Symmetry Chapter Notes | Maths Olympiad Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Line of Symmetry |

|
| Creating Shapes with Line Symmetry |

|
| Rotational Symmetry |

|
| Key Words |

|
| Practice Questions |

|
Introduction
Symmetry is an important idea in geometry. It is found in nature and used in many fields like art, fashion, car design, and architecture. You can see symmetry in beehives, flowers, leaves, rugs, and even religious symbols.
A shape has line symmetry if it can be folded along a line so that both sides match perfectly. This is like a mirror reflection. 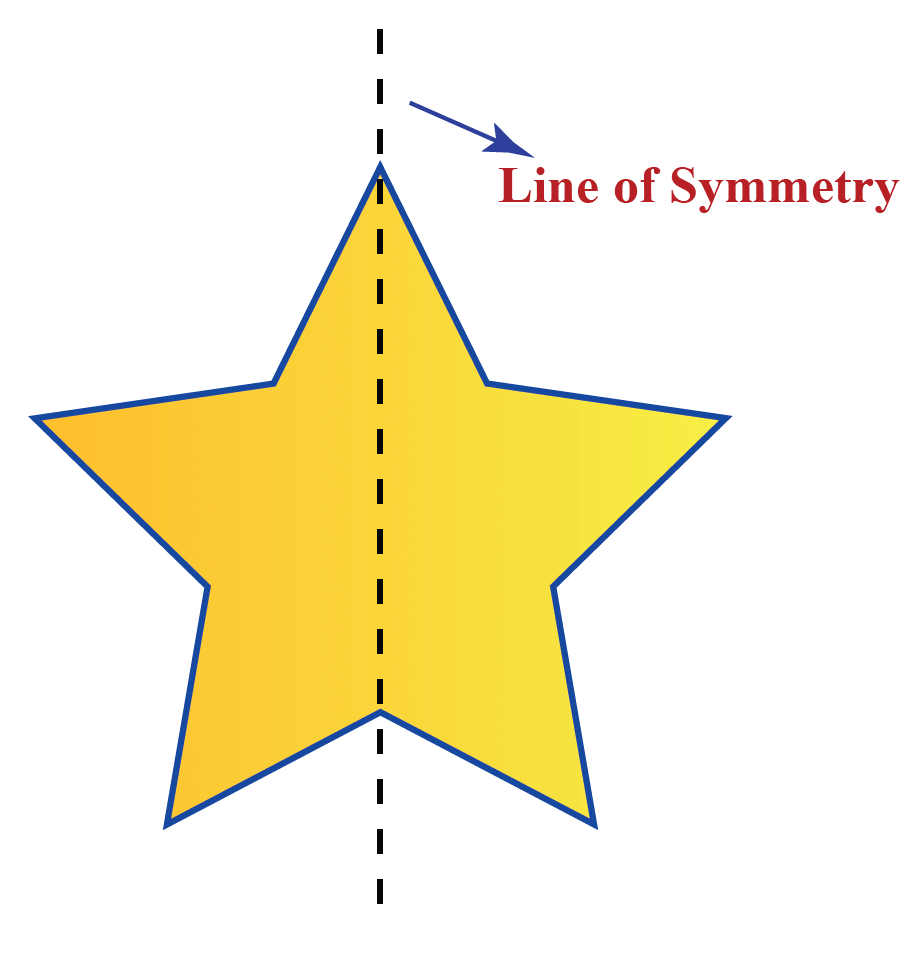
Symmetry is important because it is common in daily life and helps create beautiful designs.
Line of Symmetry
If you fold a shape and the two halves do not match, is it a line of symmetry?
No, it is not a line of symmetry.
When we fold a shape along a certain line and both halves match exactly, that line is called a line of symmetry.
