Class 9 Economics Chapter 1 Notes - The Story of Village Palampur
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Organization of Production |

|
| Farming in Palampur |

|
| Modern Farming Methods |

|
| Green Revolution |

|
| Non-Farming Activities in Palampur |

|
| Difficult Words |

|
Introduction
- Farming is the main source of income in Palampur. Other activities include small-scale manufacturing, dairy transportation, and so on.
- Various resources are combined in these production activities to create the desired goods and services.
- Palampur is well connected to nearby villages and towns. An all-weather road connects the village to Raiganj and, further on, to the nearest small town.
- This road is lined with various modes of transportation, including bullock carts, tongas, bogeys, motorcycles, jeeps, tractors, and trucks.
- Palampur is home to approximately 450 families from various castes. The majority of the land is owned by 80 upper-caste families.
- Their houses are quite large, built of brick and plastered with cement.
- The SCs (Dalits) makeup one-third of the population and live in a small section of the village in much smaller houses made of mud and straw.
- The majority of the houses are wired for electricity.
- All of the tube wells in the fields are powered by electricity. Electricity is also used in many small businesses.
- There are two primary schools and one high school in Palampur. There is one government-run primary health care centre and one private dispensary.
Organization of Production
Production of any type of goods or services necessitated the services of four production factors, which aid in the overall production organization.
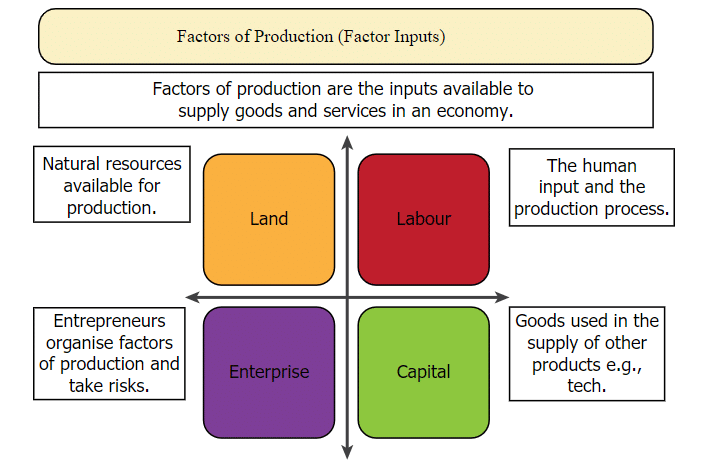
- The first requirement is land, as well as other natural resources like water, forests, and minerals.
- The second requirement is labour. Some production activities necessitate highly educated workers, while others necessitate manual labourers.
- The third requirement is physical capital, which refers to the variety of inputs needed at each stage of production. Fixed capital refers to tools, machines, and buildings that can be used in production for many years. Working capital refers to raw materials and cash on hand that are consumed during production.
- There is also the fourth requirement. To be able to combine land, labour, and physical capital and produce an output, knowledge and enterprise are required. These days, this is referred to as human capital. Every production is organized by combining factors of production such as land, labour, physical capital, and human capital.
Farming in Palampur
1. Land is Fixed
- Farming is the primary source of income in Palampur.
- Farming provides a living for 75 percent of the working population.
- There has been no increase in the amount of land under cultivation in Palampur since 1960. Some of the village's wastelands had been converted to cultivable land by that time.
- There is no more opportunity to increase farm production by cultivating new land.
2. Is there a way one can grow more from the same land?
- In Palampur, all land is farmed. There is no idle land.
- People grow jawar and bajra during the rainy (Kharif) season for cattle feed. Potatoes are grown from October to December.
- Wheat is sown during the winter (or Rabi) season. A portion of the land is also dedicated to sugarcane, which is harvested once a year.
3. Will the land be sustained?
- Land is a vital natural resource that requires careful usage.
- Modern farming methods have overused natural resources.
- The Green Revolution has led to loss of soil fertility due to increased chemical fertilizer use.
- Continuous use of groundwater for irrigation has depleted the water table.
