape.
Hence, building is the odd one out. Well done students!
Well done students!
What are the Properties of Different 3D shapes?
All three-dimensional shapes are different but have three primary properties in common. These main 3D shape properties include: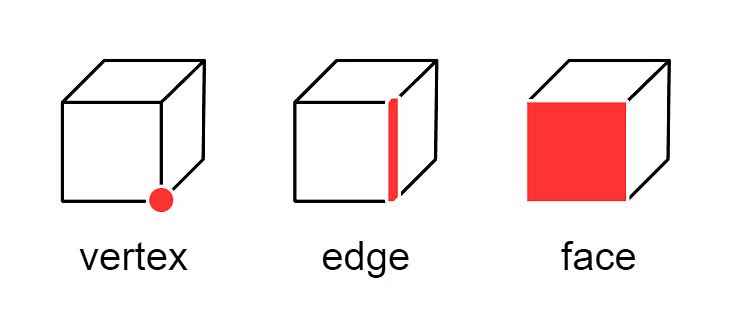
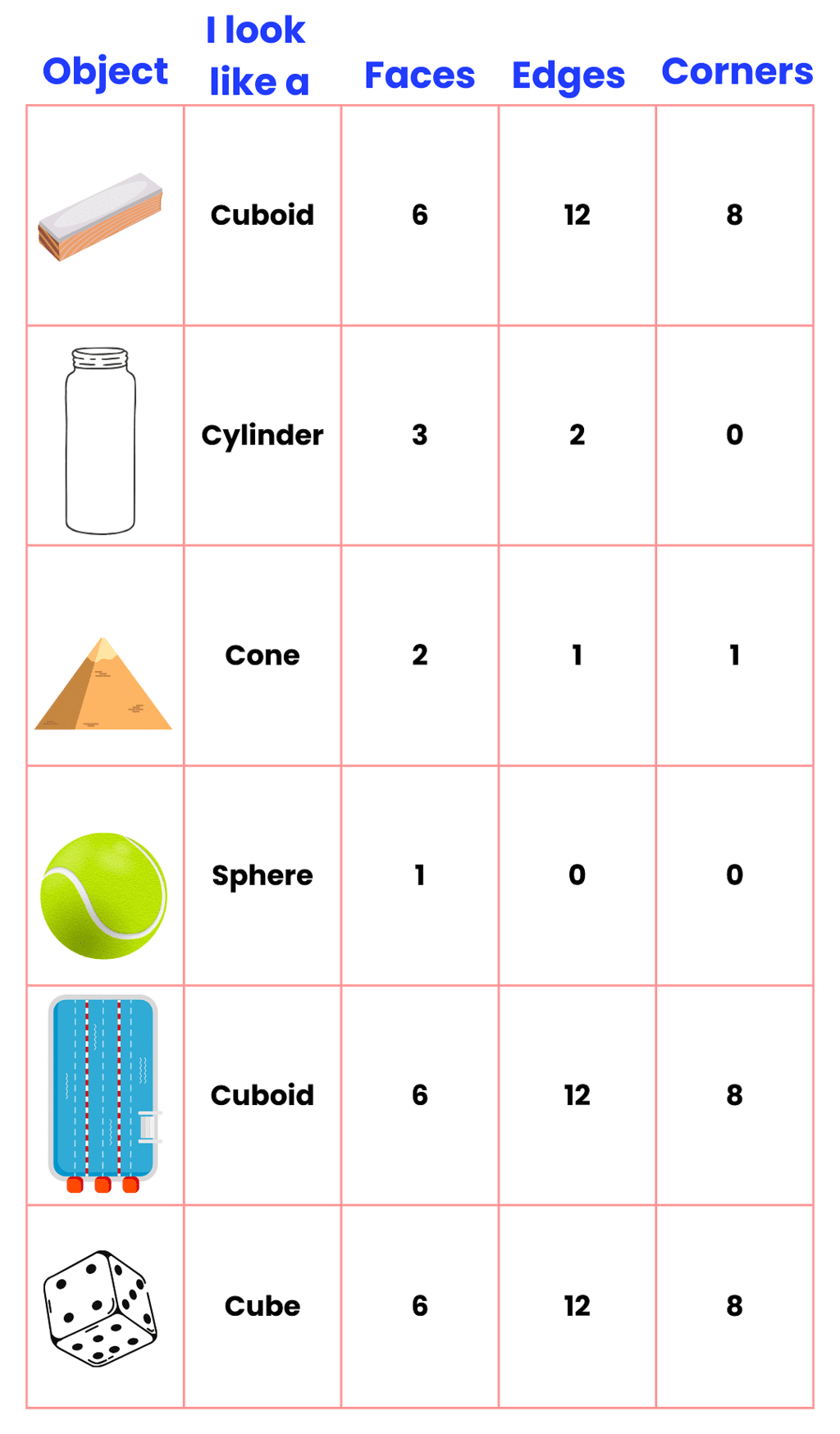
- Faces: Faces are flat surfaces on the shape.