For example, in a blue triangle, if we draw a dotted line down the middle and fold it, the two sides cover each other perfectly. This shows that the dotted line is a line of symmetry for the triangle.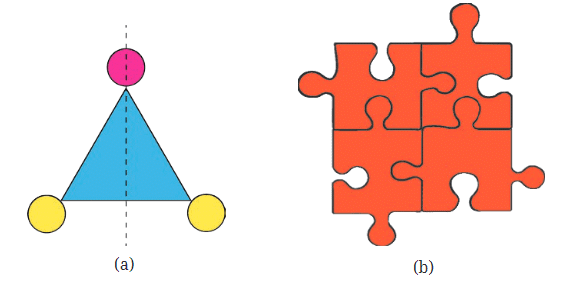
However, if we look at a shape like four puzzle pieces with a dotted line through the middle, folding it would not make the two sides match perfectly. This means that the line is not a line of symmetry for that shape.
Figures with more than one line of symmetry
Some shapes have multiple lines of symmetry:
- A square has four lines of symmetry.
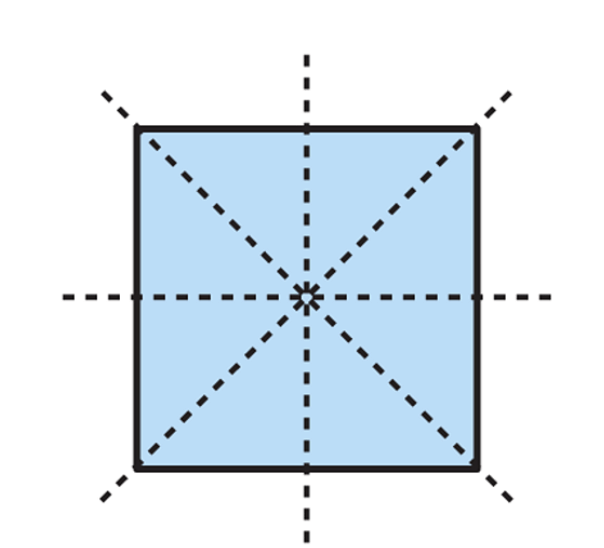
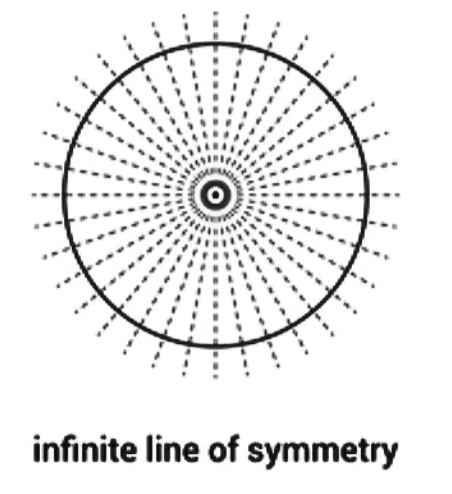
- A circle has infinite lines of symmetry.
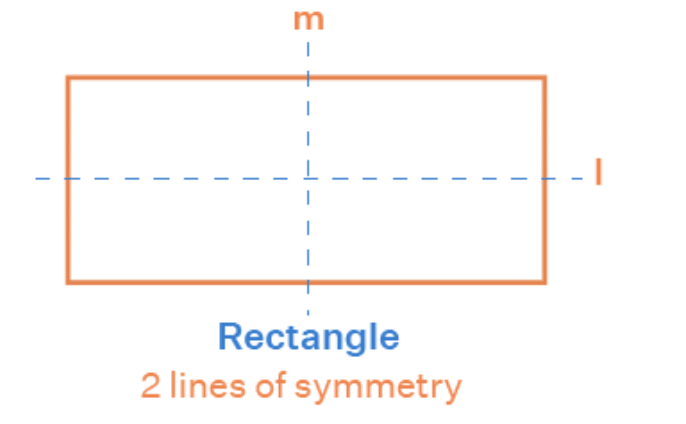
- A rectangle has two lines of symmetry (one vertical and one horizontal).
