Understanding Shapes Chapter Notes | Mathematics Class 8 ICSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Different Types of Curves |

|
| Polygon |

|
| Sum of Angles of a Polygon |

|
| Sum of Exterior Angles of a Polygon |

|
| Regular Polygon |

|
| Quadrilateral |

|
Introduction
Geometry is a fascinating branch of mathematics that deals with shapes and their properties. In this chapter, we explore various shapes, with a special focus on polygons—closed figures formed by straight lines on a plane. We will learn about different types of polygons, their angles, and properties like convexity and regularity. By understanding these concepts, we can analyse and calculate the properties of shapes like triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, and more, which are essential for solving geometric problems.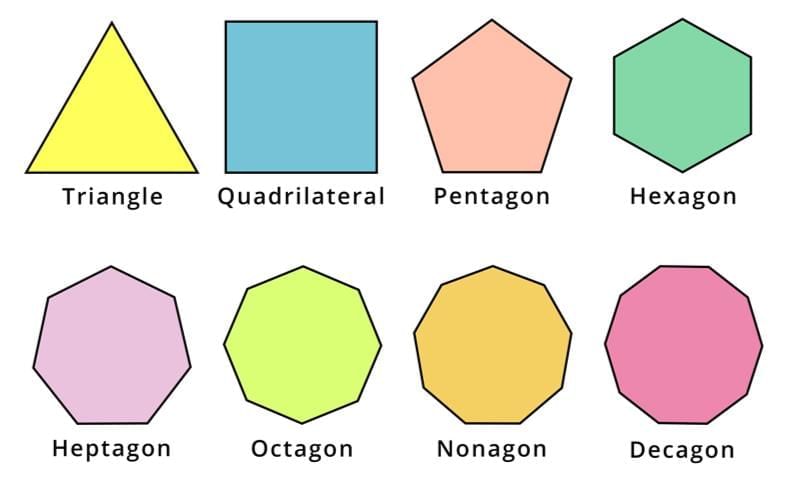
Key Points
- Geometry involves studying shapes drawn on a plane surface, like a sheet of paper.
- Shapes can be open or closed, formed by straight or curved lines.
- Polygons are special shapes that are closed and made of straight line segments.
- This chapter focuses on understanding polygons, their types, and their angle properties.
- Example: Draw different figures on a plane sheet, such as a circle, triangle, or pentagon. These shapes help us understand the difference between open, closed, curved, and straight-line figures.
Different Types of Curves
1. Open Curve: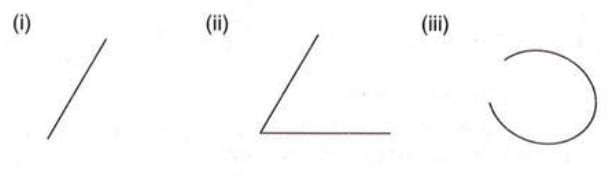
- An open curve is a line that does not connect at any point.
- It has two distinct endpoints and does not enclose any area.
- Example: A straight line segment or a single arc that does not join at any point, like a single slash (/), is an open curve.
2. Closed Curve:
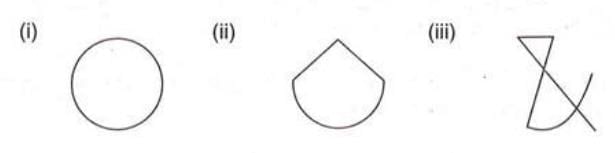 A closed curve is a line that connects at some point, forming a complete boundary.
A closed curve is a line that connects at some point, forming a complete boundary.- It encloses an area and has no endpoints.
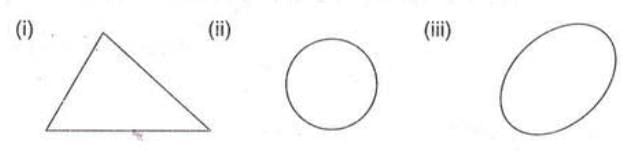
- Example: A circle or a shape like a loop that connects at one point is a closed curve.
3. Simple Closed Curve:
 A simple closed curve does not cross itself at any point.
A simple closed curve does not cross itself at any point.- It encloses a single area without any overlapping lines.
- A closed curve divides a plane into three parts:
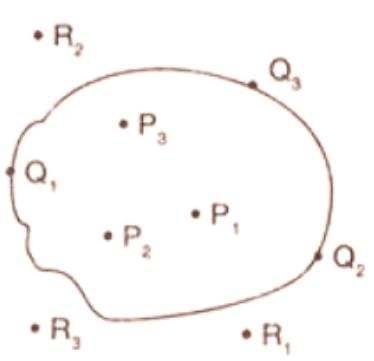
- Interior: Points inside the curve (e.g., P1, P2, P3).
- Boundary: Points on the curve itself (e.g., Q1, Q2, Q3).