A face is a flat or curved surface on a 3D shape.
For example, a cube has six faces, a cylinder has three and a sphere has just one. - Edges: Edges are straight lines that define the sides of the polygons that make up each face of the shape.
An edge is where two faces meet. For example, a cube has 12 edges, a cylinder has two and a sphere has none. - Vertices: Vertices (or corners) are points where at least three edges meet.
A vertex is a corner where edges meet. The plural is vertices. For example, a cube has eight vertices, a cone has one vertex and a sphere has none.
Have a look at the picture below, which shows these key parts of 3D shapes. A cube is taken as an example, but we can apply this knowledge to other three-dimensional shapes, too.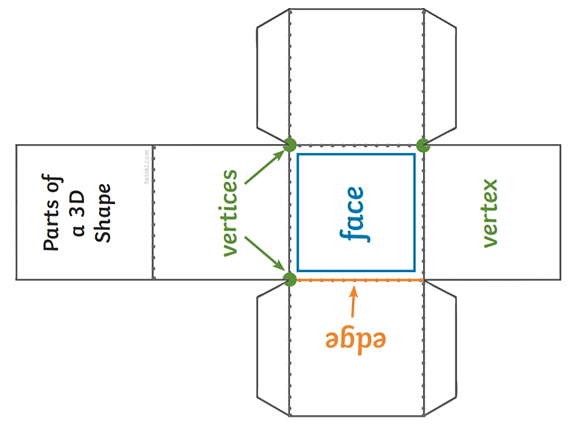
This is also an example of a net. A net shows what 3D shapes would look like if it was taken apart and flattened.
When a cardboard box is constructed, it is a 3D shape – a cuboid or a cube. When it is flattened, it becomes a 2D net, which is like an irregular 2D shape.
Now, let's talk about the properties of 3D shapes! These are the special things about each shape that make them unique. For example:
- Properties of a Sphere (2D – Circle)
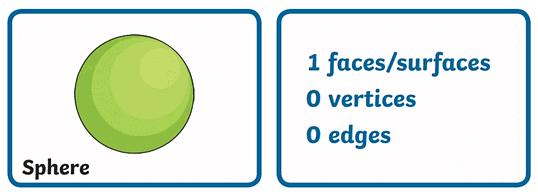
- Properties of a Cube (2D – Square)
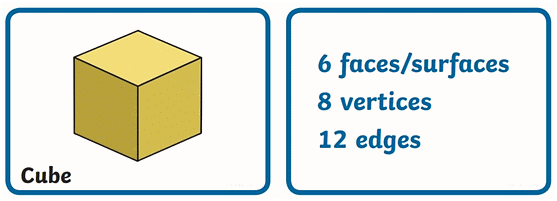
- Properties of a Square Pyramid (2D – Triangle and Square)
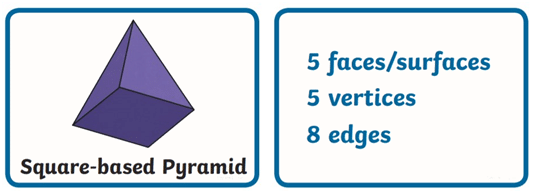
- Properties of a Cuboid (2D – Rectangle)
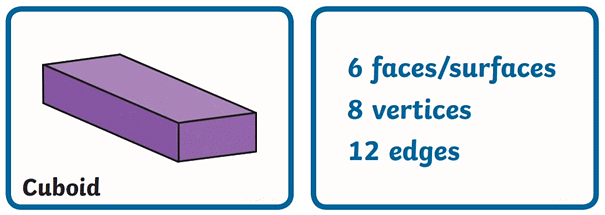
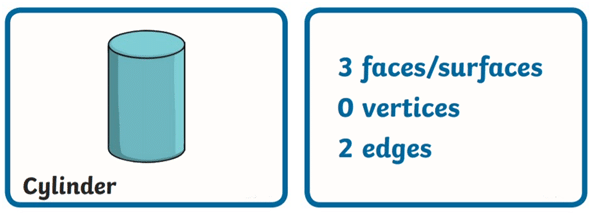
- Properties of a Cylinder (2D – Circle)
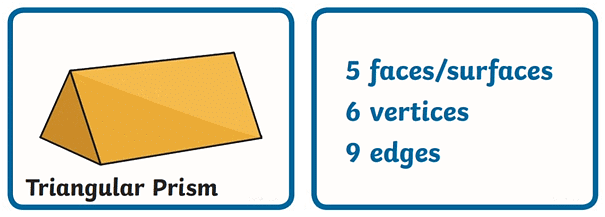
- Properties of a Triangular Prism (2D – Triangle)
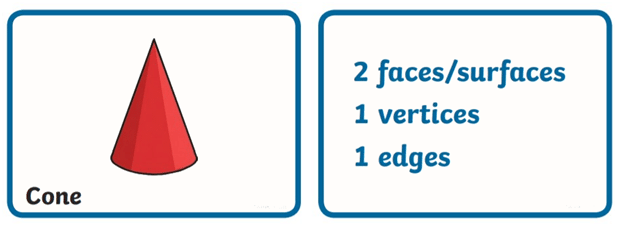
- Properties of a Cone
You can pick everyday objects, which you are familiar with or would have seen in comics or cartoons:
- a ball– a great example of a sphere;
- a Rubik's cube or a die– examples of a cube;
- a party hat– an example of a cone;
- the Egyptian pyramids – an example of square-based pyramids.
