Cheatsheet: Averages & Percentages | General Aptitude for GATE - Mechanical Engineering PDF Download
Theory
Average (A) is the ratio between sum (S) of the quantities and the number (N) of quantities.
∴ A = S/N
⇒ S = A × N
Formula
Average
- The average of n-consecutive even integers or n-consecutive odd integers is equal to the middle number if n is odd.
- The average of n-consecutive even integers or n-consecutive odd integers is equal to the Average of middle two numbers if n is even.
Note: In the above case if the average is x the middle two numbers will be (x – 1) and (x + 1) respectively. - The average of a group of n-quantities is A. If one more quantity whose value is x is added to the group such that the average increases by ‘i’ then x = A + i × (n + 1)
Note: In the above case if there is a reduction in the average then take ‘i’ as negative. - The average of a group of n-quantities is A. If a quantity whose value is y is replaced by another quantity whose value is x such that the average increases by ‘i’. Then x = y +i×n
Note 1: If there is a reduction in average take ‘i’ as negative.
Note 2: The original average ‘A’ has no effect on the equation. - The average weight of a group of n-quantities is A but while taking the values one quantity ‘p’ is erroneously read as ‘q’. Then the actual average =
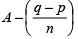
- The average of first n-positive integers
- The average of first n-positive even integers = n + 1
- The average of first n-positive odd integers = n
- The average of squares of first n-numbers
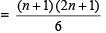
Percentage
- If any number is divided by 100 then it is called a percentage. It is denoted by radical sign%. ⇒ x% = x/100
∴ To get the fractional or decimal equivalent to a percentage divide the given number with 100. - If a number is increased by x% then the value after increase is given by
New Value (N.V) = (100 + x)% × Original Value (O.V) - If a number is successfully increased by x%, y% and z% respectively, then the final value is given by
Final Value (F.V) = (100 + x) % × (100 + y) % × (100 + z) % × Initial Value (I.V) - If a number is decreased or reduced by x% the value after reduction is given by
New Value (N.V) = (100 – x) % × Original Value (O.V) - If a number is successively decreased by x%, y% and z% respectively then the final value (F.V) is given by
Final Value (F.V) = (100 – x) % × (100 – y) % × (100 – z) % × Initial Value (I.V) - If there are two different values (one is greater and the other is smaller) then the greater value is more than the smaller one in terms of percentage is given by
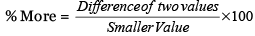
- In the above case the smaller one less than the greater one in terms of the percentage is given by
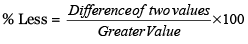
Tips
- To quickly calculate average of a list of items try to guess where the average is likely to lie. For e.g. for the list 34, 45, 67, 43, 78 the average is likely to be around 50. It does not matter what number you choose as long as it is easy to calculate the difference of the numbers with the given number.
- Then calculate the sum of the differentials around this assumed average.
- In this case the differentials are 34-50, 45-50, 67-50, 43-50, 78-50 i.e. -16, -5, 17, -7, 28. Thus the sum of the differentials= 17. The point here is that the different differentials cancel each other out and we get a sum close to zero.
- Then divide the sum of differentials by n and add it to the assumed average to get the real average.
- Hence, real average = 50 + 17/5 = 50 + 3.4 = 53.4.
- So if we have to calculate the average of 103, 102, 96, 99, 120 we can quickly calculate it as 100 + 20/5 = 104.
Solved Example
|
193 videos|169 docs|152 tests
|
