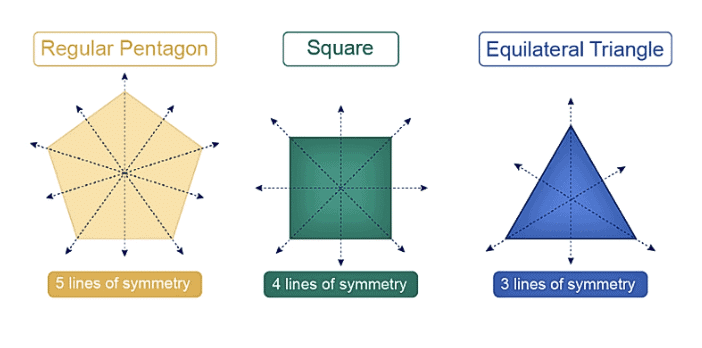
- A regular polygon has as many lines of symmetry as it has sides.A shape has line symmetry when one half is a mirror image of the other.
Reflection
When a shape has a line of symmetry, one part of the shape is a mirror image of the other. This is called reflection symmetry. It’s like looking at yourself in a mirror—what you see is a reflection of your real self.
Example: Butterfly: Its left wing is a mirror image of its right wing.
Creating Shapes with Line Symmetry
Creating symmetrical shapes is a fun and creative way to explore the concept of symmetry. There are several methods to generate such shapes, and two popular techniques are using ink blots and paper folding and cutting. Let's explore how these methods work.
1. Ink Blot Devils: This is a simple and exciting method to create symmetrical shapes using ink or paint.
Steps:
- Fold a Paper: Take a clean sheet of paper and fold it in half.

- Apply Ink or Paint: Open the paper and put a few drops of ink or paint on one half of the paper.
- Press and Open: Fold the paper back and press it so that the ink spreads. Then, carefully open the paper to reveal the design.
2. Paper Folding and Cutting: Another way to create symmetrical designs is by folding and cutting paper. This technique can produce intricate and beautiful patterns.
Steps:
- Fold the Paper: Take a sheet of paper and fold it along the dotted line (this line can be any straight line across the paper).
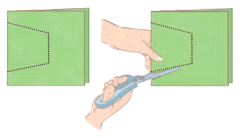
- Cut Along the Fold: While the paper is folded, cut along the dotted line as shown in the figure.
- Unfold to Reveal: After cutting, carefully unfold the paper to reveal the pattern.
Rotational Symmetry
Some shapes look the same even after being rotated (turned around a point). This is called rotational symmetry.
Rotation may be clockwise or anti-clockwise.
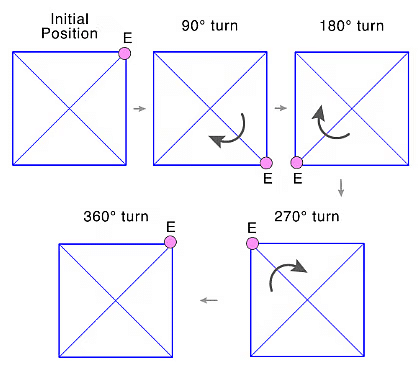
- A full turn refers to a rotation of 360o.
- A half turn refers to a rotation of 180o.
- A quarter turn refers to a rotation of 90o.
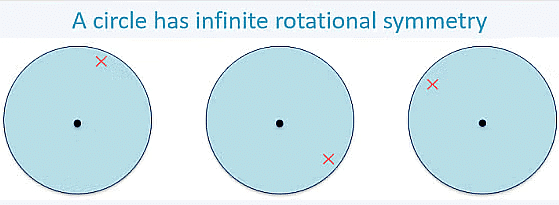
Does a circle have rotational symmetry?
Yes, a circle has infinite rotational symmetry because it looks the same at any angle.
