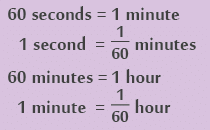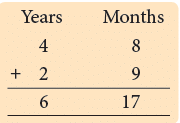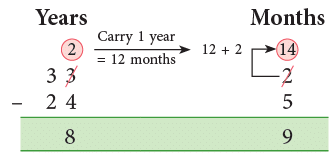Time and Calendar Class 4 Notes Maths Chapter 12 Free PDF
Clocks
Look at the following clocks. Here are some units for measuring time:
Here are some units for measuring time: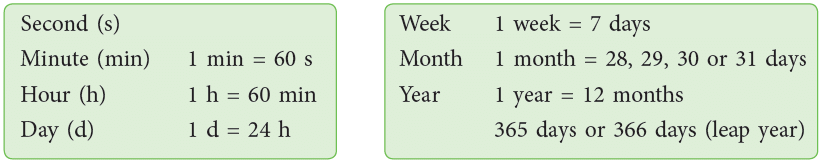
Telling the Time
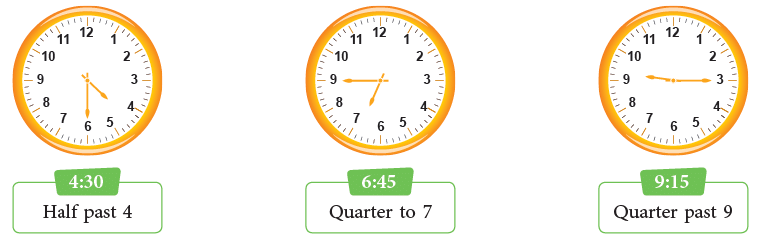
1. To the Nearest 5 Minutes
- There are 60 marks on the clock's face.
- Out of these marks, 12 are numbered.
- The numbers represent 5-minute intervals.
- For example, when the minute hand points to 1, it means it is 5 minutes past the hour.
- When the hand is at 2, it indicates 10 minutes past the hour.
- This pattern continues around the clock.

- On the clock dial, there are sub-divisions between the numbers.
- Each sub-division represents 1 minute.
- There are a total of 60 divisions on the dial, indicating 60 minutes.
- The minute hand makes one complete turn around the dial in 1 hour, which equals 60 minutes.
Now, read the following clocks:

2. To the Nearest Minute
Whatever we have studied in Class 3, let us recall with the help of the examples given below.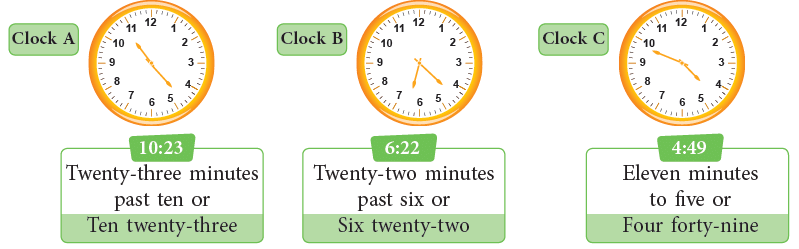 In Clock A, the minute hand has moved 23 divisions and the hour hand is between 10 and 11, so the time is 10:23 or twenty-three minutes past ten.
In Clock A, the minute hand has moved 23 divisions and the hour hand is between 10 and 11, so the time is 10:23 or twenty-three minutes past ten.
Similarly, the times for Clock B and Clock C are shown above.
Edurev Tips:
- When the minute hand is before 6, we read it as past.
- When the minute hand is after 6, we read it as to...
Using A.M. and P.M. Time
The time shown on the clock given alongside is 8:25, but we are not able to determine whether it is 8:25 in the morning or evening.
- A day consists of 24 hours.
- In a 12-hour clock system, the hour hand makes two complete rotations around the clock face.
- This means that the same time appears twice a day.
- To tell the difference between these times, we use a.m. and p.m.
- a.m. stands for ante meridian, which refers to the time from midnight until noon.
- p.m. stands for post meridian, covering the time from noon until midnight.
- For example, 8:25 in the morning is written as 8:25 a.m.
- The same time in the evening is expressed as 8:25 p.m.
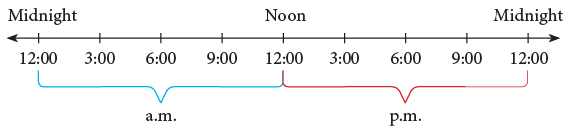
Edurev Tips: A day begins at 12 midnight and ends at 12 midnight of the following day.
24-Hour Time Notation
- We have already learned about the 24-hour clock in Class 3.
- The 24-hour time system is also known as the “24-hour clock”.
- This clock shows the time from 12 midnight to 12 midnight the next day, covering 1 full day.
