Solids, Liquids and Gases Class 4 Notes Science
| Table of contents |

|
| What Is Matter? |

|
| What Is Matter Made Up of? |

|
| The States of Matter |

|
| Solids |

|
| Change of States of Matter |

|
What Is Matter?
Matter is everything around us that has mass and takes up space. It's what things are made of. You, your toys, the air, water, and even the food you eat are all examples of matter. Everything that you can touch, feel, or see is made up of matter.
Look around you in the classroom. Tick the things you see.
- Plant
- Chair
- Desk
- Blackboard
- Chalk
- Water
- Lizard
- Book
All the things mentioned above have two things in common:
- They take up space.
- They have mass.
The space taken up by an object is called its volume and the amount of matter contained in an object is its mass. Anything that has mass and takes up space is called matter. Thus people, animals, plants, water, chairs, aeroplanes, kites and all other things around us matter.
Does air matter? Yes. It has mass, and it takes up space.
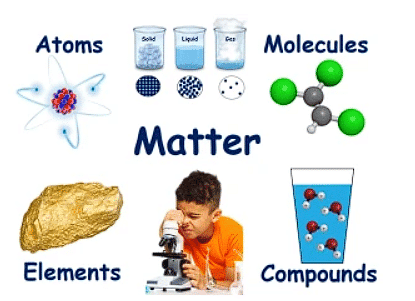
What Is Matter Made Up of?
All matter is made up of tiny particles called molecules. They are made of atoms. The molecules of every substance are different.
The States of Matter
Matter around us can either be solid, liquid or gas. A brick is a solid, water is a liquid and air is a gas. Solid, liquid and gas are the three states of matter.
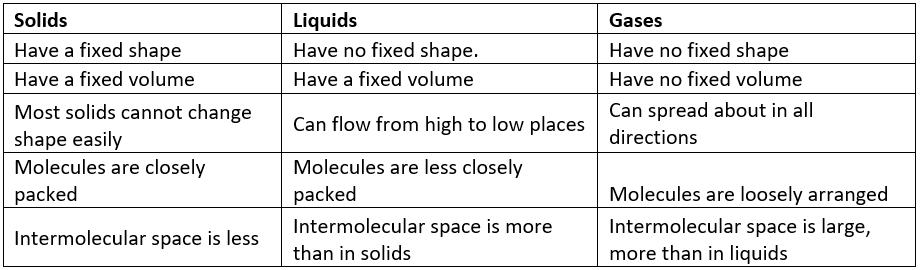
The three states of matter have different properties. The arrangement of the molecules in them is also different. The space between the molecules, called intermolecular space, varies in the three states of matter.
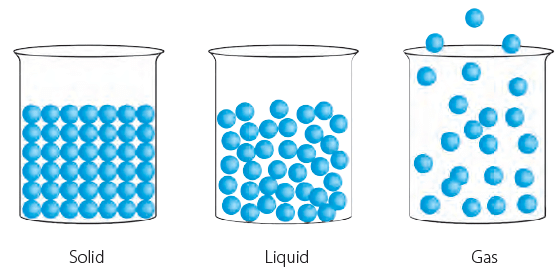 Intermolecular spaces in solids, liquids and gases
Intermolecular spaces in solids, liquids and gases
There are 3 states of matter.
Solids
A pencil, a slice of bread, a piece of wood and a pair of shoes are solid things.
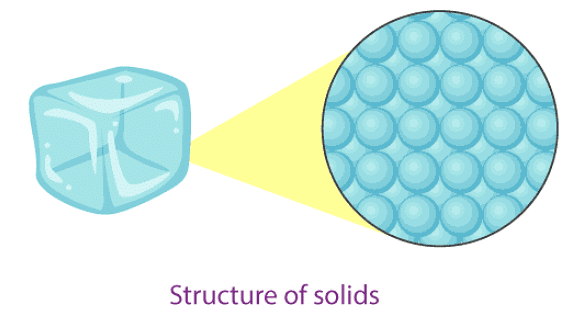
Properties of solids
- In solids, particles are tightly or closely packed.
- The gaps between the particles are tiny and hence it is tough to compress them.
- Solid has a fixed shape and volume.
- Due to its rigid nature, particles in solid can only vibrate about their mean position and cannot move.
- Force of attraction between particles is adamant.
- The rate of diffusion in solids is very low.
- An example of solids: solid ice, sugar, rock, wood, etc.
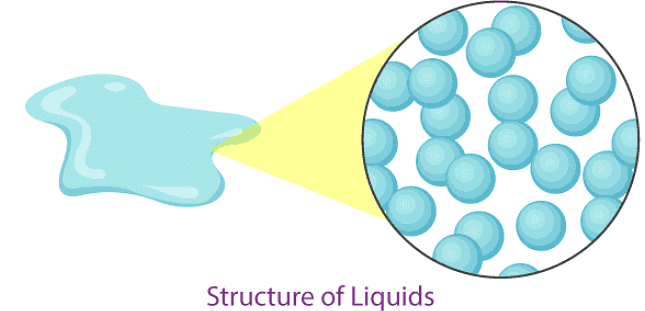
Liquid
- In a liquid state of matter, particles are less tightly packed as compared to solids.