When identifying rotational symmetry, consider:
(i) Center of rotation: During the rotation, the object rotates around a fixed point. Its shape and size do not change. This fixed point is called the centre of rotation.
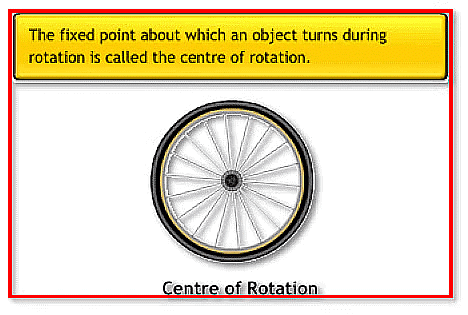
(ii) Angle of rotation: It is the angle at which a shape or an object looks exactly the same during rotation.
(iii) Direction of rotation: The direction of rotation is also referred to as the sense of rotation and indicates the direction (clockwise or anti-clockwise) in which bodies rotate around an axis.
(iv) Order of rotational symmetry: It can be defined as the number of times that a shape appears exactly the same during a full 360o rotation.
Examples:
- The paper windmill in the picture has rotational symmetry because it looks the same when rotated by 90 degrees (a quarter turn) around the red point at its center.

- Angles of symmetry for the windmill are 90 degrees, 180 degrees, 270 degrees, and 360 degrees. When rotated by 360 degrees, any figure returns to its original position, making it a universal angle of symmetry.
- Other shapes, like a square, also have multiple angles of symmetry. A square overlaps with itself after rotating 90 degrees.

- For example, when rotating a strip shape, it does not return to its original position until a full 360-degree rotation, indicating it lacks rotational symmetry.
- Shapes like the windmill and square help us understand how rotational symmetry works with different angles and fixed points.
For Example:
The Ashok Chakra in the Indian national flag has both, line symmetry and rotational symmetry.
Ashok Chakra
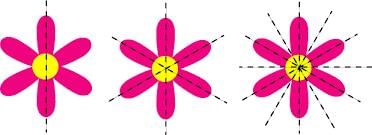
Rotational Symmetry of Figures with Radial Arms
When a shape has radial arms (like the blades of a fan), it can have rotational symmetry. The number of arms often tells us how many times the shape looks the same during one full rotation.
Example: Fan with four blades: It has four angles of symmetry—90°, 180°, 270°, and 360°.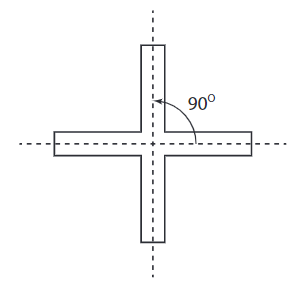
- The figure with 4 radial arms has 4 angles of symmetry. The angles of symmetry are at 90° intervals around the center.
- If you change the angles between the radial arms, you can still have 4 angles of symmetry as long as the total of the angles is 360° and they are evenly spaced.
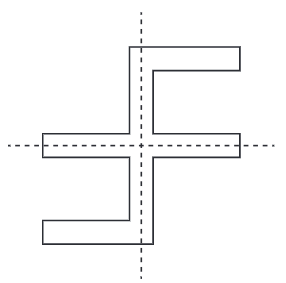
- To create a figure with only 2 angles of symmetry, you can modify the angles between the radial arms so that they are not evenly spaced. For example, having one angle much larger than the others can achieve this.
- With 3 radial arms, the figure has rotational symmetry only with a full rotation of 360°. To have 3 angles of symmetry, the angles between the radial arms must be equal, specifically 120° each.
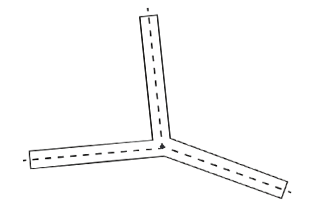
- To achieve this, the angles between the dotted lines must be 120° each, which allows the figure to overlap with its rotated versions.