Can you now notice the difference between a ball for example and a circle drawn on a piece of paper?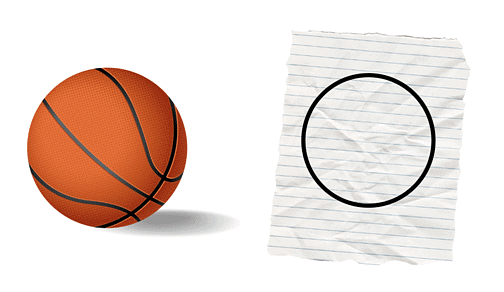
Yes, you are right, now you are able to tell that the ball on the right is real and 3D in shape. And What's the shape? Yes, you are right again, it’s a Sphere; while the one on the right is a 2D shape of circle drawn on a paper.
Students, look around your surroundings and look at different objects. Try matching them to shapes and count how many faces, edges and vertices they have.
Look at the table below, we have taken a few of the objects that you see in your daily life and have mentioned the number of faces, edges and vertices.
Corners
Let's go on a fun adventure to find objects with different numbers of corners!
No Corners:
Let's think about things that are super round and don't have any corners at all.
A. Balloon
B. Cloud
C. Soap Bubble
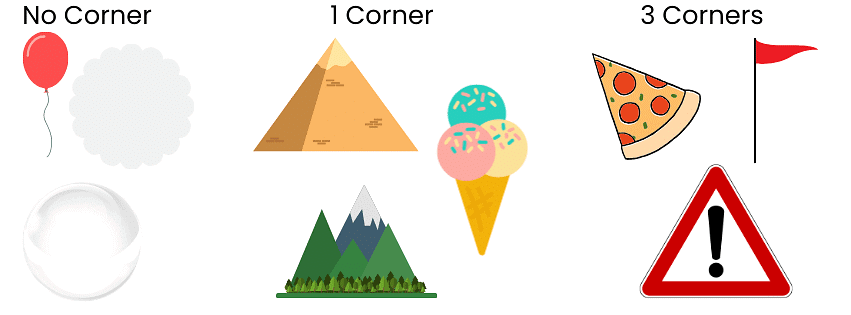
One Corner:
Now, let's search for something with just one little corner. Hmm, what could it be?
A. Pyramid
B. Mountain
C. Icecream
Three Corners:
Okay, last but not least, let's find something with three corners. Hmm, where could we find that?
A. Triangle road sign
B. Pizza slice
C. Flag
Hope you'll continue to look around your surroundings with curious eyes. You'll be amazed at how many fascinating shapes and objects you can find! Whether it's a round ball, a triangular slice of pizza, or a rectangular door, shapes are everywhere, waiting to be discovered. So, keep exploring and noticing the world around you. Who knows what interesting shapes you'll find next!
|
28 videos|262 docs|22 tests
|
FAQs on Shapes Around Us Chapter Notes - Mathematics for Class 2 (Joyful-Mathematics)
| 1. What are some examples of 3D shapes? |  |
| 2. How do 3D shapes differ from 2D shapes? |  |
| 3. What are the properties of different 3D shapes? |  |
| 4. Can you provide an example of an odd one out among 3D shapes? |  |
| 5. How are 3D shapes commonly used in everyday life? |  |