- The time is written as 0000 hours to 2400 hours.
- In this format, the first two digits indicate the hours, while the last two digits show the minutes.
 The table given below shows the 24-hour time equivalent to 12-hour time:
The table given below shows the 24-hour time equivalent to 12-hour time:
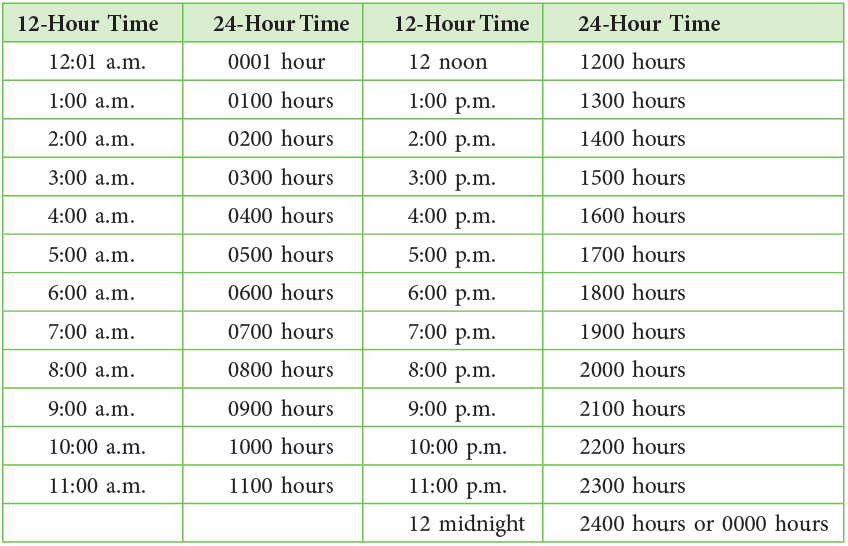
Thus,
- 8:35 a.m. = 0835 hours;
- 3:15 p.m. = 1515 hours;
- 11:40 a.m. = 1140 hours;
- 11:50 p.m. = 2350 hours.
Conversion of Time
Look at the following clocks and tell what time they show.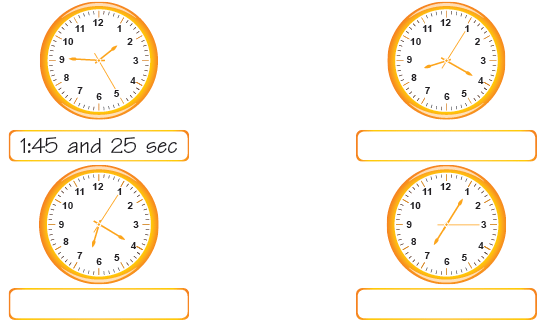
Edurev Tips:
Converting from Hours to Minutes and Minutes to Hours
- Hours to minutes: 1 h = 60 min
Examples:
(a) 5 h = 5 × 60 min = 300 min
(b) 2 h 45 min = 2 h + 45 min = 2 × 60 min + 45 min
= 120 min + 45 min
= 165 min - Minutes to hours:
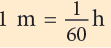
Examples:
(a) 480 min = (480 ÷ 60) h = 8 h
(b) 352 min = (352 ÷ 60) h
= 5 h 52 min
Or
352 min = 300 min + 52 min
= (300 ÷ 60) h + 52 min
= 5 h + 52 min
= 5 h 52 min
Operations on Measures of Time
1. Addition
Example 1: Add 6 hours 45 minutes and 11 hours 39 minutes.
Thus, 6 hours 45 minutes + 11 hours 39 minutes = 18 hours 24 minutes.
Think:
45 min + 39 min = 84 min
= 60 min + 24 min
= 1 h + 24 min
2. Subtraction
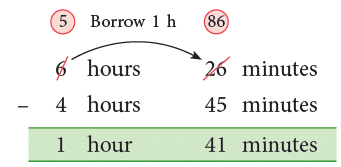
Example 2: Raju completes a painting in 6 hours 26 minutes and Rohit completes it in 4 hours 45 minutes. How much more time does Raju take to complete the painting?
You have to subtract 4 hours 45 minutes from 6 hours 26 minutes to find the required time.
Thus, Raju takes 1 hour 41 minutes more to complete the painting.
Think:
45 min cannot be subtracted from 26 min.
Borrow, 1 h = 60 min from 6 hours.
60 min + 26 min = 86 min
86 min – 45 min = 41 min
5 h – 4 h = 1 h
Elapsed Time
- Using 24-hour time notation, we can easily calculate the elapsed time by adding or subtracting time.
- Elapsed time refers to the duration between two specific times.
- We can determine the starting time if we know the finishing time and the duration of the activity.
- Alternatively, we can find the finishing time if we have the starting time and the duration of the activity.
