Grade 6 Exam > Grade 6 Notes > Social Studies for Grade 6 > Chapter Notes: The Middle East: Society and Environment
The Middle East: Society and Environment Chapter Notes | Social Studies for Grade 6 PDF Download
Introduction
The Middle East is a fascinating region where ancient history meets modern life. It is a place with diverse cultures, languages, and traditions. The region includes many countries, deserts, mountains, and rivers, making its environment unique. In this chapter, we will learn about the people, their way of life, and the natural surroundings of the Middle East. This region has been important for thousands of years because of its location, connecting Asia, Africa, and Europe.
Region Profile: The Middle East
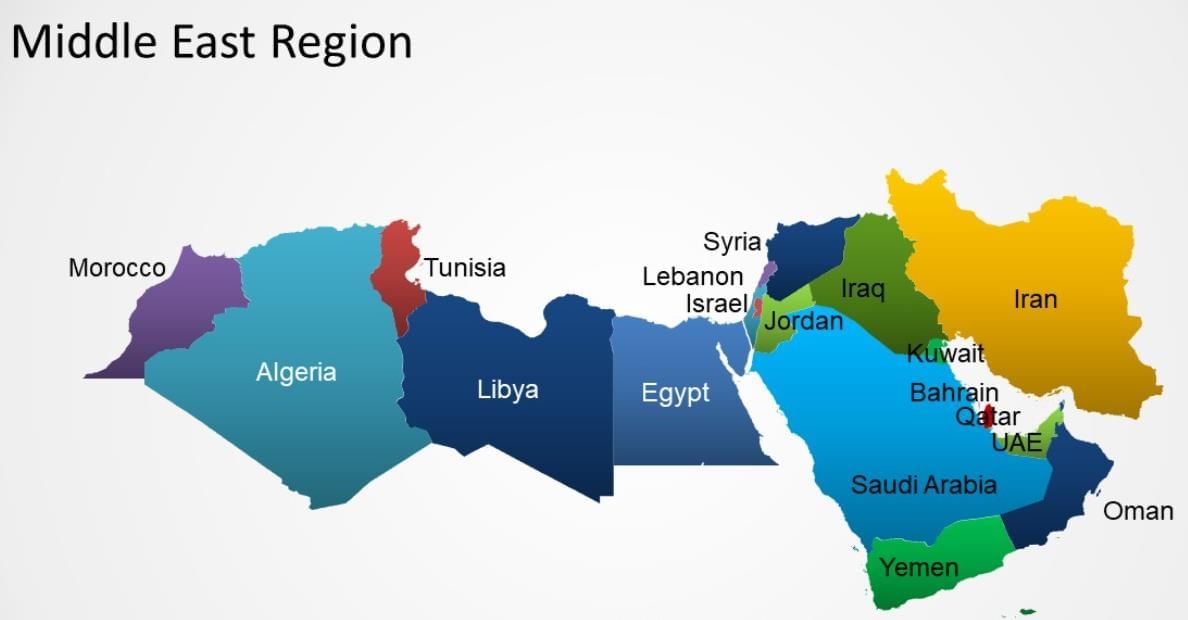
- Location and Countries:
- The Middle East is located at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe.
- It includes countries like Saudi Arabia, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Syria, Turkey, Egypt, and others.
- Some countries are on the Arabian Peninsula, like Yemen, Oman, and the United Arab Emirates.
- The region is near important bodies of water, such as the Persian Gulf, Red Sea, and Mediterranean Sea.
- Geography and Landforms:
- The Middle East has varied landscapes, including deserts, mountains, and rivers.
- The Arabian Desert is one of the largest deserts in the world, covering much of the Arabian Peninsula.
- The Zagros Mountains in Iran and the Taurus Mountains in Turkey are important mountain ranges.
- Rivers like the Tigris and Euphrates in Iraq support farming and are known as the "Cradle of Civilization."
- The Dead Sea, located between Israel and Jordan, is the lowest point on Earth’s surface.
- Climate:
- Most of the Middle East has a hot and dry climate, with deserts covering large areas.
- Summers are very hot, with temperatures often above 100°F (38°C).
- Winters can be cooler, especially in mountainous areas, but are usually mild in most places.
- Some areas near the Mediterranean Sea have a milder climate with wet winters and dry summers.
