Cheat Sheet: Indian Economy on the Eve of Independence | Economics Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Low Level of Economic Development |

|
| Agriculture Sector |

|
| Industrial Sector |

|
| Foreign Trade |

|
| Demographic Transition |

|
| Occupational Structure |

|
| Infrastructure |

|
| Conclusion |

|
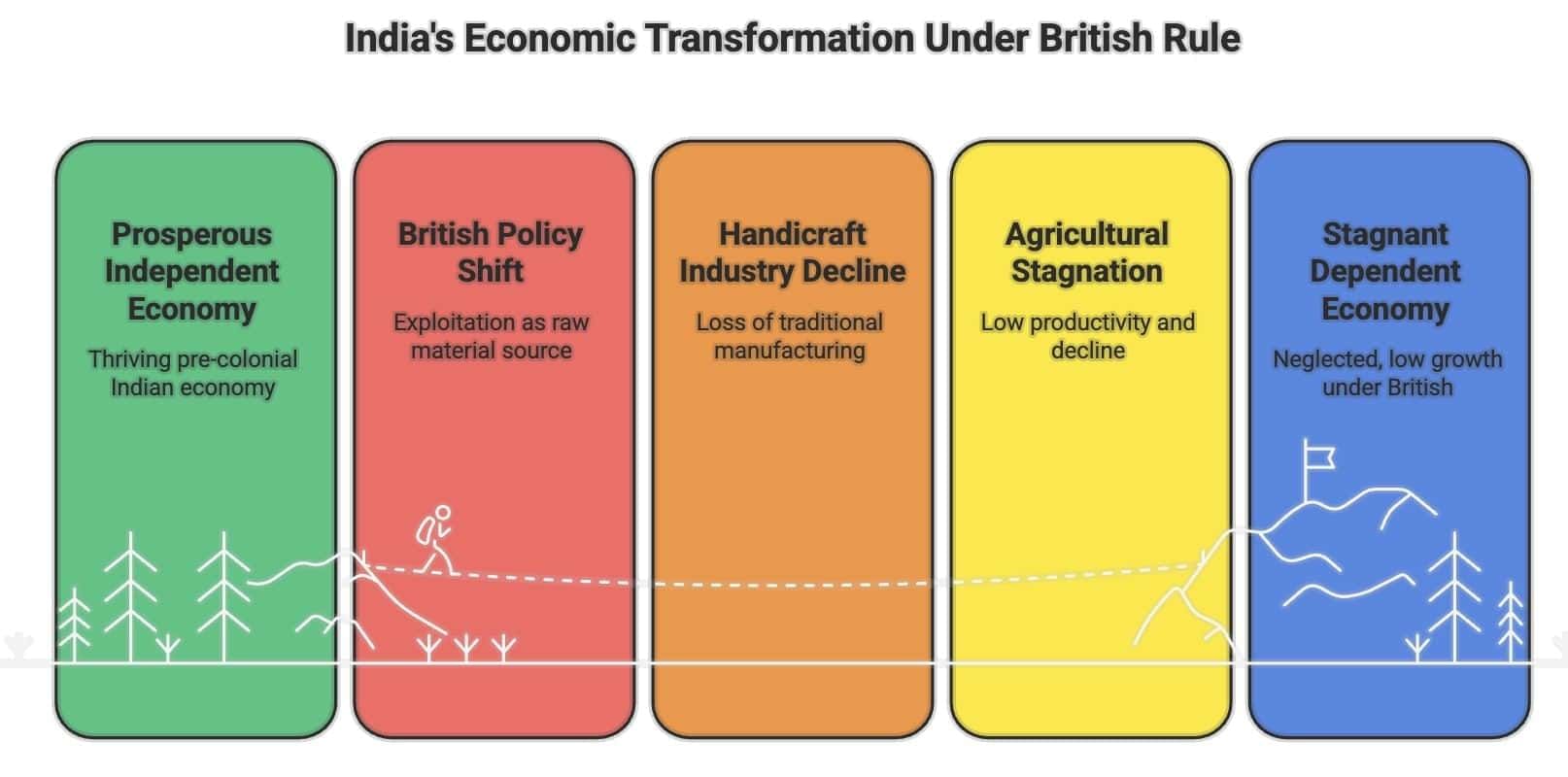
Low Level of Economic Development
- Pre-Colonial Economy: Independent, prosperous, with renowned handicrafts (e.g., cotton/silk textiles, metalwork, precious stones) and agriculture supporting most livelihoods.
- British Policy Objectives: Turn India into a raw material supplier for British industries and a market for British goods, causing de-industrialisation.
- Handicraft Decline: Collapse of industries like Dhaka’s Muslin without a modern industrial base replacement.
- Agricultural Stagnation: Despite 85% population reliance, agriculture faced decline and low productivity.
- Economic Growth: Overall output growth <2% (1900-1950), per capita output growth ~0.5% annually.
- Economists’ Estimates: Dadabhai Naoroji, William Digby, Findlay Shirras, V.K.R.V. Rao, R.C. Desai assessed national/per capita income due to British neglect.
Agriculture Sector
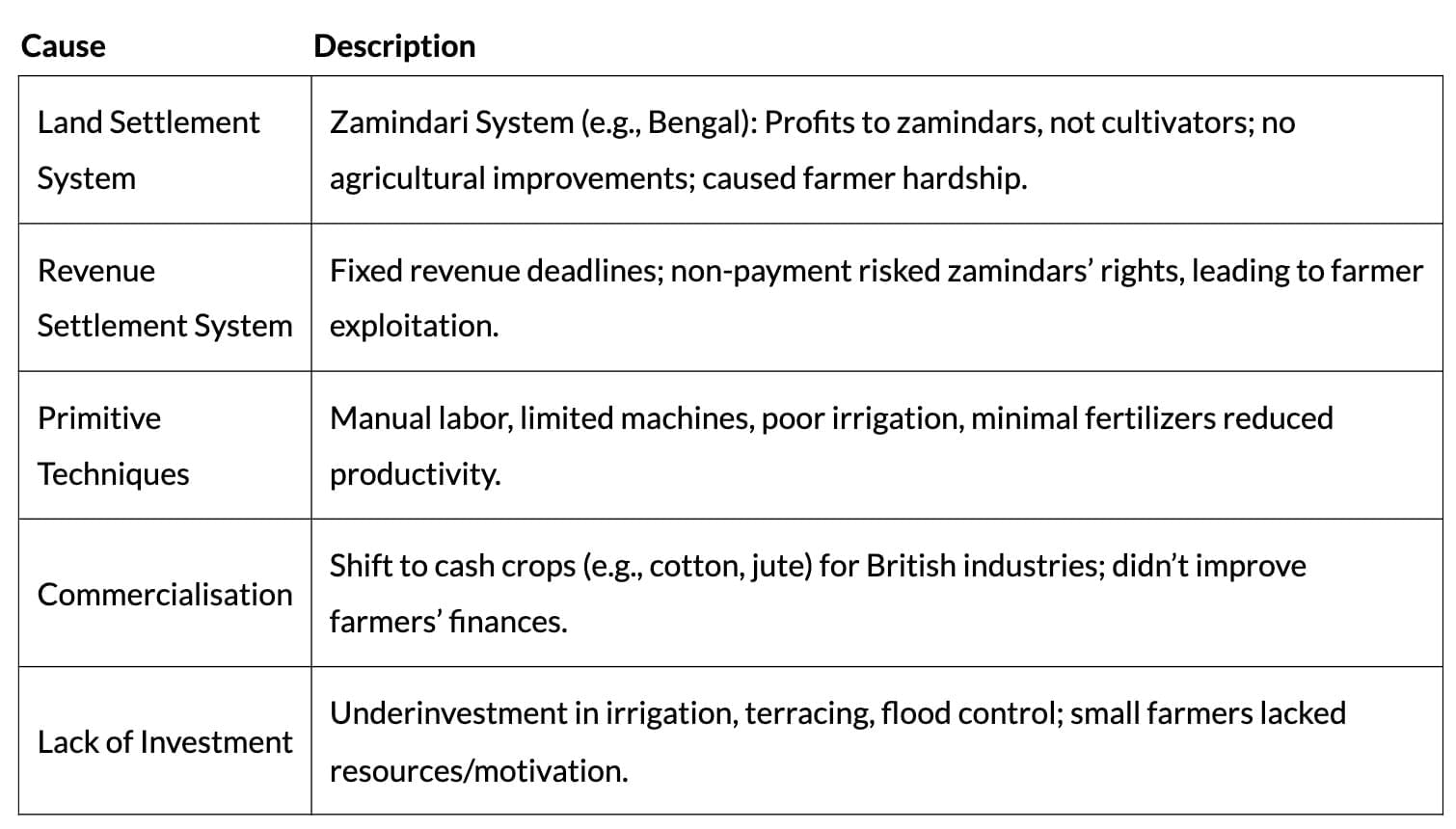
Overview: 85% population lived in villages, relied on agriculture, yet faced stagnation and low productivity.
Causes of Decline:
Industrial Sector
Overview: No sound industrial base developed due to British policies.
Key Issues:- Systematic Deindustrialisation: India as a raw material supplier and market for British goods.
- Handicraft Destruction: Collapse caused unemployment, increased demand for British imports.
