The Dairy Farm Chapter Notes | Mathematics (Maths Mela) Class 5 - New NCERT PDF Download
Introduction
This chapter will help you learn and understand multiplication in many different ways. There are stories, examples, and many ways to multiply numbers which will make your calculations easier and faster. You will see how multiplication helps in our daily life, especially on a dairy farm!
Multiplication is a method of adding the same number over and over again. It helps us find out how much we have in total when we have many groups of the same size.
What is Multiplication?
Suppose you have 3 bags, and each bag has 4 apples. If you want to know how many apples you have in total, you can add:
4 + 4 + 4 = 12
But instead of adding many times, we can use multiplication:
3 bags × 4 apples in each bag = 12 apples
So, multiplication makes our work much quicker and easier!
The Parts of Multiplication
The number of groups: 3 bags
The number in each group: 4 apples
The answer (total): 12 apples
We write it as:
3 × 4 = 12
'×' means 'times' or 'groups of'
Order of Numbers in Multiplication
Daljeet Kaur arranges butter packets different ways:
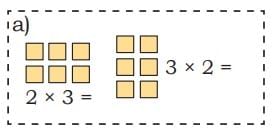
What pattern do you notice?
- 3 × 2 = 6
- 2 × 3 = 6
Pattern: Changing the order of numbers does not change the answer.
This is called the commutative property.
Examples:
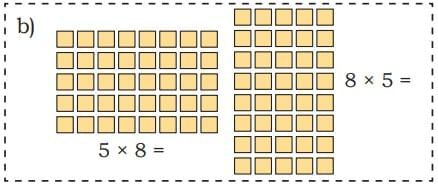
| Multiplication | Answer |
|---|---|
| 5 × 8 | 40 |
| 8 × 5 | 40 |
| 6 × 13 | 78 |
| 13 × 6 | 78 |
Notice: You can multiply numbers in any order; product remains the same!
Patterns in Multiplication by 10s and 100s
When you multiply by 10:
The number becomes 10 times larger.
Each digit moves one place to the left (increases place value).
Examples:
4 × 10 = 40
20 × 10 = 200
100 × 90 = 9,000
When you multiply by 100:
The number becomes 100 times larger.
Each digit moves two places left.
Many Ways to Multiply
Let’s see the number 18 × 5. Here are some ways students multiply:
Rahul’s Way:
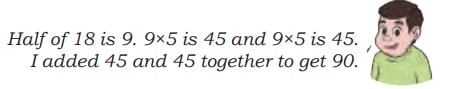
Half of 18 is 9. 9 × 5 = 45. Add two times (45 + 45 = 90).
Kanti’s Way:
 Double 18 to get 36. Double 36 to get 72. Add 18 (72 + 18 = 90).
Double 18 to get 36. Double 36 to get 72. Add 18 (72 + 18 = 90).
Sahil’s Way:
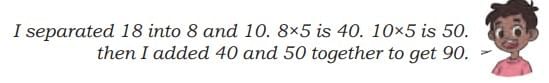
Break 18 into 10 + 8. 10 × 5 = 50; 8 × 5 = 40 (50 + 40 = 90).
Using Nearest Multiple:
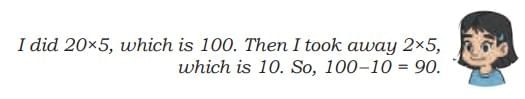
Think 20 × 5 = 100, then subtract 2 × 5 =10, so 100-10=90.
Therefore, All ways are correct! Multiplication can be done in many ways to make calculation easier.
Doubling and Halving
Butter packets are arranged in the following ways. Let us find some strategies to calculate the total number of packets.
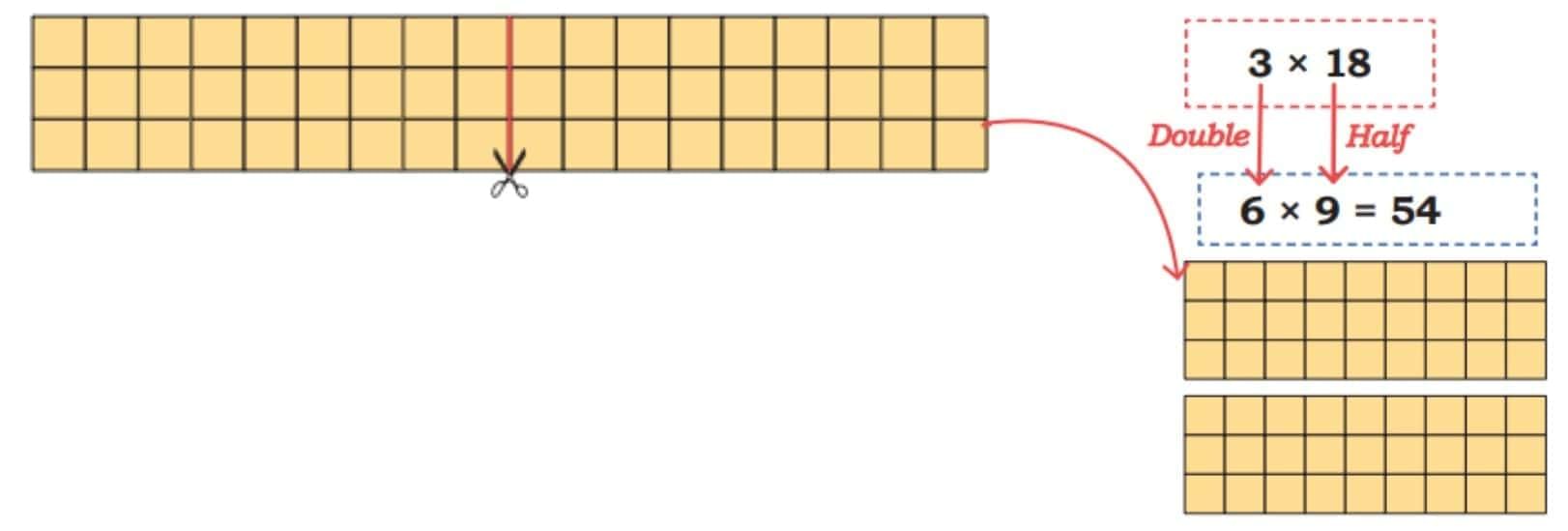
Key Trick:
Halving one number and doubling the other does not change the product.