- Environmental resources like soil fertility and groundwater take years to develop and are hard to restore once destroyed.
- Chemical fertilizers provide minerals that are readily available to plants but can leach from the soil and pollute water sources.
- These fertilizers can kill beneficial soil microorganisms, reducing soil fertility over time.
- Punjab has the highest chemical fertilizer consumption in India, leading to soil health degradation.
- Punjab farmers must use more fertilizers and other inputs to maintain production, increasing cultivation costs.
- Sustainable agriculture requires careful environmental management.
4. How is land distributed between the farmers of Palampur?
- Not everyone involved in agriculture has enough land to cultivate. In Palampur, approximately one-third of the 450 families are landless, i.e. 150 families, the majority of whom are Dalits, lack cultivable land.
- 240 of the remaining land-owning families cultivate small plots of land less than 2 hectares in size.
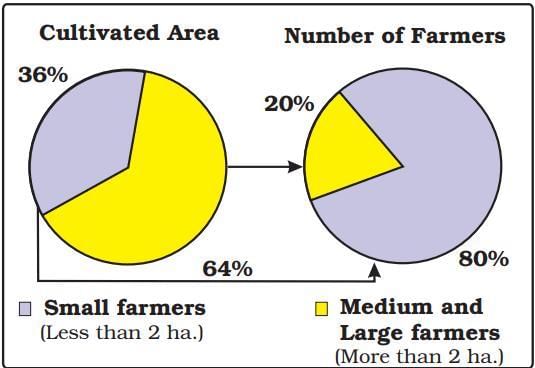 Land Distribution between Farmers of Palampur
Land Distribution between Farmers of Palampur
- There are 60 families of medium and large farmers in Palampur who cultivate more than 2 hectares of land. A few of the large farmers own 10 hectares or more of land.
5. Who will Provide the Labour?
- Farming requires a great deal of effort. Small farmers cultivate their own fields with their families. As a result, they provide the labour required for farming. Farm labourers are hired by medium and large farmers to work in their fields.
- Farm labourers are either from landless families or from families who cultivate small plots of land. Farm labourers, unlike farmers, have no ownership of the crops grown on the land. Instead, they are paid by the farmer for whose benefit they work. Wages can be paid in cash or in crop form. Labourers are sometimes provided with meals as well.
- Wages vary greatly from region to region, crop to crop, and farm activity to farm activity (such as sowing and harvesting). There is also a wide variation in the duration of employment; a farm labourer may be employed on a daily basis, for one specific farm activity such as harvesting, or for the entire year.
6. The Capital needed in Farming
- To obtain capital, the majority of small farmers must borrow money. They borrow from large farmers, village moneylenders, or traders who supply various agricultural inputs.
- The interest rate on such loans is extremely high. They are put in a difficult situation in order to repay the loan.
- In contrast to small farmers, medium and large farmers have their own farming savings. As a result, they are able to arrange or the capital required.
- Small farmers have a small surplus because their total production is small, and a significant portion of this is kept for their own family needs. As a result, wheat is supplied to the market by medium and large farmers.
- Large and medium-sized farmers sell excess farm products. A portion of the earnings is saved and kept for the purpose of purchasing capital for the following season. As a result, they are able to arrange for farm capital from their own savings. Some farmers may also use their savings to purchase cattle, trucks, or to open new businesses.
7. Sale of Surplus Farm Products
- Farmers produce wheat using the three factors of production.
- After harvest, farmers keep part of the wheat for family consumption and sell the surplus.
- Small farmers have little surplus due to smaller production and higher family needs.
- Medium and large farmers are the primary suppliers of wheat to the market.
- Traders buy wheat from farmers and sell it to shopkeepers in towns and cities.