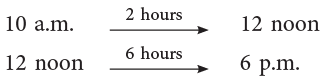
Example 3: Mr Verma’s office starts at 10 a.m. and closes at 6 p.m. How many hours does the office remain open?
Thus, Mr Verma’s office remains open for 2 hours + 6 hours = 8 hours.
Example 4: A flight took off for Mumbai from New Delhi at 3:10 p.m. The plane landed in Mumbai at 4:55 p.m. What was the duration of the flight?
∴ Duration of the flight = 50 minutes + 55 minutes
= 105 minutes = 60 minutes + 45 minutes
= 1 hour + 45 minutes
∵ 1 hour = 60 min
Thus, the duration of the flight was 1 hour 45 minutes.
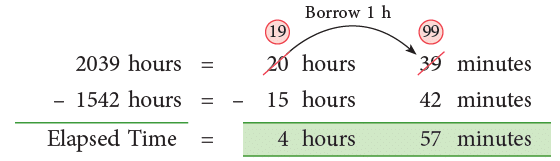
Example 5: How long is the time from
(a) 1542 hours to 2039 hours?
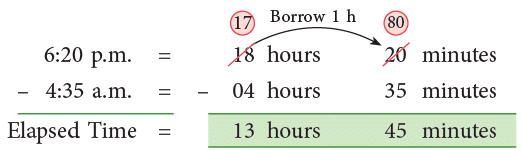
(b) 4:35 a.m. to 6:20 p.m.?
(a) The elapsed time is 2039 hours – 1542 hours.
Thus, the elapsed time is 4 hours 57 minutes.
(b) To find the elapsed time between 4:35 a.m and 6:20 p.m., first convert the time into 24-hour time.
Thus, the elapsed time is 13 hours 45 minutes.
Example 6: Find the time using a 24-hour clock.
(a) 4 hours 25 minutes after 2040 hours
(b) 8 hours 15 minutes before 2:35 p.m.
(a) Add 4 hours 25 minutes to 2040 hours to find the required time.
20 h 40 min + 4 h 25 min
= 24 h 65 min = 24 h + 1 h + 5 min
= 1:05 a.m. (It becomes next day.) 1 h 5 min after 12:00 midnight.
(b) 2:35 p.m. = 1435 hours = 14 h 35 min
∴ Required time = 14 h 35 min – 8 h 15 min
= 6 h 20 min
= 0620 hours or 6:20 a.m.
Calendar
- A calendar is a way to keep track of the months, weeks, and days in a year.
- The calendar for the year 2019 is presented below.
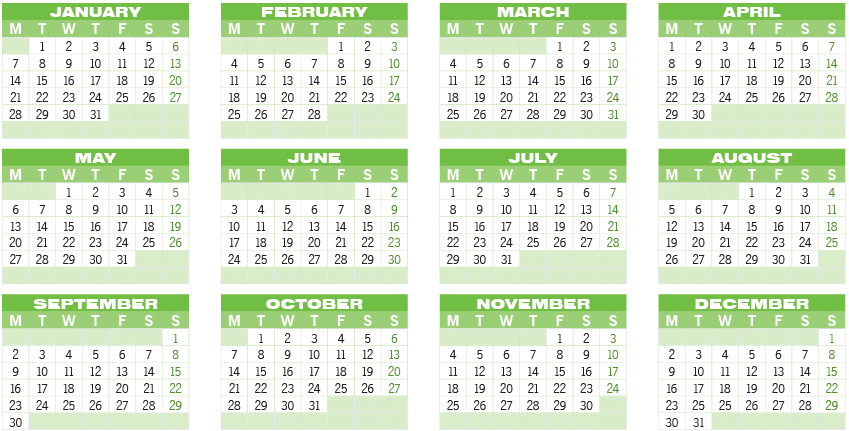
- A year consists of 12 months.
- One year has 365 days.
- A year is made up of 52 weeks.
- One day is the time it takes for the Earth to make one full rotation on its axis.
- The standard unit of time is one day.
- Each year is equal to 365 days.
- A week consists of 7 days.
Starting from the first day of the week, the names of different days of the week are:
 This cycle of days is repeated again and again.
This cycle of days is repeated again and again.
The short forms for the days of the week are as follows:
Mon., Tues., Wed., Thurs., Fri., Sat., Sun.
If today is a Monday, after 7 days it will again be Monday.
Months and Days
There are 12 months in a year. These are January, February, March, April, May, June, July, August, September, October, November and December.
The number of days in various months are as follows:
April, June, September and November have 30 days. All the rest have 31, except February which has 28 days and 29 days in a leap year.
To find the number of days in a year:
(7 × 31) + (4 × 30) + (1 × 28) = _________.
- There are 365 days in a year.
- Every four years, there is an additional day.
- A year that has 366 days is known as a leap year.
