The Wonderful World of Science Chapter Notes | Chapter Notes For Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| What is Science? |

|
| Exploring Our Home, Planet Earth |

|
| The Importance of Food |

|
| The Scientific Method |

|
| Key Notes |

|
Introduction
From a young age, humans are naturally curious about the world around them. This curiosity drives us to explore and ask questions. Think about how babies and toddlers constantly touch, taste, and observe everything around them. This natural curiosity is the foundation of science.
What is Science?
Science is a method of thinking and observing to understand our world and the secrets of the universe.
- It’s like a grand adventure where we ask questions, explore, and learn how things work.
- The key to this journey is Curiosity, which is the inspiration for this book.
 Science is Curiosity
Science is Curiosity
- Curiosity: Curiosity is the eagerness to learn more about our surroundings. It is essential in science because it encourages us to explore and discover.
- Example: If you've ever taken apart a toy to see how it works, you were showing curiosity and doing a bit of science.
Science is Everywhere
Science is all around us. From tiny grains of sand to huge mountains, from a single leaf to an entire forest.
Examples:
- Stars shining in the night sky: Science explains that stars shine because of reactions happening inside them.
- Flowers blooming: Plants respond to light and temperature, which helps them know when to bloom.
Science helps us answer questions and solve mysteries. It helps us understand the world better. For example: Knowing how plants grow helps farmers grow better crops.
Exploring Our Home, Planet Earth
Earth: The only planet we know that has life. It has many different environments and living things.
 Earth
Earth
Examples:
- Plants: How does a seed grow into a plant? A seed needs water, sunlight, and nutrients from the soil to grow.
- Animals: How does a caterpillar turn into a butterfly? This change is called metamorphosis.
Ecosystems: Various environments such as forests, oceans, deserts, and wetlands, each with its own plants, animals, and conditions.