- Large farmers like Tejpal Singh sell substantial surplus wheat and earn significant income.
- Tejpal Singh uses his earnings for:
- Savings in a bank account
- Lending to other farmers in need
- Working capital for the next farming season
- Buying additional farming equipment, such as another tractor
- Other medium and large farmers similarly save part of their earnings for future capital needs.
- Savings may be used to buy cattle, trucks, or set up non-farm businesses.
- These activities contribute to the capital for non-farm activities.
9. Sustainable use of Land
- Because land is a natural resource, it must be used with caution. Modern farming methods have depleted the earth's resources.
- Because of the increased use of chemical fertilizers, the Green Revolution is associated with a loss of soil fertility.
- The continuous use of groundwater for tube well irrigation has resulted in a decrease in the water level beneath the ground.
- Environmental resources, such as soil fertility and groundwater, are built up over time. It is extremely difficult to restore them once they have been destroyed.
10. How does Electricity help the Farmers in Palampur?
- The main impact of the spread of electricity in Palampur was the transformation of the irrigation system.
- Electricity helped farmers in transitioning from traditional Persian wheels to electricity-powered tube wells.
- The irrigation capacity of electricity-powered tube wells far exceeds that of Persian wheels.
 Solar Tube Wells
Solar Tube Wells
- The spread of electrical wires literally shifted the entire society from darkness to light. It altered all social and economic norms. It's like entering a different world.
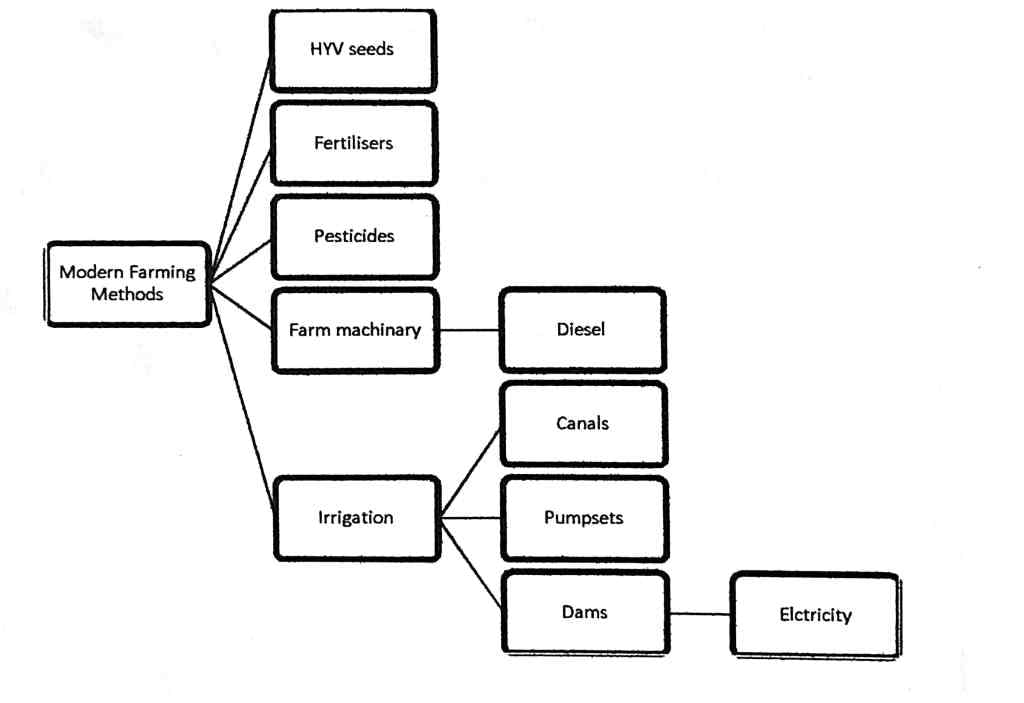
Modern Farming Methods
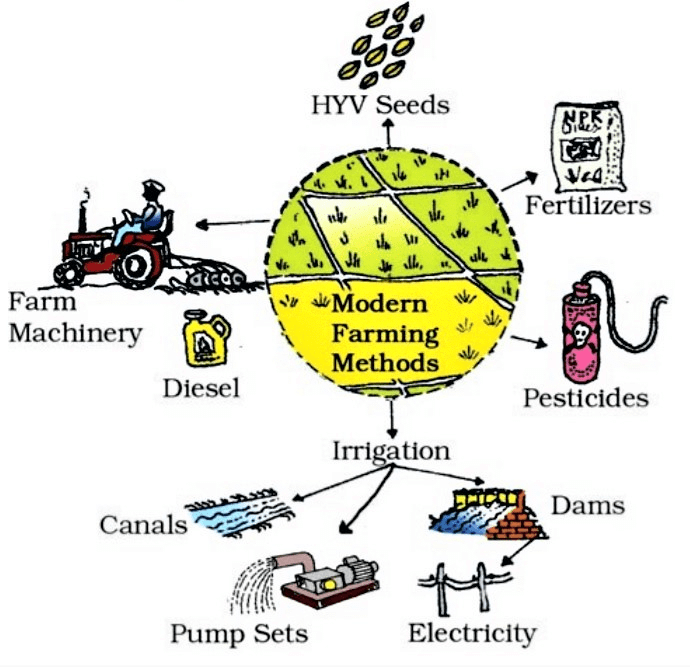
The main reasons why farmers are able to grow three different crops in a year are:
(i) As a result of the coming of electricity in the Palampur village, people have greatly improved the system of irrigation. They can now irrigate more lands quite effectively.
(ii) Tube wells were first installed by the government but soon people were able to set up their own tube wells.
(iii) By multiple cropping more than one crop is grown on a piece of land during the same year. All farmers in Palampur grow at least two main crops; many are growing potato as the third crop.
(iv) The other way is to use modern farming methods for higher yield. Higher yields are possible from a combination of HYV seeds, irrigation, chemical fertilizers, pesticides etc.
Green Revolution
- The large increase in crop yields, leading to record food production, began in our country in 1960 and marked a turning point in Indian agriculture, leading to our country's green revolution.
- The Green Revolution refers to the significant increase in the production of food grain crops, particularly wheat, in our country over the last 30 years. This is due to a sort of agricultural revolution in India, which has resulted in massive food grain production.
- The revolution is called because it has led to unmatched greenery of crops everywhere. The period 1960 to 1980 is also called the ‘golden era’ for the record food grain production.
- It is because of the green revolution that our country has become self-sufficient in food production and even buffer stocks of food grains have been created for use in times of natural calamities like drought and floods.
Non-Farming Activities in Palampur
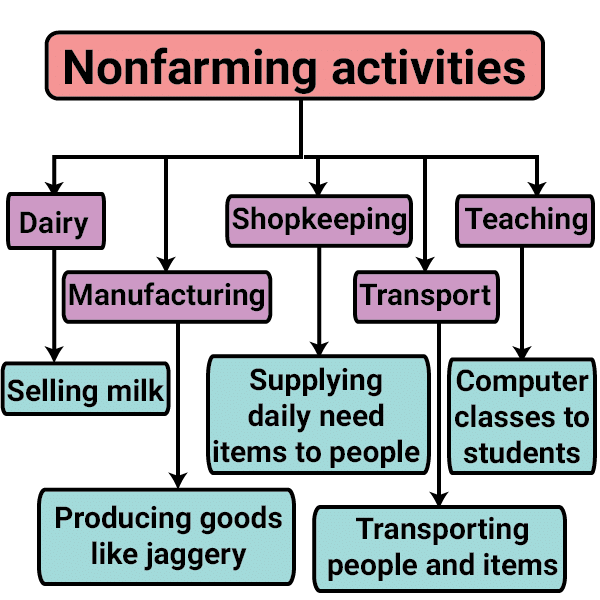
Dairy
- Dairy is a common activity in many families of Palampur. People feed their buffalos on various kinds of grass and the jawar and bajra that grow during the Kharif season.

