Class 6 Geography Chapter 1 Notes - The Earth in the Solar System
| Table of contents |

|
| Our Wonderful Earth |

|
| The Solar System |

|
| Important Definitions |

|
| Frequently Asked Questions |

|
Our Wonderful Earth
Twinkling of stars, Poornima & Amavasya, Constellations, and many amazing phenomena happen very frequently on our planet earth making it awesome and wonderful!
 Planet Earth
Planet Earth
Let's have a look at different amazing phenomena:
- Twinkling of Stars: If we look at the sky in the night it seems to be filled with tiny shining objects-some are bright, others are dim. They seem to be twinkling.
- Poornima & Amavasya: We can see the full moon only once in about a month’s time. It is called Full moon night or Poornima. A fortnight later, you cannot see it at all, that is called a New moon night or Amavasya. On this day, you can watch the night sky best, provided it is a clear night.
 Picture of Full Moon on Left & No Moon on Right
Picture of Full Moon on Left & No Moon on Right - Celestial Bodies: The sun, the moon, and all those objects shining in the night sky are called Celestial bodies. Some celestial bodies are very big and hot. They are made up of gases. They have their own heat and light, which they emit in large amounts. These celestial bodies are called stars. The sun is also a star
- Constellations: While watching the night sky, we notice various patterns formed by different groups of stars. These are called Constellations. Ursa Major or Big Bear is one such constellation.
 Saptarishi & North Star
Saptarishi & North Star - Saptarishi: One of the most easily recognizable constellations is the Saptarishi (Sapta - seven, rishi-sages). It is a group of seven stars that forms a part of Ursa Major Constellation.
- In ancient times, people used to determine directions during the night with the help of stars.
- Pole Star: The North star indicates the north direction. It is also called Pole Star. It always remains in the same position in the Sky.
- We can locate the position of the Pole Star with the help of the Saptarishi.
- Some celestial bodies do not have their own heat and light. They are lit by the light of the stars. Such bodies are called planets.
- The word ‘planet’ comes from the Greek word “Planetai” which means ‘wanderers’.
- The earth on which we live is a planet. It gets all its heat and light from the sun, which is our nearest star
- The moon that we see in the sky is a satellite. It is a companion of our earth and moves around it. Like our earth, there are seven other planets that get heat and light from the sun. Some of them have their moons too.
The Solar System
The sun, eight planets, satellites, and some other celestial bodies known as asteroids and meteoroids form the solar system.
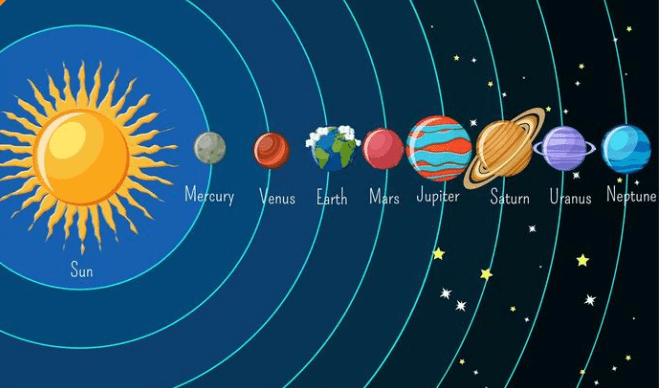 Solar System
Solar System
The Sun
‘Sol’ in Roman mythology is the ‘Sun god’. ‘Solar’ means ‘related to the sun’. The family of the sun is, therefore, called the solar system.
- The sun is the center of the solar system.
- It is huge and made up of extremely hot gases.
- The sun is the ultimate source of heat and light for the solar system.
- It provides the pulling force that binds the solar system.
- The sun is the ultimate source of heat and light for the solar system. But that tremendous heat is not felt so much by us because despite being our nearest star, it is far away from us.
- The sun is about 150 million km away from the earth.
Planets
There are eight planets in our solar system. In order of their distance from the Sun-Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. 
- All the eight planets of the solar system move around the sun in fixed paths. These paths are elongated. They are called orbits.
- Mercury is nearest to the sun. It takes only about 88 days to complete one round along its orbit.
- Venus is considered as ‘Earth’s-twin’ because its size and shape are very much similar to that of the earth.
- Till recently (August 2006), Pluto was also considered a planet. However, in a meeting of the International Astronomical Union, a decision was taken that Pluto-like other celestial objects (Ceres, 2003 UB313) discovered in the recent past may be called ‘dwarf planets.
The Earth
The Earth is the third nearest planet to the sun and is our home.
- It is the fifth-largest planet.
- It is slightly flattened at the poles. That is why its shape is called Geoid.
- Geoid means an earth-like shape.
- Conditions favorable to support life are probably found only on the earth.
- The earth is neither too hot nor too cold.
- It has water and air, which are very essential for our survival.
- The air has life-supporting gases like oxygen. Because of these reasons, the earth is a unique planet in the solar system.
- From outer space, the earth appears blue because its two-thirds s surface is covered by water. It is, therefore, called a blue planet.
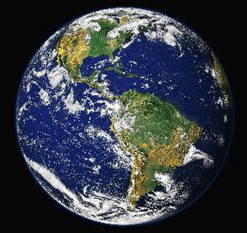 Earth
Earth
The Moon

