Class 4 Exam > Class 4 Notes > Mathematics Class 4 ICSE > Chapter Notes: Time and Temperature
Time and Temperature Chapter Notes | Mathematics Class 4 ICSE PDF Download
Introduction
Time and temperature are fascinating concepts that help us organize our day and understand the world around us! Imagine planning your playtime without knowing the hours or minutes, or stepping outside without checking if it’s hot or cold. In this chapter, we’ll dive into reading clocks, converting time units, understanding the 24-hour clock, calculating elapsed time, and measuring temperature in Celsius and Fahrenheit. Get ready to become a time-telling and temperature-reading expert!
Time in Hours, Minutes, and Seconds
- Time is measured using hours (h), minutes (min), and seconds (s).
- A clock face has numbers from 1 to 12 to show hours.
- Smaller marks between hour numbers represent minutes.
- The hour hand completes one full circle in 12 hours.
- The minute hand completes one circle in 1 hour, which is 60 minutes.
- The second hand completes one circle in 1 minute, which is 60 seconds.
- 1 day equals 24 hours, 1 hour equals 60 minutes, and 1 minute equals 60 seconds.
- To read time:
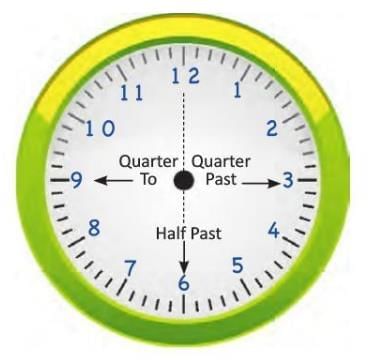
- If the minute hand is on the right side of the clock (past the 12), it shows minutes past the hour.
- If the minute hand is on the left side (before the 12), it shows minutes to the next hour.
- Example: If the minute hand is on 6 (right side) and the hour hand is on 3, the time is 3:30 (30 minutes past 3).
Time in a.m. and p.m.
- A day has 24 hours, and the hour hand makes two rounds of the clock.
- From 12 midnight to 12 noon, time is written with a.m.
- From 12 noon to 12 midnight, time is written with p.m.
- Example: 8:00 a.m. is morning time (before noon), and 8:00 p.m. is evening time (after noon).
24-Hour Clock
- Places like railway stations, airports, and hospitals use a 24-hour clock instead of a.m./p.m.
- The 24-hour clock runs from midnight to midnight, divided into 24 hours.
- Time is written as hours : minutes or hours : minutes : seconds (e.g., 14:30 or 14:30:00).
- This format is used in digital watches and computers.
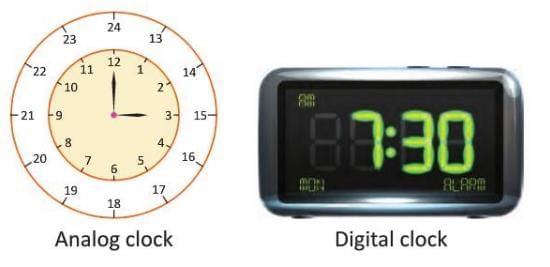
Conversion of 24-Hour Clock Time to 12-Hour Clock Time
- For 0000 to 0059 hours: Add 1200 hours and use a.m.
- For 0100 to 1159 hours: Use the time as is with a.m.
- For 1200 to 1259 hours: Use the time as is with p.m.
- For 1300 to 2359 hours: Subtract 1200 hours and use p.m.
- Example: 2305 hours = 2305 - 1200 = 1105 hours = 11:05 p.m.
Conversion of 12-Hour Clock Time to 24-Hour Clock Time
- For 12:00 midnight to 12:59 a.m.: Subtract 12 hours (1200 hours).
- For 1:00 a.m. to 12:59 p.m.: Use the time as is.
- For 1:00 p.m. to 11:59 p.m.: Add 12 hours (1200 hours).
- Example: 6:20 p.m. = 0620 hours + 1200 hours = 1820 hours or 18:20.
Converting Days to Hours and Vice Versa
- 1 day equals 24 hours.
- 1 hour equals 1/24 day.
Conversion of Days to Hours
- Multiply the number of days by 24 to get hours.
- For days and hours, multiply days by 24 and add the hours.
- Example: 5 days 16 hours = (5 × 24) + 16 = 120 + 16 = 136 hours.
Conversion of Hours to Days
- Divide the hours by 24 to get days.
- For days and hours, divide hours by 24. The quotient is days, and the remainder is hours.
- Example: 428 hours ÷ 24 = 17 days with 20 hours remainder (428 = 17 × 24 + 20).
Converting Hours to Minutes and Vice Versa
- 1 hour equals 60 minutes.
- 1 minute equals 1/60 hour.
Conversion of Hours to Minutes
- Multiply hours by 60 to get minutes.
- For hours and minutes, multiply hours by 60 and add the minutes.
- Example: 9 hours 12 minutes = (9 × 60) + 12 = 540 + 12 = 552 minutes.
Conversion of Minutes to Hours
- Divide minutes by 60 to get hours.
- For hours and minutes, divide minutes by 60. The quotient is hours, and the remainder is minutes.