- Example: In a forest, trees provide homes for animals and plants make oxygen.
The Importance of Food
Food provides us with energy and supports our growth. In India, there are many different types of food from various regions.
- Consider: What ingredients are in these dishes? How can we learn about them? For example, when you eat, think about where each ingredient originates from.
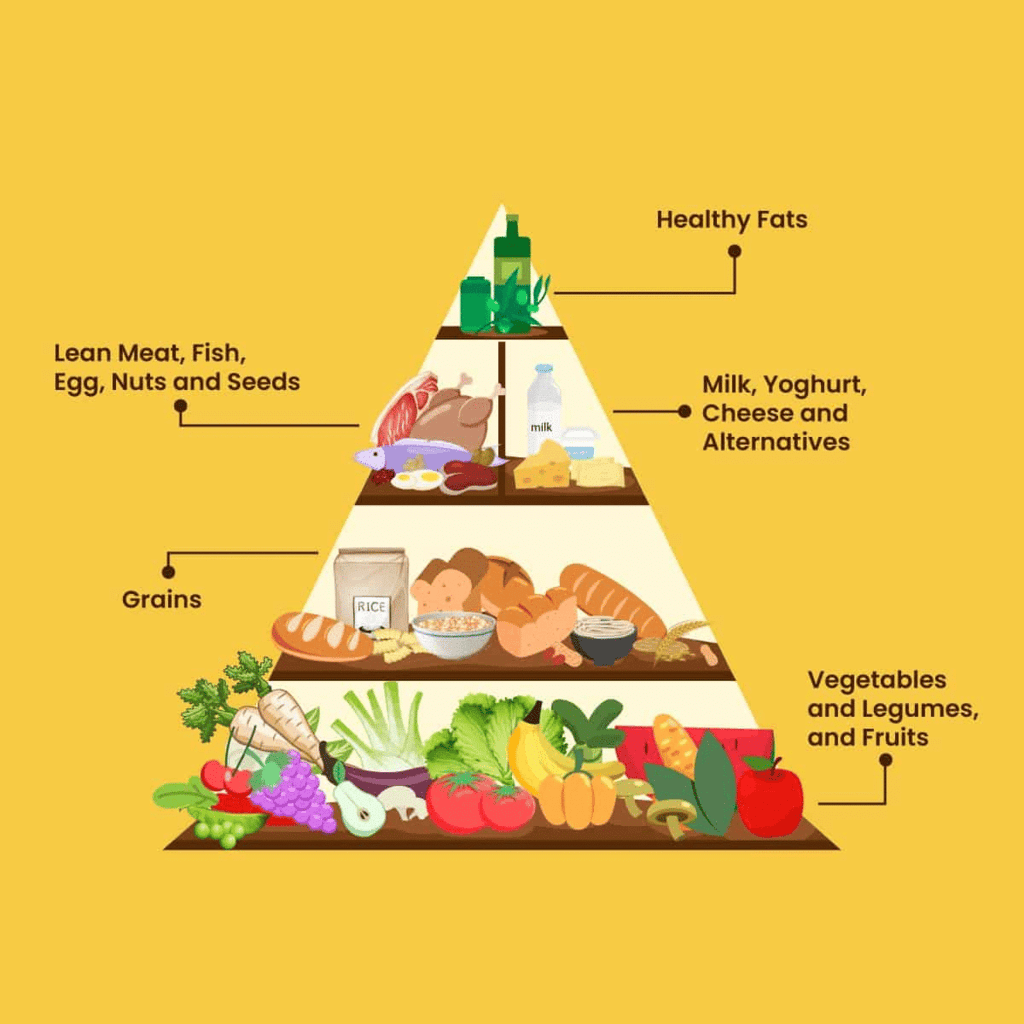 Components of Food
Components of Food
The Importance of Water
Water is vital for survival. It's such a wonderful substance.
- Have you ever jumped in a puddle after it rains? Do you wonder why it rains?
Properties of water: Water can be solid (ice), liquid (water), or gas (steam). Forms of WaterObservations:
Forms of WaterObservations:
- Freezing and boiling: Water freezes at 0°C to become ice and boils at 100°C to become steam.
- Temperature: We measure temperature to know how hot or cold something is.
- Fun with water: Playing in the rain or jumping in puddles shows how water can be enjoyable and important in our daily lives.
Materials Around Us
Look at things you use every day – paper, metal keys, plastic rulers, rubber erasers, magnets, clothes, cups, and more. Different items are made from different materials like metal, plastic, rubber, and fabric.
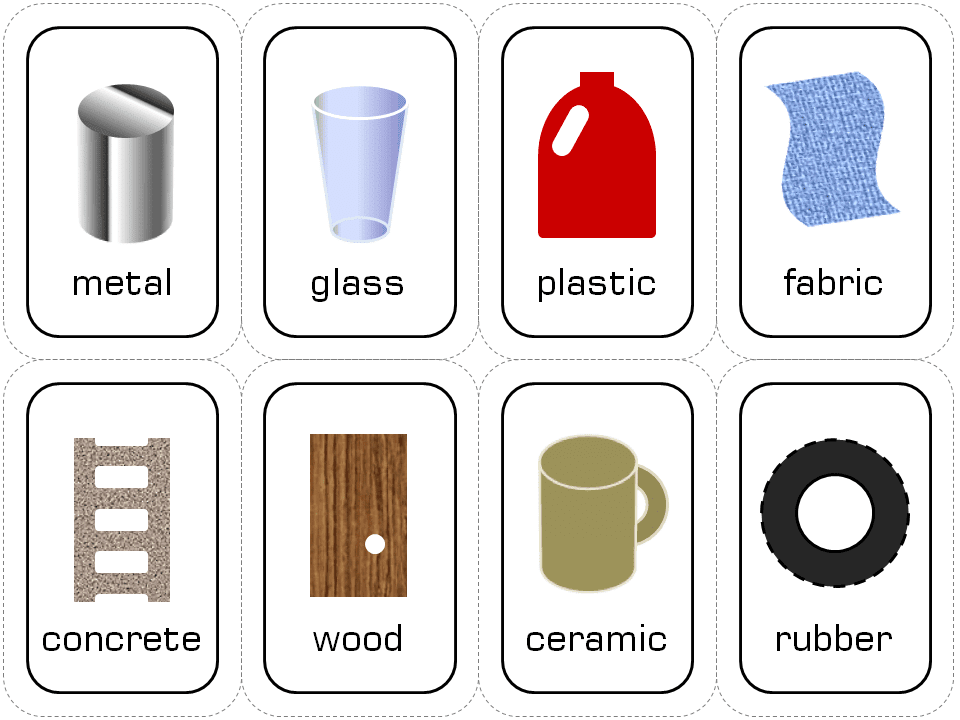 Materials around us
Materials around us
How do we separate different materials?
Knowing the properties of materials helps us sort and recycle them. Example: Recycling involves separating paper, plastic, and metal so they can be reused.
The Scientific Method
The scientific method is a simple way to find answers to questions and solve problems. It helps us understand things step by step. Let’s break it down:
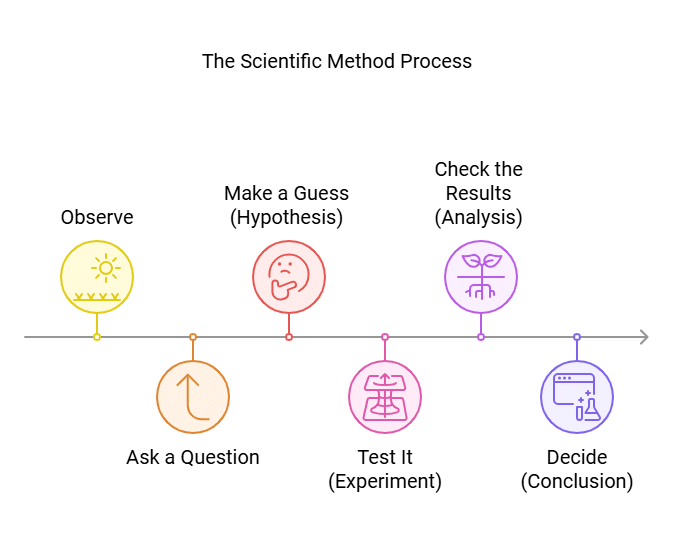
1. Observe
- Look closely at something interesting or puzzling.
- Example: You see a plant growing towards the light.
2. Ask a Question
- Think of a question about what you saw.
- Example: Why does the plant grow towards the light?
3. Make a Guess (Hypothesis)
- Take a smart guess about the answer to your question.
- Example: The plant grows towards the light to get more sunlight.