- Liquids take the shape of the container in which they are kept.
- Liquids are difficult to compress as particles have less space between them to move.
- Liquids have fixed volume but no fixed shape.
- The rate of diffusion in liquids is higher than that of solids.
- Force of attraction between the particles is weaker than solids.
- Example of a liquid state of matter: water, milk, blood, coffee, etc.
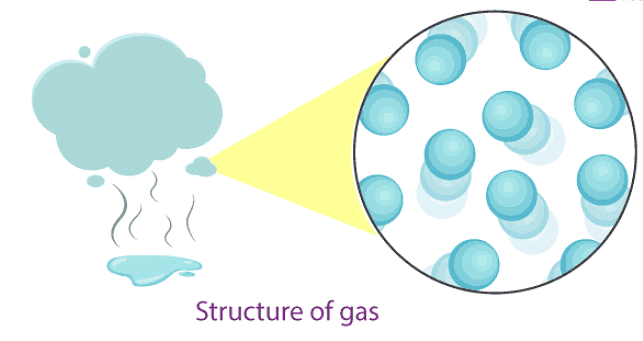
Gases
- In gases, particles are far apart from each other.
- Force of attraction between the particles is negligible, and they can move freely.
- Gases have neither a fixed volume nor a fixed shape.
- The gaseous state has the highest compressibility as compared to solids and liquids.
- The rate is diffusion is higher than solids and liquids.
- The kinetic energy of particles is higher than in solids and liquids.
- An example of gases: air, helium, nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, etc.
Change of States of Matter
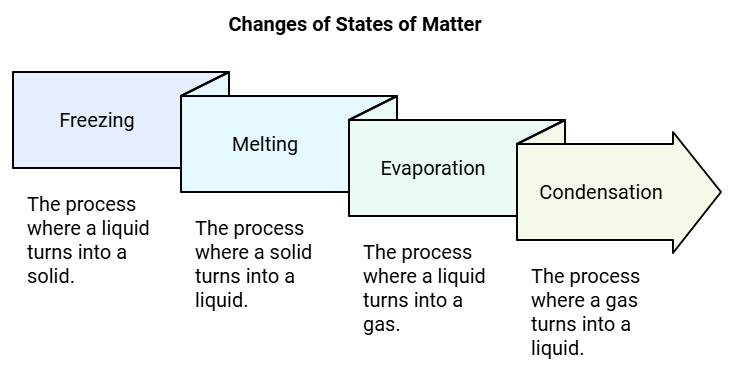
Water is a liquid. But it can also be a solid, as ice. It can be a gas too, as water vapour. In all cases, the arrangement of molecules changes.
Freezing
Freezing is the process by which a substance changes from a liquid state to a solid state upon cooling. When kept in freezer for 2-3 hours. The water changes into ice.
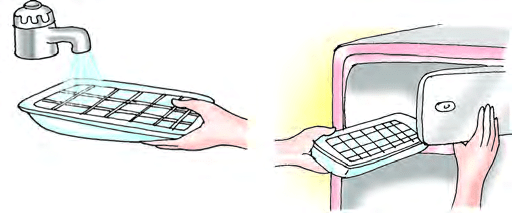 Freezing
Freezing
Melting
Melting is the process by which a substance changes from the solid state to the liquid state upon heating. Keep some ice cubes in a pan and heat it gently. The ice melt to form water.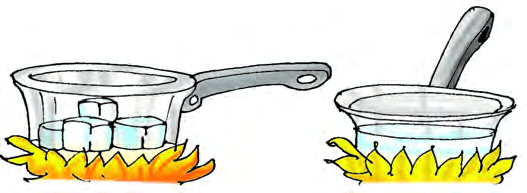 Melting
Melting
Evaporation
Evaporation is the process by which a substance changes from the liquid state into its vapour form upon heating. Heat water in a kettle. After some time the water starts boiling and you can see steam escaping from water. When water is boiled in a kettle, steam or gas appears.
When water is boiled in a kettle, steam or gas appears.
Condensation
- Condensation happens when a substance changes from gas to liquid when it cools down.
- Water vapor, like steam from boiling water, can turn back into liquid water when it cools.
- To see condensation, place a cold steel plate over the steam coming from a boiling kettle.
- The steam touches the cold plate, cools down, and becomes water again.
- We can also see state changes in materials like butter and wax, where they can melt and solidify again.
 Condensation
Condensation
 Melting of butter