- Example: Convert 932 minutes to hours and minutes
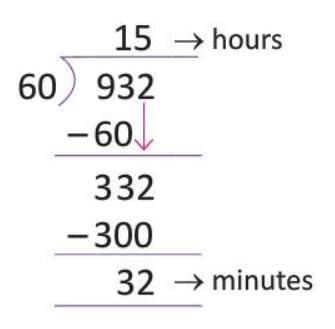 932 minutes ÷ 60 = 15 hours with 32 minutes remainder (932 = 15 × 60 + 32).
932 minutes ÷ 60 = 15 hours with 32 minutes remainder (932 = 15 × 60 + 32).
Converting Minutes to Seconds and Vice Versa
- 1 minute equals 60 seconds.
- 1 second equals 1/60 minute.
Conversion of Minutes to Seconds
- Multiply minutes by 60 to get seconds.
- For minutes and seconds, multiply minutes by 60 and add the seconds.
- Example: 12 minutes 40 seconds = (12 × 60) + 40 = 720 + 40 = 760 seconds.
Conversion of Seconds to Minutes
- Divide seconds by 60 to get minutes.
- For minutes and seconds, divide seconds by 60. The quotient is minutes, and the remainder is seconds.
- Example: Convert 156 seconds to minutes.
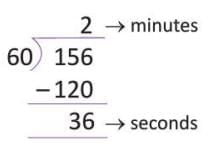 156 seconds ÷ 60 = 2 minutes with 36 seconds remainder (156 = 2 × 60 + 36).
156 seconds ÷ 60 = 2 minutes with 36 seconds remainder (156 = 2 × 60 + 36).
Conversion of Seconds to Hours, Minutes, and Seconds
- Step 1: Divide seconds by 60 to get minutes and seconds.
- Step 2: Divide the minutes from Step 1 by 60 to get hours and minutes.
- Step 3: Combine hours, minutes, and seconds.
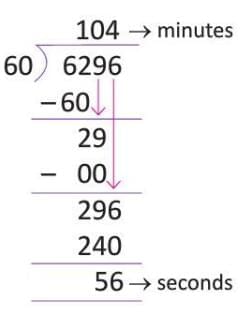
Example: 6,296 seconds:
- Step 1: 6,296 ÷ 60 = 104 minutes 56 seconds.
- Step 2: 104 ÷ 60 = 1 hour 44 minutes.
- Step 3: 6,296 seconds = 1 hour 44 minutes 56 seconds.
Addition of Time
- Step 1: Add seconds. If 60 or more, subtract 60 and add 1 to minutes. Repeat if needed.
- Step 2: Add minutes. If 60 or more, subtract 60 and add 1 to hours. Repeat if needed.
- Step 3: Add hours.
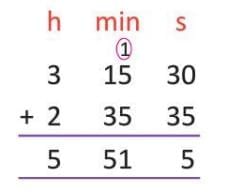
Example: Add 3 hours 15 minutes 30 seconds + 2 hours 35 minutes 35 seconds:
- Seconds: 30 + 35 = 65 = 1 minute 5 seconds (65 - 60 = 5).
- Minutes: 1 (carry over) + 15 + 35 = 51 minutes.
- Hours: 3 + 2 = 5 hours.
- Result: 5 hours 51 minutes 5 seconds.
Subtraction of Time
- Step 1: Subtract seconds. If not enough seconds, borrow 1 minute (60 seconds) from minutes, reduce minutes by 1, and add 60 to seconds.
- Step 2: Subtract minutes. If not enough minutes, borrow 1 hour (60 minutes) from hours, reduce hours by 1, and add 60 to minutes.
- Step 3: Subtract hours.
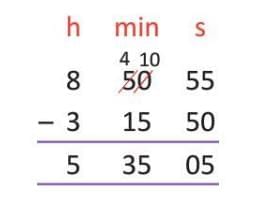
Example: Subtract 3 hours 15 minutes 50 seconds from 8 hours 50 minutes 55 seconds:
- Seconds: 55 - 50 = 5 seconds.
- Minutes: 50 - 15 = 35 minutes.
- Hours: 8 - 3 = 5 hours.
- Result: 5 hours 35 minutes 5 seconds.
Elapsed Time
- Elapsed time is the duration between the start and end of an event.
- It can be calculated using forward/backward counting or addition/subtraction.
By Forward or Backward Counting
- Step 1: Draw a number line with start and end times.
- Step 2: Count forward from the start time to the nearest hour and note the minutes.
- Step 3: Count backward from the end time to the nearest hour and note the minutes.
- Step 4: Count hours between the two nearest hours.
- Step 5: Add the minutes and hours, converting 60 minutes to 1 hour if needed.
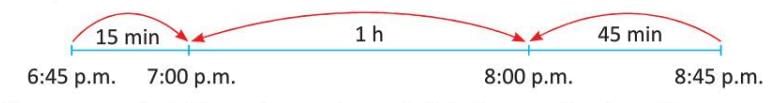
Example: Homework from 6:45 p.m. to 8:45 p.m.:
- Step 1: Mark 6:45 p.m. and 8:45 p.m. on a number line.