- Rain is scarce in many parts, making water a valuable resource.
- Natural Resources:
- The Middle East is rich in oil and natural gas, especially in countries like Saudi Arabia, Iran, and Iraq.
- Oil is a major resource that helps the economies of many Middle Eastern countries.
- Other resources include minerals like phosphate and dates, which are grown in desert oases.
- Water is limited, so many countries use advanced methods like desalination to get fresh water.
- People and Culture:
- The Middle East is home to many ethnic groups, including Arabs, Persians, Turks, and Kurds.
- Islam is the main religion, but there are also Christians, Jews, and other religious groups.
- Arabic is the most common language, but Persian, Turkish, and Hebrew are also spoken.
- People celebrate traditions like Ramadan, a Muslim holy month, and other cultural festivals.
- Traditional clothing, like robes and headscarves, is worn in many countries, but modern styles are also common.
- History and Civilization:
- The Middle East is called the "Cradle of Civilization" because some of the world’s first cities were built there.
- Ancient civilizations like Mesopotamia, Egypt, and Persia started in this region thousands of years ago.
- The Middle East is home to important historical sites, like the pyramids in Egypt and ancient cities in Iraq.
- It is also the birthplace of major religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam.
- Daily Life and Society:
- Many people live in modern cities like Dubai, Istanbul, and Cairo, with tall buildings and busy streets.
- Some people still live as nomads, moving with their animals to find food and water.
- Families are important, and many people live with their extended families, like grandparents and cousins.
- Food includes dishes like hummus, falafel, and kebabs, often made with local ingredients like olives and dates.
- Education is valued, and many children go to school to learn reading, writing, and math.
- Economy and Trade:
- Oil and gas are the biggest parts of the economy in many Middle Eastern countries.
- Some countries, like the United Arab Emirates, have modern economies with tourism and technology.
- Trade has always been important because the Middle East connects Asia, Africa, and Europe.
- Markets, called souks, are popular places where people buy and sell goods like spices, clothes, and jewelry.
- Environment and Challenges:
- Water scarcity is a big challenge because of the dry climate and limited rivers.
- Countries use technology like desalination to turn seawater into drinking water.
- Desertification, where land turns into desert, is a problem in some areas.
- People work to protect the environment by saving water and planting trees.
- Some animals, like camels and falcons, are well-adapted to the desert environment.
The document The Middle East: Society and Environment Chapter Notes | Social Studies for Grade 6 is a part of the Grade 6 Course Social Studies for Grade 6.
All you need of Grade 6 at this link: Grade 6
|
83 docs|22 tests
|
FAQs on The Middle East: Society and Environment Chapter Notes - Social Studies for Grade 6
| 1. What are the main geographical features of the Middle East? |  |
Ans. The Middle East is characterized by diverse geographical features, including vast deserts, mountain ranges, and rivers. Notable deserts include the Arabian Desert and the Syrian Desert. The region is also home to important rivers like the Tigris and Euphrates, which are vital for agriculture and settlements.
| 2. What is the significance of oil in the Middle East's economy? |  |
Ans. Oil is a crucial component of the Middle East's economy, contributing significantly to the region's wealth and development. The area holds some of the largest oil reserves in the world, making it a key player in global energy markets. This wealth from oil has funded infrastructure, education, and healthcare improvements in several countries.
| 3. How has the history of the Middle East influenced its current society? |  |
Ans. The history of the Middle East, marked by ancient civilizations, colonial influences, and conflicts, has shaped its current society. The region is home to many historical sites and cultures, which contribute to its rich heritage. Ongoing conflicts and historical grievances also impact social dynamics and governance in various countries.
| 4. What are the predominant religions in the Middle East? |  |
Ans. The Middle East is the birthplace of several major religions, primarily Islam, Christianity, and Judaism. Islam is the most widely practiced religion, with two main sects, Sunni and Shia. Christianity and Judaism also have deep historical roots in the region, influencing its cultural and social landscape.
| 5. How do environmental issues affect the Middle East? |  |
Ans. Environmental issues such as water scarcity, desertification, and pollution significantly impact the Middle East. The region experiences limited freshwater resources, making water management critical. Climate change poses additional challenges, leading to extreme weather patterns that affect agriculture and livelihoods.
Related Searches




