- The milk is sold in Raiganj, the nearby large village. Two traders from Shahpur town have set up collection cum chilling centres at Raiganj from where the milk is transported to faraway towns and cities.
An Example of Small Scale Manufacturing in Palampur
- Less than fifty people are engaged in manufacturing in Palampur, unlike the manufacturing that takes place in the big factories in the towns and cities.
- Manufacturing in Palampur involves very simple production methods and is done on a small scale. It is carried out mostly at home or in the fields with the help of family labour.
The Shopkeepers of Palampur
- People involved in the trade (exchange of goods) are not many in Palampur. the traders of Palampur are shopkeepers who buy various goods from wholesale markets in the cities and sell them in the village.
- There are a few small general stores in the village selling a wide range of items like rice, wheat, sugar, tea, oil, biscuits, soap, toothpaste, batteries, candies, notebooks, pen, pencil, and even some cloth.
Transport: A Fast Developing Sector
- There are a variety of vehicles on the road connecting Palampur and Raiganj, including rickshawalas, tanga walas, jeep, tractor, truck drivers, and people driving the traditional bullock cart and bogey.
- They transport people and goods from one location to another for a fee.
Watch the video below for detailed explanation:
Difficult Words
All-weather road: A road constructed in a manner that ensures it is usable all year round, regardless of weather conditions.
Dalits: Members of the lowest social group in the Hindu caste system; traditionally regarded as untouchables or outcastes.
Physical capital: Assets used in the production of goods and services, which in this context include tools, machines, and buildings.
Human capital: The skills, knowledge, and experience possessed by an individual or population, viewed in terms of their value or cost to an organization or country.
Fixed capital: Long-term assets used over time in the production process, such as machinery and buildings.
Working capital: Short-term assets used in day-to-day operations, including raw materials and cash on hand.
Kharif season: The cropping season in India during the southwest monsoon, typically from June to October, when crops like jawar (sorghum) and bajra (pearl millet) are grown.
Rabi season: The cropping season in India that begins after the monsoon and continues during the cooler months, usually from October/November to March/April, when crops like wheat are sown.
Green Revolution: A large increase in crop production in developing countries achieved by the use of fertilizers, pesticides, and high-yield crop varieties starting in the 1960s.
HYV seeds: High-yielding variety seeds that are engineered to produce more than traditional seeds when given sufficient irrigation, pesticides, and fertilizers.
Tube well: A deep well that is made by driving a tube into the earth to a stratum that bears water, equipped with a pump to draw water, commonly powered by electricity in modern farming.
Sustainable use of land: Agricultural practices that attempt to ensure the viability of the land to continue to yield crops and livestock into the future, without irreversible damage to soil fertility and overall environment.
Solar tube wells: Tube wells that operate on solar power instead of traditional electricity or diesel, reflecting a move towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly farming practices.
Persian wheel: An irrigation device used to lift water, traditionally powered by animals or humans, now largely replaced by electric-powered pumps.
|
55 videos|525 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Economics Chapter 1 Notes - The Story of Village Palampur
| 1. What is the significance of the Green Revolution in Palampur? |  |
| 2. What are some examples of non-farming activities in Palampur? |  |
| 3. How has modern farming methods impacted agriculture in Palampur? |  |
| 4. How has the organization of production contributed to the success of farming in Palampur? |  |
| 5. What are some of the difficult words used in the chapter "The Story of Village Palampur" and their meanings? |  |





