4. Test It (Experiment)
- Do an experiment to see if your guess is correct.
- Example: Put plants in different places with light and see how they grow.
5. Check the Results (Analysis)
- Look at what happened in your experiment. Did it match your guess?
- Example: Did plants in brighter light grow towards the light?
6. Decide (Conclusion)
- Say if your guess was correct or not based on your experiment.
- Example: If the plants grew towards the light, your guess was correct. If not, think of another reason and test again.
Why Is This Important?
The scientific method helps us find true answers and understand how things work.
Example: Why Did My Pen Stop Writing?
- Observe: The pen isn’t writing.
- Question: Why did it stop?
- Guess: Maybe the ink is finished.
- Test It: Check the ink refill.
- Check the Results: If the ink is empty, your guess is right. If not, think of another guess.
- Next Steps: Maybe the ink dried up because the pen was left uncapped.
This method helps you find the right answer step by step!
Key Notes
- Science: Science is a method of thinking, observing, and doing things to grasp the world around us and to discover the mysteries of the universe.
- Curiosity: The most important aspect is to be curious and closely observe your environment, as curiosity drives scientific breakthroughs.
- Scientific Method: The scientific method is a systematic process that guides us to find trustworthy answers to our questions. The steps include:
Noticing something intriguing or unclear.
Asking a question.
Making a prediction (hypothesis).
Testing the prediction through experiments or observations.
Examining results to determine if they address the question. - Collaborative Nature: Scientists collaborate to make discoveries, and teamwork is vital in the scientific community.
FAQs on The Wonderful World of Science Chapter Notes - Chapter Notes For Class 6
| 1. What is the definition of science? |  |
| 2. Why is Earth considered a unique planet? |  |
| 3. How does food impact our health and well-being? |  |
| 4. Why is water vital for life on Earth? |  |
| 5. What are the steps of the scientific method? |  |
