- Exterior: Points outside the curve (e.g., R1, R2, R3).
- The interior and boundary together form the region of the curve.
- Example: A triangle or a circle, which does not cross itself and encloses an area, is a simple closed curve.
Polygon
- A polygon is a closed shape made of straight line segments on a plane.
- The line segments (sides) meet only at their endpoints, called vertices.
- Each vertex connects exactly two line segments.
- Conditions for a shape to be a polygon:
- It must be a closed figure.
- It must be made of straight line segments only.
- Line segments must meet only at their endpoints.
- Each endpoint (vertex) must connect exactly two segments.
- Polygons are named based on the number of sides:
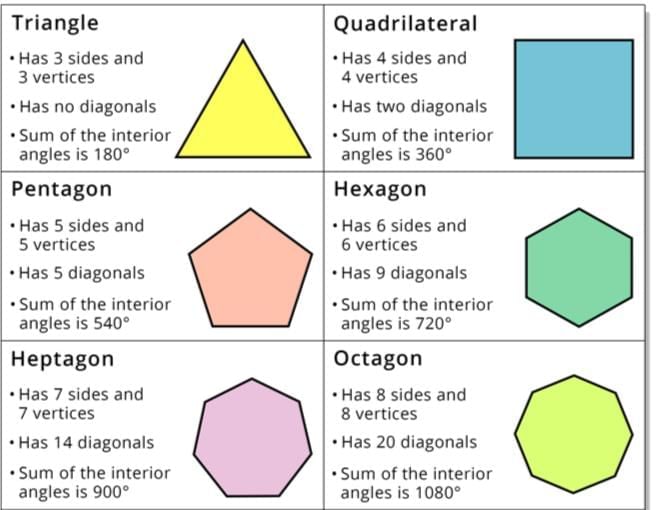
- Example: A shape with 5 straight sides, like ABCDE where A, B, C, D, and E are vertices and each side meets only at these points, is a pentagon (a polygon).
Types of Polygons
Polygons are named based on the number of sides they have, like a triangle (3 sides), a quadrilateral (4 sides), a pentagon (5 sides), etc.
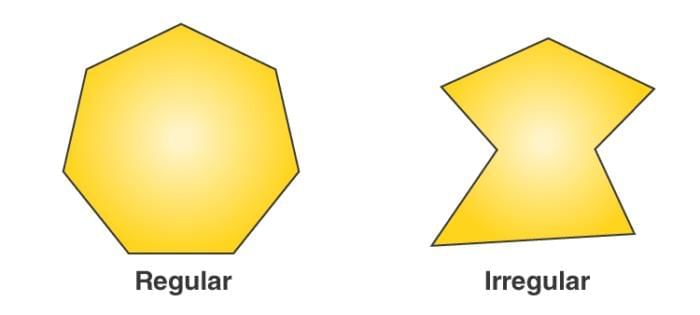
Polygons are classified into two main types: 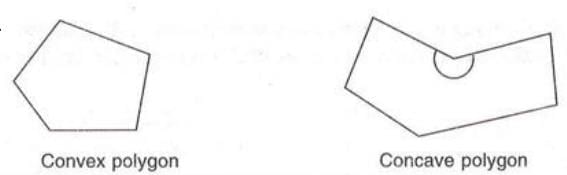
- Convex Polygon:
- A polygon where all interior angles are less than 180°.
- All vertices point outward, and no part of the shape bends inward.
- Example: A pentagon ABCDE where all angles (e.g., ∠A, ∠B, ∠C, ∠D, ∠E) are less than 180° is a convex polygon.
- Concave Polygon:
- A polygon with at least one interior angle greater than 180°.
- At least one vertex points inward, creating a "dent" in the shape.
- Example: A pentagon ABCDE with one angle, say ∠C, measuring more than 180° is a concave polygon.
Unless specified, a polygon is assumed to be convex.
Diagonal: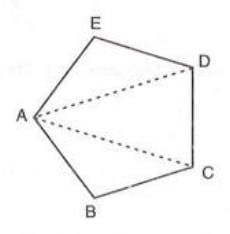
- A line segment connecting two non-consecutive vertices of a polygon.
- Example: In pentagon ABCDE, line segment AC joins non-consecutive vertices A and C, making it a diagonal. Similarly, BD is another diagonal.
Sum of Angles of a Polygon
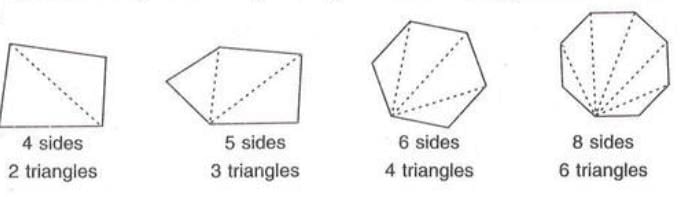
- To find the sum of interior angles, draw all possible diagonals from one vertex to divide the polygon into triangles.
- The number of triangles formed is always two less than the number of sides (n - 2).
- Each triangle has an angle sum of 180°.
- Therefore, the sum of the interior angles of a polygon with n sides is:
- (n - 2) × 180°
- Alternatively, (2n - 4) × 90° (since 180° = 2 × 90°).
