Structure and Support Chapter Notes | Science for Grade 6 PDF Download
Introduction
This chapter is all about how living things, like humans, animals, and plants, have special parts that help them stay strong and move around. In humans, muscles and bones work together to help us stand, walk, and even do cool things like a handstand! Animals without bones, like worms, use other ways to support their bodies and move. Plants also have their own structures, like roots and stems, to stay upright and grow. This chapter explains how these systems work in simple terms, so you can understand how different organisms are built to stand tall and move.
What supports a body and enables it to move?
Muscles
- Muscles are strong tissues that help the body move by contracting (getting shorter).
- When muscles relax, they return to their original length.
- Muscle cells have many mitochondria, which produce energy needed for muscle movement.
- Muscles work with bones to make the body move, like pulling on bones to lift an arm.
Skeletal System
- The skeletal system, made of bones, works with muscles to support and move the body.
- Bones provide a strong framework that muscles attach to for movement.
- The muscular system (muscles) and skeletal system (bones) team up to help you walk, run, or do activities like a handstand.
Joints
- Joints are places where two or more bones meet, allowing the body to bend and move.
- Ligaments are tissues that connect bones at joints, keeping them in place during movement.
- Joints provide flexibility, like when a girl uses her arm joints to hold a handstand.
Did You Know?
- Arms and legs act like simple machines called levers, where muscles pull on bones to create movement.
- Joints act as the fixed point (like a hinge or pivot) where the lever rotates.
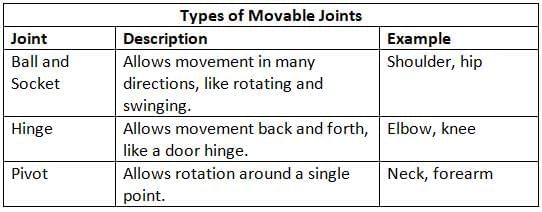
- There are three types of movable joints that help the body move in different ways: ball and socket, hinge, and pivot joints.
Other Functions of the Skeletal System
Protection
- If you touch your head and then your stomach, you'll notice that the stomach is softer, while the head feels hard and rigid.
- The hard part of your head is the skull, which protects the soft and delicate brain tissue from injury.
- Other bones in the body also offer protection to vital organs like the spinal cord, heart, lungs, and various internal organs.
Production and Storage
- Bones have another important role — they produce and store materials that the body needs.
- Red blood cells are made inside bones.
- Bones also store fat and calcium.
- Calcium is essential for strong bones and is also involved in many cellular processes.
In what ways are different animals supported and provided with structure?
Fluid Support
- Some animals have a hydrostatic skeleton, which is an internal cavity filled with fluid and surrounded by muscle tissue.
- The muscles push the fluid in different directions, allowing the organism to move.
- Examples of animals with hydrostatic skeletons include:
- Flatworms
- Sea anemones
- Earthworms
External Support
- Many animals are supported and protected by hard outer coverings, often called shells.
- These outer coverings give structure and defense to animals like:
- Crabs
- Snails
- Scorpions
- A thick, hard outer covering that protects and supports the animal’s body is known as an exoskeleton.
How Nature Works: Propulsion
The Secret of a Squid's Speed
- Squids swim slowly using fins but use jet propulsion to move fast.
- Jet propulsion is when water is pushed out of the squid’s body to move it forward, like air escaping a balloon.
- The mantle, a wall around the squid’s organs, expands to take in water and contracts to push it out through a funnel.
- Squids can change direction by bending the funnel to shoot water in different directions.
- Other animals like octopuses and cuttlefishes also use jet propulsion to move quickly.
What do different types of muscles do?
There are three types of muscle cells: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth, each with different jobs.
Skeletal Muscle
- Skeletal muscles are the type of muscles that attach to bones.
- They are also called voluntary muscles because you can control them consciously.
- These muscles can contract quickly and powerfully, like when you run fast.
Cardiac Muscle
- The heart is made of cardiac muscle, which is found only in the heart.
- Cardiac muscle is an involuntary muscle, meaning you cannot control it consciously.
- When these muscles contract and relax, they pump blood through the heart and blood vessels throughout the body.
Smooth Muscle
- Smooth muscles line blood vessels and many organs like the stomach.
- They are involuntary muscles and are called “smooth” because of their smooth appearance.
What systems do plants have that give them structure?
Plants don’t have muscles or bones but use roots and stems for support and structure.
Roots
- Roots anchor plants in soil, to other plants, or objects like rocks, keeping them upright.
- Roots absorb water and nutrients from the soil.
- Taproots are large main roots with smaller roots branching off, like in carrots or radishes.
- Prop roots grow above ground to support plants, like in corn.
- Fibrous roots are many small, branching roots that spread out, like in grasses.
- Some roots store food, like sugar in sugar maple trees, which is used to make maple sap and syrup.
Stems
- Stems support branches and leaves and transport water, minerals, and food in the plant.
- Stems produce new cells for plant growth in certain areas.
- Woody stems are stiff and not green, found in trees and shrubs.
- Herbaceous stems are soft and green, found in plants like flowers or herbs.
- Some stems, like those in potatoes or irises, grow underground and are mistaken for roots.
A Bionic Arm
How It Works?
- Scientists have made bionic arms that look real but work with machines instead of muscles.
- Signals from the patient’s brain control the bionic arm.
Steps in Using a Bionic Arm:
- Doctors do surgery and attach nerves where the arm was damaged to the patient’s chest muscles.
- These nerves send signals from the brain to the chest muscles.
- When the patient’s brain sends signals to move the arm or hand, the signals travel from the brain to the chest muscles.
- Electronic sensors in the bionic arm’s harness detect the chest muscle movements.
- These sensors send signals to the bionic arm that match the movements.
- A computer processes the signals from the harness and moves the arm and hand.
- The movements of the bionic arm and hand are similar to those of a real arm.
|
124 docs|8 tests
|
FAQs on Structure and Support Chapter Notes - Science for Grade 6
| 1. What types of structures support different animals? |  |
| 2. How do muscles enable movement in animals? |  |
| 3. What systems do plants have that give them structure and support? |  |
| 4. What is the role of the skeleton in vertebrates? |  |
| 5. Why is it important for animals to have a support system? |  |