- Slow Modern Industry Growth: Cotton mills (Indian-run, Maharashtra/Gujarat), jute mills (foreign-run, Bengal) emerged late 19th century; TISCO (1907) started iron/steel; sugar, cement, paper post-WWII.
- No Capital Goods Industry: Lack of machinery/tools production hindered growth.
- Low GDP Contribution: Minimal industrial sector growth and GDP impact.
- Limited Public Sector: Focused on railways, power, communications, ports; needed post-independence expansion.
Foreign Trade
Overview: Restrictive British policies reshaped India’s trade to benefit Britain.
Changes:- Composition: Exported primary products (e.g., raw silk, cotton, jute); imported finished goods (e.g., textiles, machinery).
- Direction: Over 50% trade with Britain; limited with China, Ceylon, and Persia.
- Volume: The Suez Canal (1869) increased trade by reducing transport costs.
- Structure: Large export surplus caused local shortages (e.g., food grains, clothing).
- Use of Surplus: Funded British offices, wars, invisible imports; drained Indian wealth.
Demographic Transition
Definition: Shift from high birth/death rates to low rates with development.
India’s Transition:- The first census (1881) showed uneven growth.
- Pre-1921: First stage (high birth/death rates).
- Post-1921: Second stage began; low population growth rate; 1921 called ‘Year of Great Divide.’
- Literacy: <16% overall, 7% for females.
- Health: Inadequate public facilities; high disease spread.
- Mortality: High, infant mortality ~218/1000 (vs. 33/1000 now).
- Life Expectancy: ~32 years (vs. 69 now).
- Poverty: Widespread, worsened population conditions.
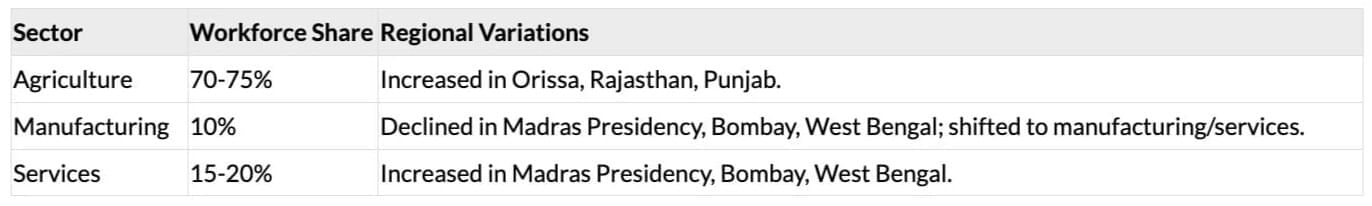
Occupational Structure
Infrastructure
Overview: Developed to serve colonial interests, not public welfare.