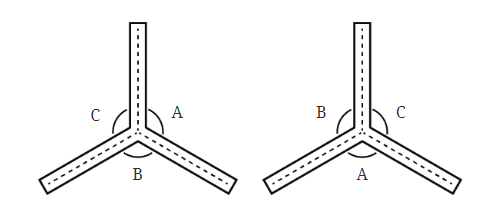
- The figure with 3 arms will have the following angles of rotation: 120°, 240°, 360°
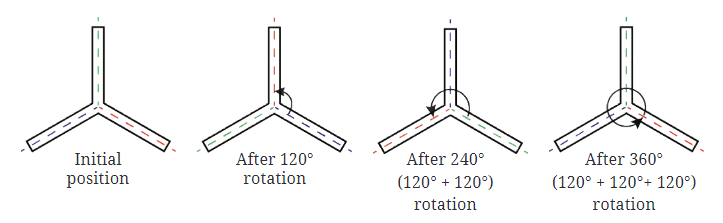
- These angles correspond to rotating the figure by 120° or 240°, and the full rotation of 360° brings it back to the original position.
Symmetries of a Circle
A circle is a special shape because it has infinite lines of symmetry. Specifically, every line that goes through the centre (every diameter) creates a line of reflectional symmetry. The circle is the most perfect symmetrical shape because it can be rotated around its centre by any angle, and it also has an unlimited number of lines of symmetry. If you look at any circular pattern, you'll see that every line through the centre acts as a line of reflectional symmetry, and it maintains its shape when rotated around the centre at any angle.
Example: Wheel: No matter how you turn it, it always looks the same.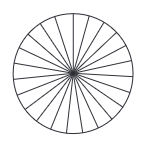
Key Words
- Symmetry: A shape has symmetry if parts of it repeat in a clear pattern.
- Line of Symmetry: A line that divides a shape into matching parts.
- Reflection Symmetry: One part of the shape looks like a mirror image of the other, especially in circles where each diameter serves as a line of symmetry.
- Rotational Symmetry: A shape appears unchanged after being turned a certain amount; for a circle, this symmetry exists around its centre for every angle.
- Circle Symmetry: A circle has infinite lines of symmetry and can be rotated by any angle without altering its appearance.
Practice Questions
1. Identify the Lines of Symmetry
Look at the following shapes:
(a)A square
(b)A rectangle
(c)A triangle Which shape has four lines of symmetry? Which shape has only one line of symmetry?
Which shape has four lines of symmetry? Which shape has only one line of symmetry?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer:
- A square has four lines of symmetry.
- A triangle (if it is an isosceles or equilateral triangle) has one line of symmetry.
2. True or False: Symmetry in Shapes
State whether the following statements are True or False:
(a) A rectangle has four lines of symmetry.
(b) A circle has infinite lines of symmetry.
(c) A rhombus has two lines of symmetry.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer:
a) False (A rectangle has only two lines of symmetry: one vertical and one horizontal.)b) True (A circle has infinite lines of symmetry.)
c) True (A rhombus has two lines of symmetry, along its diagonals.)
3. Folding Test for Line of Symmetry
Rohan folds a butterfly drawing exactly in half along a straight line. Both halves match perfectly. What does this tell us about the butterfly’s symmetry?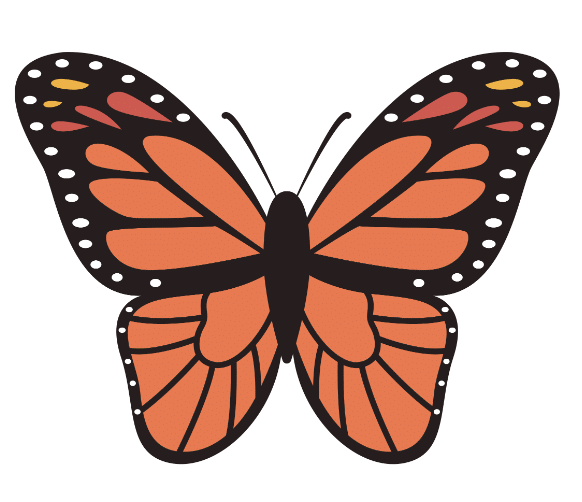
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer:
Since both halves of the butterfly match perfectly, the folding line is a line of symmetry. This means the butterfly has reflection symmetry.