- Example: For a quadrilateral (4 sides), the number of triangles = 4 - 2 = 2. Sum of interior angles = 2 × 180° = 360°. For a pentagon (5 sides), the number of triangles = 5 - 2 = 3, so the sum = 3 × 180° = 540°.
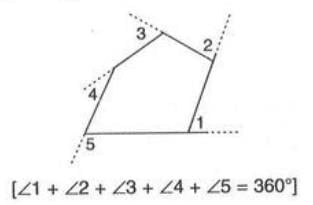
Sum of Exterior Angles of a Polygon
- Exterior angles are formed by extending each side of the polygon in one direction (produced in order).
- The sum of all exterior angles of any polygon is always 360° (4 right angles).
- This holds true regardless of the number of sides.
- "Produced in order" means extending each side in the same direction, like following a path around the polygon.
- Example: In a pentagon, if sides are extended in order, the exterior angles (e.g., ∠1, ∠2, ∠3, ∠4, ∠5) always sum to 360°, regardless of the pentagon’s shape.
Regular Polygon
- A regular polygon has:
- All interior angles are equal.
- All sides are equal in length.
- All exterior angles are equal.
- For a regular polygon with n sides:
- Sum of interior angles = (2n - 4) × 90°.
- Each interior angle = [(2n - 4) × 90°] / n.
- Sum of exterior angles = 360°.
- Each exterior angle = 360° / n.
- Number of sides (n) = 360° / (exterior angle).
- At each vertex: interior angle + exterior angle = 180° (forms a straight line).
- Example: If each interior angle of a regular polygon is 144°, then the exterior angle = 180° - 144° = 36°. Number of sides = 360° / 36° = 10. Thus, the polygon is a decagon.
Quadrilateral
A quadrilateral is a polygon with four sides, four vertices, four angles, and two diagonals.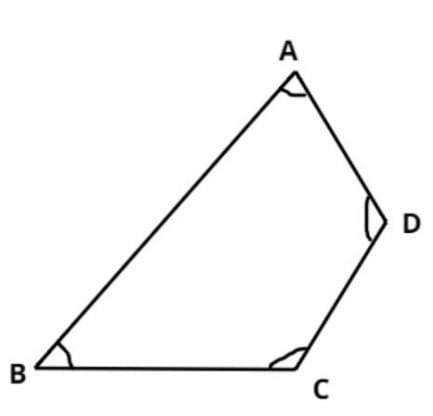 Quadrilateral Properties
Quadrilateral Properties
Properties
- Sides: AB, BC, CD, DA (for quadrilateral ABCD).
- Vertices: A, B, C, D.
- Angles: ∠ABC, ∠BCD, ∠CDA, ∠DAB.
Theorem 1: The sum of the angles of a quadrilateral is 360°.
- Proof: Draw diagonal AC, dividing quadrilateral ABCD into triangles ABC and ADC.
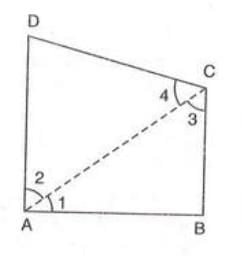
- Sum of angles in triangle ABC = ∠1 + ∠B + ∠3 = 180°.
- Sum of angles in triangle ADC = ∠2 + ∠D + ∠4 = 180°.
- Since ∠A = ∠1 + ∠2 and ∠C = ∠3 + ∠4, adding gives:
- (∠1 + ∠2) + ∠B + ∠D + (∠3 + ∠4) = 180° + 180° = 360°.
- Thus, ∠A + ∠B + ∠C + ∠D = 360°.
|
23 videos|98 docs|14 tests
|
FAQs on Understanding Shapes Chapter Notes - Mathematics Class 8 ICSE
| 1. What are the different types of curves? |  |
| 2. What are polygons and how are they classified? |  |
| 3. What is the formula for calculating the sum of angles in a polygon? |  |
| 4. How do you calculate the sum of exterior angles of a polygon? |  |
| 5. What is a regular polygon and can you give examples? |  |




