Key Features:- Roads: Built for army movement, raw material transport; lacked all-weather rural access, worsened during rains/famines.
- Railways (1850): Enabled long-distance travel, broke cultural barriers; commercialised agriculture, reducing village self-sufficiency; benefited Britain, not India.
- Waterways: Inland trade/sea lanes developed but uneconomical (e.g., Orissa’s Coast Canal abandoned).
- Post and Telegraph: Expensive telegraph for law/order; inadequate postal services.
- Tata Airlines (1932): Started the aviation sector.
- Modern education: Created a clergy class.
- Modern banking: Supported British administrative accounts.
Conclusion
By independence, British rule had left India’s economy weakened. Agriculture suffered from over-reliance and low productivity, handicrafts collapsed without a modern industry replacement, and trade favoured Britain, draining wealth. Infrastructure served colonial needs, not public welfare. Widespread poverty and unemployment underscored the need for a welfare-focused policy post-independence.
|
64 videos|308 docs|51 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: Indian Economy on the Eve of Independence - Economics Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What were the characteristics of the agriculture sector in India before independence? |  |
| 2. How did the industrial sector in India evolve prior to independence? |  |
| 3. What role did foreign trade play in India's economy before independence? |  |
| 4. How did India's demographic transition affect its economy prior to independence? |  |
| 5. What were the infrastructural challenges faced by India on the eve of independence? |  |




