- Leap years occur every fourth year.
- The extra day is added to February, which then has 29 days.
- Examples of leap years include: 2004, 2008, 2012 and 2016
 What leap year comes next after 2016? How did you find it?
What leap year comes next after 2016? How did you find it?
1. A year is a leap year, if it is divisible by 4.
2. If a year ends in a hundred, it will not be a leap year, unless it is divisible by 400.
- The year 2000 is a leap year, but 1900 is not.
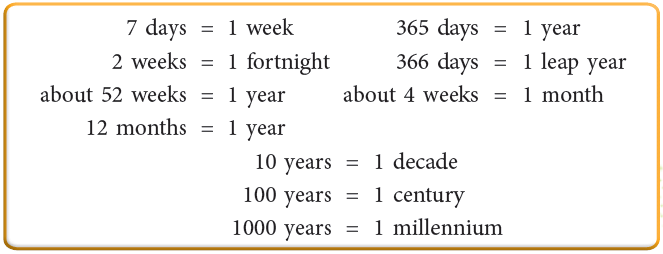
- To calculate the number of weeks in a year, you need to divide 365 by 7, since there are 7 days in each week.
- The division 365 ÷ 7 equals 52 weeks and 1 extra day.
- This means that in a typical year, there are 52 weeks and 1 additional day left over.
By studying the calendar, we learn that:
 We call the years from 1900 to 1999 the twentieth century. The years from 2000 to 2099 is the twenty-first century.
We call the years from 1900 to 1999 the twentieth century. The years from 2000 to 2099 is the twenty-first century.
Months and Years
- We know that 12 months equals 1 year.
- We can convert 1 year 7 months into just months like this:
1 year is 12 months.
Adding 7 months gives us a total of 19 months. - We can also convert 20 months into years and months:
20 months includes 12 months.
This leaves us with 8 months, which can be stated as 1 year 8 months.
Solved Examples
Example 7: If 10 April 2018 was a Tuesday, what was the day on 30 April, 2018?
The same day is repeated after every 7 days. After 10 April, the next Tuesday fell on 17 April and then on 24 April.
Therefore, counting ahead from 24 April, 30 April, 2018 was a Monday.
Example 8: Rahul is 4 years 8 months old. His sister Divya is 2 years 9 months elder to him. How old is she?
Divya’s age = Rahul’s age + 2 years 9 months
= 4 years 8 months + 2 years 9 months
= 6 years 17 months
= 6 years + 12 months + 5 months
= 6 years + 1 year + 5 months (12 months = 1 year)
= 7 years 5 months.
Example 9: Piyush went for a project to London when he was 24 years 5 months old. Now he is 33 years 2 months old. How long has he been there?
Piyush stayed in London for: (33 years 2 months – 24 years 5 months)
Thus, Piyush stayed in London for 8 years 9 months.
5 months cannot be subtracted from 2 months. So, we borrow one year from 33 years. 1 year = 12 months; 12 + 2 = 14.
Subtract 5 months from 14 months and 24 years from remaining 32 years.
Number of Days Between Two Given Dates
We can find the number of days between two given dates as under:
For example, to find the number of days between 20 July, 1947 and 2 October, 1947, we proceed as follows.
Leaving out 20 July, take 11 days for July, that is, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30 and 31 of the month. Also, leave out 2 October.
Note: Whether you should count the first or the last day or both depends on the particular situation or nature of question.

Edurev Tips: If you have to find the number of days from (not between) 20 July to 2 Oct., then the number of days are 12 + 31 + 30 + 2 = 75
Example 10: The football team reached England on 10 February, 2017 and stayed for 45 days. Find the date on which the team returned?
Number of days the team stayed in England in February
= 19 days (10th February is also counted.)
(Count from 10 to 28: 11, 11, ..., 28)
Number of days the team stayed in England in March,
= 45 – 19 = 26 days
Thus, the team stayed till 26 March, 2017 and returned on 27 March 2017.
Example 11: Nishant started reading “Charlie and the Chocolate Factory” on 15 May. It took him 21 days to complete the book. On what day did he finish reading?
Number of days on which Nishant read the book in May = 31 – 14 = 17
(Here, 15 May is also counted.)
Number of days he read in June = 21 – 17 = 4.
Thus, Nishant finished reading the book on 4 June.
|
52 videos|70 docs|53 tests
|
FAQs on Time and Calendar Class 4 Notes Maths Chapter 12 Free PDF
| 1. How do I convert A.M. and P.M. time to 24-hour time notation? |  |
| 2. What is elapsed time and how can I calculate it? |  |
| 3. How can I read a 24-hour clock? |  |
| 4. What are some common operations I can perform on measures of time? |  |
| 5. How do I use a calendar to determine the day of the week for a specific date? |  |