The Brain Chapter Notes | AP Psychology - Grade 11 PDF Download
Introduction
The Brain
- Brain acts as body’s command center.
- Contains specialized parts for different functions.
- Brainstem manages vital functions like breathing.
- Cerebral cortex handles advanced thinking and processing.
- Scientists use tools like fMRI and EEG to study brain activity.
- Split-brain studies show how brain adapts and processes information.
- Brain plasticity allows learning and recovery from injury.
Quick Cram Review
Different brain structures control behavior and thinking.
- Frontal Lobe: Governs decision-making, problem-solving, and voluntary movements.
- Parietal Lobe: Processes touch, spatial orientation, and body awareness.
- Occipital Lobe: Handles visual processing, including color, shape, and motion.
- Temporal Lobe: Manages auditory input, memory, and emotional responses.
- Limbic System: Regulates emotions and motivation.
- Brainstem: Controls essential survival functions like breathing and heart rate.
Neuroanatomy
Brain Structures and Functions
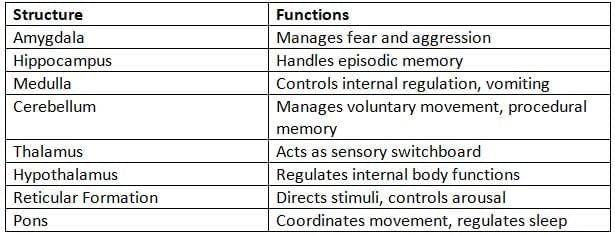
Brain structures and functions
Brain stem functions
The brainstem, linking the brain to the spinal cord, is critical for maintaining life-sustaining functions and regulating consciousness.
- Manages vital processes like heart rate, breathing, and blood pressure.
- Controls sleep-wake cycles and arousal levels.
- Relays sensory and motor signals between the brain and body.
- Includes the medulla oblongata, pons, and midbrain .
Reticular Activating System (RAS) functions
The RAS, a network within the brainstem, filters sensory information and regulates attention and alertness.
- Modulates arousal, focus, and consciousness.
- Directs attention to relevant stimuli while filtering out distractions.
- Contributes to motivation, emotion, and learning processes like habituation.
- Damage may result in coma or impaired consciousness.
The RAS enables us to stay alert, focus on priorities, and learn effectively by managing attention.
Cerebellum functions
Located at the brain’s rear, the cerebellum ensures smooth movement, balance, and contributes to cognitive tasks.
- Coordinates precise movements and maintains balance.
- Supports motor learning and procedural memory formation.
- Processes sensory data related to body position.
- May influence certain cognitive functions.
Cerebral Cortex Structure
- Cerebral cortex is brain’s most advanced part.
- Handles complex mental abilities.
- Consists of two hemispheres connected by corpus callosum.
- Each hemisphere specializes in different tasks.
- Right hemisphere:
- Processes spatial information.
- Handles nonverbal communication.
- Takes big-picture approach.
- Left hemisphere:
- Manages language processing.
- Handles logical operations.
- Divided into four lobes and limbic system.
- Lobes: Frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital.
- Limbic system: Manages emotion and memory.
Lobes
Occipital Lobe
Located at the back of the brain, the occipital lobe is dedicated to vision .
- Interprets visual input, including color, shape, and motion.
- Damage may lead to blindness, visual agnosia, or hallucinations.
Temporal Lobe
The temporal lobe, found on the brain’s sides, processes auditory information and supports memory and emotion .
- Handles auditory processing and language comprehension (Wernicke’s area).
- Forms and retrieves memories (hippocampus).
- Regulates emotions and social perception (amygdala).
- Damage can impair hearing, language, or personality.
Parietal Lobe
The parietal lobe integrates sensory data and supports spatial awareness .
- Processes touch, pressure, temperature, and pain.
- Coordinates sensory input with motor responses.
- Facilitates spatial navigation and body awareness.
Frontal Lobe
The frontal lobe drives higher-order thinking, movement, and personality .
- Manages planning, decision-making, and problem-solving.
- Controls voluntary movements (motor cortex).
- Regulates emotions and social behavior.
- Supports language production (Broca’s area).
Split-Brain Research
Split-brain studies, originally conducted to treat epilepsy, reveal how the brain’s hemispheres function independently and collaboratively.
- Highlights specialized roles of the left and right hemispheres.
- Demonstrates isolated information processing.
- Shows the brain’s adaptability.
Language Areas in Brain
- Language processing uses specialized brain regions.
- Most language functions are in the left hemisphere.
- Broca’s area (left frontal lobe):
- Controls speech production.
- Damage causes difficulty producing speech.
- Wernicke’s area (left temporal lobe):
- Manages language comprehension.
- Damage leads to trouble understanding language.
Cortical Specialization Testing
- Studies how different brain regions process information.
- Uses split-brain patients to examine hemispheres separately.
- Methods include presenting stimuli to specific visual fields.
- Examines contralateral organization of pathways.
- Reveals:
- Differences in perception between hemispheres.
- Specialized cognitive processing.
- Motor pathway organization.
Brain Plasticity Concept
The brain’s plasticity allows it to adapt and reorganize throughout life, supporting learning and recovery.
- Forms new neural connections.
- Strengthens or weakens existing pathways.
- Most active during development but persists lifelong.
- Enables recovery from injury.
Brain Research Methods
Neuroscience uses advanced tools to explore brain function and structure.
Methods include:
- EEG: Tracks electrical activity.
- fMRI: Monitors blood flow changes.
- PET Scans: Visualizes metabolism and neurotransmitters.
- Lesion Studies: Examine effects of brain damage.
- TMS: Temporarily disrupts brain activity.
- Optogenetics: Precisely controls neural activity.
|
35 docs
|
FAQs on The Brain Chapter Notes - AP Psychology - Grade 11
| 1. What is the role of the brainstem in survival? |  |
| 2. How does the Reticular Activating System (RAS) influence consciousness? |  |
| 3. What functions does the cerebellum perform beyond movement? |  |
| 4. How do the different lobes of the cerebral cortex contribute to various cognitive functions? |  |
| 5. What insights have split-brain research provided about brain lateralization? |  |