- Our earth has only one natural satellite that is the moon.
- Its diameter is only one-quarter that of the earth.
- It appears so big because it is nearer to our planet than other celestial bodies. It is about 3,84,400 km away from us.
- The moon moves around the earth in about 27 days.
- It takes exactly the same time to complete one spin. As a result, only one side of the moon is visible to us on the earth.
- The moon does not have conditions favorable for life. It has mountains, plains, and depressions on its surface. These cast shadows on the moon’s surface
Asteroids
- Apart from the stars, planets, and satellites, there are numerous tiny bodies that also move around the sun. These bodies are called Asteroids.
- They are found between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.
 Asteroid Belt
Asteroid Belt - Scientists are of the view that asteroids are parts of a planet that exploded many years back.
Meteoroids
- The small pieces of rocks which move around the sun are called meteoroids.
 Meteoroids
Meteoroids
- Sometimes these meteoroids come near the earth and tend to drop upon it.
- During this process due to friction with the air, they get heated up and burn. It causes a flash of light.
- Sometimes, a meteor without being completely burnt falls on the earth and creates a hollow.
- They’re all related to the flashes of light called “shooting stars” sometimes seen streaking across the sky. But we call the same object by different names, depending on where it is.
- Meteoroids are objects in space that range in size from dust grains to small asteroids. Think of them as “space rocks."
- When meteoroids enter Earth’s atmosphere (or that of another planet, like Mars) at high speed and burn up, the fireballs or “shooting stars” are called meteors.
- When a meteoroid survives a trip through the atmosphere and hits the ground, it’s called a meteorite
The Milky Way Galaxy is a whitish broad band, like a white glowing path across the sky. It is a cluster of millions of stars.
Milky Way Galaxy
Our solar system is a part of this galaxy.
It was named Akash Ganga, as it was imagined to be a river of light flowing in the sky.
There are millions of such galaxies that make the Universe
Important Definitions
1. Celestial Body - An object in the universe (but not on the earth) is said to be a celestial body. Examples are sun, earth, moon, stars, etc.
2. Orbit - The particular and definite elliptical path in which a planet (or satellite) always remains, is called the orbit of that planet (or satellite).
3. Full Moon Night - A night when the moon is visible from the earth as a full sphere is called the Full Moon night, and it occurs once a month.
4. New Moon Night - The fifteenth night after the Full Moon night, when the moon is not visible at all in the sky, is called the New Moon night.
5. Constellation - A group of several stars which can usually be recognized by a definite pattern is called a constellation. An example is Ursa Major.
6. Planets - A celestial body that revolves around a particular star in an orbit, and gets all its light from that star, is called a planet. Earth is a planet.
7. Satellites - A celestial body that revolves around a planet in a particular orbit is called a satellite. The moon is a satellite of the Earth.
8. Sun - The Sun is a star that acts as the “head” of the solar system and around which all planets revolve: Note that the sun is not at the center of the orbit, instead it is like in the figure above.
9. Inner Planets - The Inner Planets are the planets that orbit around the sun between the sun and the asteroid belt, that is, are close to the sun. These are Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars.
10. Outer Planets - The Outer Planets are the planets that orbit the sun beyond the asteroid belt, that is, are very far away from the sun. These are Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
11. Geoid - The shape of the earth is called a geoid. A geoid is spherical except for the flattening at two places diametrically opposite to each other.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q.1. What is the Pole Star? How can the Saptarishi be used to locate it?
Ans: The Pole Star is the star that is known to retain its position in the sky always. We can locate the position of the Pole Star with the help of the constellation Saptarishi. If an imaginary line is drawn joining the "pointer stars" of the Saptarishi and extended further, it will point to the Pole Star.
In Fig. Shown here, 1 and 2 represent the "pointer stars". The Pole Star and the pointer stars lie on the same line.
Q.2. State some characteristics of stars.
Ans:
- Stars are very big and hot bodies.
- They are made up of various gases.
- They emit a large amount of heat and light.
- There are numerous stars.
- They are so far away from us that we cannot see them with our naked eyes.
Q.3. Name the largest and the smallest planets. Which planets are bigger and which are smaller than the Earth?
Ans:
- The largest and the smallest planets. Jupiter is the largest and Mercury is the smallest of all the planets.
- Planets bigger than the Earth. (i) Neptune (ii) Uranus (iii) Saturn and (!u) Jupiter are bigger planets than the Earth.
- Planets Smaller than the Earth. (i) Venus, (ii) Mars, and Mercury are smaller planets than the Earth.
FAQs on Class 6 Geography Chapter 1 Notes - The Earth in the Solar System
| 1. What is the Solar System? |  |
| 2. What is the importance of the Solar System? |  |
| 3. What is the Earth's position in the Solar System? |  |
| 4. What are some important definitions related to the Solar System? |  |
| 5. What are some interesting facts about the Earth in the Solar System? |  |
