This method is extremely useful when multiplying with numbers like 4, 8, 5, 25, or 50.
Nearest Multiple
When a number is close to a multiple that is easy to multiply with, use that:
Example:
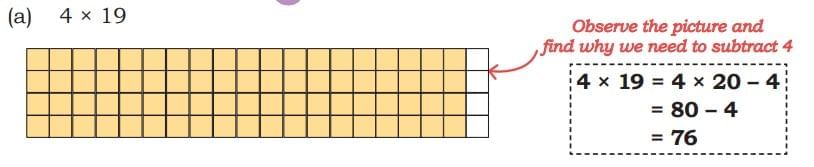
Here, 20 is close to 19, and multiplying with 20 is alot easier, so we multiply 4 x 20 instead of 4 x 19, because multiplying with 19 is very hard. Now, see the figure, when we multiply 4 with 20, we actually added 1 more column of 4 squares. So, we get extra 4 squares, we need to subtract these squares after multiplying 4 x 20 to get the result of 4 x 19.
This method is useful if one of the numbers is close to a multiple of 10, like 19, 99, etc.
Waste and Composting
A family makes 35kg waste in one month. How much waste will the family produce in a year?
Quantity of kitchen waste in 1 month is 35 kg.
Quantity of kitchen waste in 12 months is 12 × 35 kg
Lets calculate this number
Different Ways to Multiply:
1. Nida's solution
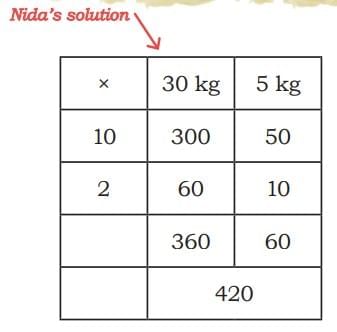
Lets understand what Nida did:
Nida split the numbers in 2 parts: 35 = 30 + 5, 12 = 10 + 2 and then she multiplied these numbers.
This method splits the numbers into parts, multiplies each pair, and then adds everything together. It's based on the distributive property:
Lets see how it works
= (10×30)+(10×5)+(2×30)+(2×5)
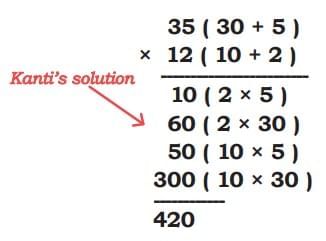
Lets understand what Kanti did:
10. Multiplication Using Place Value
When we multiply large numbers, we break them into parts using their place value.
Example:
574 × 125
574 × 100
574 × 20
574 × 5
Add up the answers.
This is called the expanded form method, or Mili’s father’s method.
11. Practice Problems
You get to practice multiplying using different methods:
Using breaking into parts (expanded form method)
Using doubling and halving
Using nearest multiple
Changing the order of numbers
Example Problems:
Multiply: 78 × 4, 83 × 9, 86 × 3, 94 × 5, etc.
Solve word problems based on multiplication
12. Dairy Cooperative Examples
How Many Cows?
If 1 villager has 4 cows, and there are 268 villagers:
Total cows = 268 × 4 = 1,072
How Much Milk?
453 Gir cows, each cows gives 13 litres:
Total milk = 453 × 13 = 5,889 litres
How Much Ghee Sold?
1kg ghee = ₹574
125kg produced = 574 × 125 = ₹71,750
13. Patterns in Multiplication
Multiplying by 10s and 100s adds 0s or two 0s to the product.
Multiplying in any order gives the same product (commutative).
Multiplying in parts, you can break any big number to smaller parts, multiply, and add.
14. The King’s Reward Story
3 ministers get different numbers of coins with different rules.
You must multiply and see which gives the most coins.
(Double, triple, or five times every day for 7 days)
Moral:
Multiplication grows very fast when we multiply every day!
15. Multiplication Patterns and Tricks
Look at how numbers and products change in patterns.
E.g., 11 × 11 = 121, 111 × 111 = 12,321
You can predict the next numbers using observed patterns.
16. Practice Section
Match multiplication problems to their answers
Find different ways to solve a multiplication
Some numbers are easier to multiply if broken down cleverly
|
36 videos|276 docs|7 tests
|
FAQs on The Dairy Farm Chapter Notes - Mathematics (Maths Mela) Class 5 - New NCERT
| 1. What is the order of numbers in multiplication, and why is it important? |  |
| 2. How do patterns in multiplication by 10s and 100s help in calculations? |  |
| 3. What are some different methods to multiply numbers? |  |
| 4. How does doubling and halving relate to multiplication? |  |
| 5. What is meant by "nearest multiple" in multiplication? |  |
