Melting of butter
Soluble Substances
- Certain solids dissolve in water, known as soluble substances.
- When you add a spoon of sugar to water and stir it, the sugar disappears because it dissolves in the water.
- This means sugar is soluble in water, just like salt, sugar, soap, and orange juice.
- Sugar crystals break down and occupy the spaces between water molecules when dissolved.
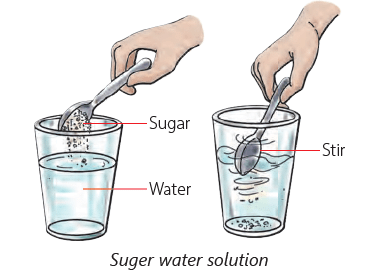
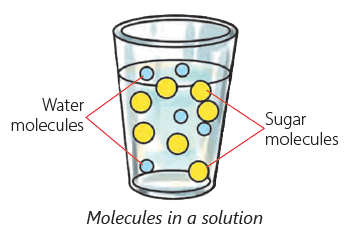
Solute, Solvent and Solution
The substance that dissolves in a liquid to form a solution is called a solute. Salt and sugar are solutes.
The liquid in which a solute dissolves is called a solvent. Water is a solvent. Water is known as a universal solvent as it can dissolve many substances such as salt, sugar, coffee and many more.
A solution is the mixture formed when a solute dissolves in a solvent.
Solvent + Solute = Solution
Edurev Tips:
Petrol and kerosene are also solvents. Kerosene is used to dissolve oil paint whereas petrol is used to dissolve grease.
Insoluble Substances
Some solids do not dissolve in water. When we make tea at home, we mix water, milk, sugar and tea leaves together. The sugar dissolves in the tea but the tea leaves do not. We can say that the sugar is soluble whereas tea leaves are insoluble in water. We can separate insoluble solids from liquids by two methods.
Filtration
Tea leaves are taken out from the tea by filtration method. Tea is poured through a sieve and tea leaves are separated from the tea.
 Filtration
Filtration
Sedimentation and decantation
Mix some sand in a glass of water. Does it get dissolved? No, sand in also insoluble in water. Leave the water-sand mixture for some time. You will see that the sand is collected at the bottom of the glass. This process is called sedimentation. Now you can slowly pour the water from the glass, leaving sand undisturbed at the bottom of the glass. This process is called decantation.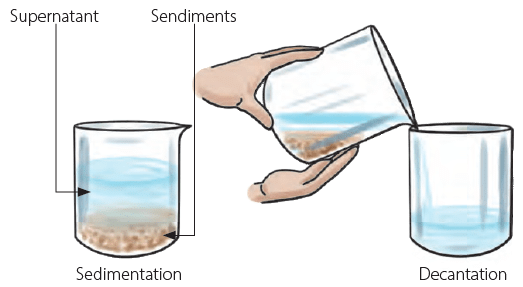 Separating a mixture of sand and water using sedimentation and decantation
Separating a mixture of sand and water using sedimentation and decantation
|
48 videos|156 docs|34 tests
|
FAQs on Solids, Liquids and Gases Class 4 Notes Science
| 1. What is matter and why is it important? |  |
| 2. What are the three main states of matter? |  |
| 3. How do solids differ from liquids and gases? |  |
| 4. What causes a change in the state of matter? |  |
| 5. What is the difference between soluble and insoluble substances? |  |
