- Step 2: From 6:45 p.m. to 7:00 p.m. = 15 minutes.
- Step 3: From 8:00 p.m. to 8:45 p.m. = 45 minutes.
- Step 4: From 7:00 p.m. to 8:00 p.m. = 1 hour.
- Step 5: 15 min + 45 min + 1 hour = 60 min + 1 hour = 2 hours.
- Result: 2 hours.
By Addition or Subtraction
- Add duration to the start time to find the end time.
- Subtract start time from end time to find duration.
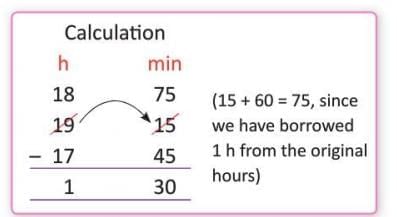
Example: Music class from 5:45 p.m. to 7:15 p.m.:
- Start: 5:45 p.m. = 17 hours 45 minutes.
- End: 7:15 p.m. = 19 hours 15 minutes.
- Duration: 19h 15min - 17h 45min = 1 hour 30 minutes.
- Result: 1 hour 30 minutes.
Temperature
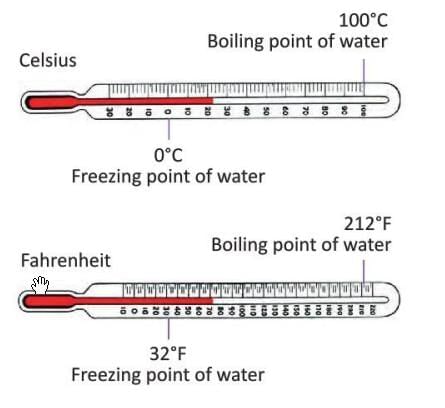
- Temperature measures how hot or cold something is.
- It is measured in degrees Celsius (°C) or degrees Fahrenheit (°F) using a thermometer.
- Celsius scale: 0°C is the freezing point of water, 100°C is the boiling point.
- Fahrenheit scale: 32°F is the freezing point of water, 212°F is the boiling point.
- Clinical thermometers measure body temperature.
- Example: A Celsius thermometer shows 25°C.
Converting Temperature from °C to °F
- Use the formula:
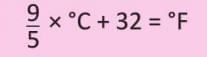
- Step 1: Multiply °C by 9.
- Step 2: Divide the result by 5.
- Step 3: Add 32 to get °F.
Example: Convert 25°C to °F:
- Step 1: 25 × 9 = 225.
- Step 2: 225 ÷ 5 = 45.
- Step 3: 45 + 32 = 77.
- Result: 25°C = 77°F.
Converting Temperature from °F to °C
- Use the formula:

- Step 1: Subtract 32 from °F.
- Step 2: Multiply the result by 5.
- Step 3: Divide by 9 to get °C.
Example: Convert 113°F to °C:
- Step 1: 113 - 32 = 81.
- Step 2: 81 × 5 = 405.
- Step 3: 405 ÷ 9 = 45.
- Result: 113°F = 45°C.
The document Time and Temperature Chapter Notes | Mathematics Class 4 ICSE is a part of the Class 4 Course Mathematics Class 4 ICSE.
All you need of Class 4 at this link: Class 4
|
82 docs|14 tests
|
FAQs on Time and Temperature Chapter Notes - Mathematics Class 4 ICSE
| 1. How do I convert hours into minutes and vice versa? |  |
Ans.To convert hours into minutes, multiply the number of hours by 60, since there are 60 minutes in an hour. For example, 2 hours is equal to 2 x 60 = 120 minutes. To convert minutes back into hours, divide the number of minutes by 60. For instance, 120 minutes is equal to 120 ÷ 60 = 2 hours.
| 2. What is the difference between a.m. and p.m.? |  |
Ans.a.m. stands for "ante meridiem," which means "before noon" in Latin and refers to the time from midnight (12:00 a.m.) to just before noon (11:59 a.m.). p.m. stands for "post meridiem," meaning "after noon," and refers to the time from noon (12:00 p.m.) to just before midnight (11:59 p.m.).
| 3. How do I add and subtract time? |  |
Ans.To add time, align the hours, minutes, and seconds, then add each column starting from the rightmost (seconds). If the sum exceeds 60 seconds, convert to minutes. Repeat for minutes and hours. To subtract time, do the same but subtract each column. If you cannot subtract (for example, 5 minutes from 3 minutes), borrow 1 hour and convert it to minutes.
| 4. How can I calculate elapsed time? |  |
Ans.To calculate elapsed time, identify the start time and end time. Convert both times to the same format (either a.m./p.m. or 24-hour). Subtract the start time from the end time. If the result is negative, it means the end time is on the next day. Ensure you account for the full hours and minutes correctly.
| 5. How do I convert days into hours? |  |
Ans.To convert days into hours, multiply the number of days by 24, as there are 24 hours in a day. For example, 3 days is equal to 3 x 24 = 72 hours. To convert hours back into days, divide the number of hours by 24. For instance, 72 hours is equal to 72 ÷ 24 = 3 days.
Related Searches