4. Rotational Symmetry in Objects
Which of the following objects has rotational symmetry?
(a) A square
(b) A scalene triangle
(c) A windmill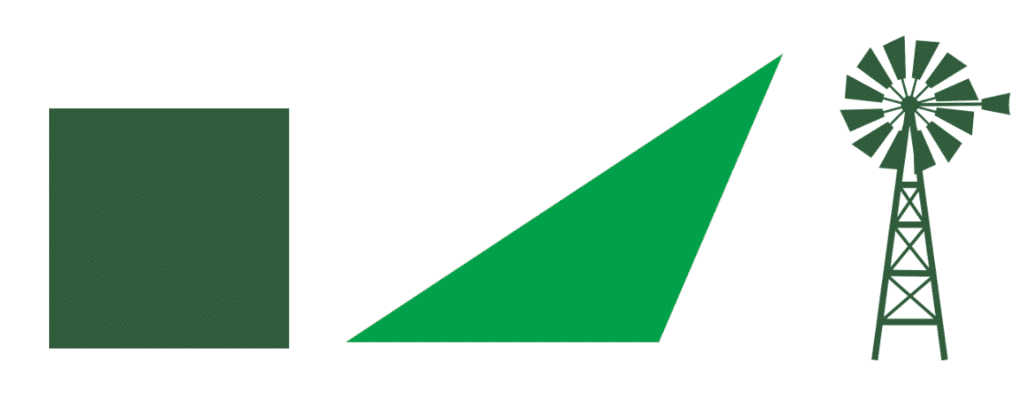
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer:
- A square has rotational symmetry at 90°, 180°, 270°, and 360°.
- A scalene triangle does not have rotational symmetry.
- A windmill has rotational symmetry because it looks the same when rotated at certain angles (like 90° or 180°).
5. Symmetry in Nature
Give two examples of natural objects that have symmetry and explain why.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer:
- Flowers – Many flowers have symmetrical petals arranged around the center, creating radial symmetry.
- Leaves – Some leaves have a central vein acting as a line of symmetry, making both halves look identical.
6. Rotational Symmetry of a Fan
A fan has four blades. How many angles of symmetry does it have?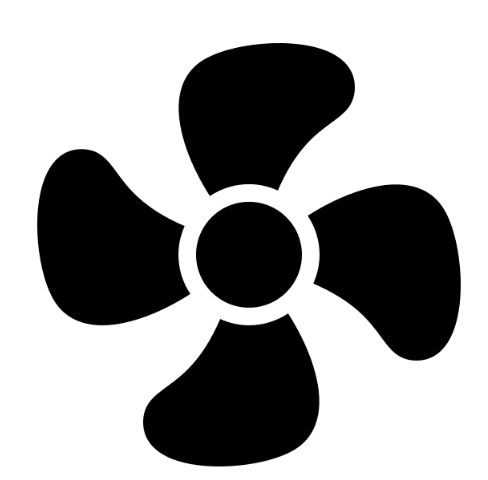
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer:
A fan with four blades has rotational symmetry at 90°, 180°, 270°, and 360°. It looks the same when rotated by these angles.
|
31 videos|122 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Symmetry Chapter Notes - Maths Olympiad Class 6
| 1. What is a line of symmetry? |  |
| 2. How can I create shapes with line symmetry? |  |
| 3. What is rotational symmetry? |  |
| 4. How do I perform the folding test for line symmetry? |  |
| 5. Can all objects have rotational symmetry? |  |