Circles and its Properties | The Complete SAT Course - Class 10 PDF Download
Definition of a Circle
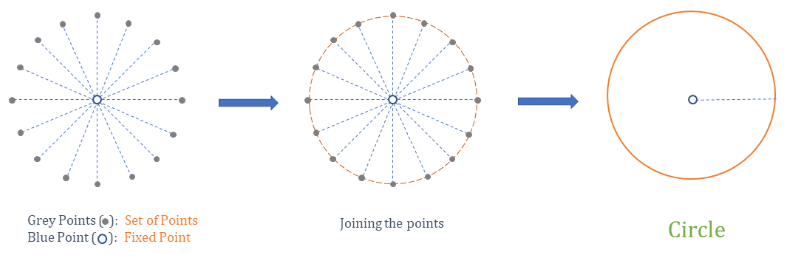
- When a set of all points that are at a fixed distance from a fixed point are joined then the geometrical figure obtained is called circle.
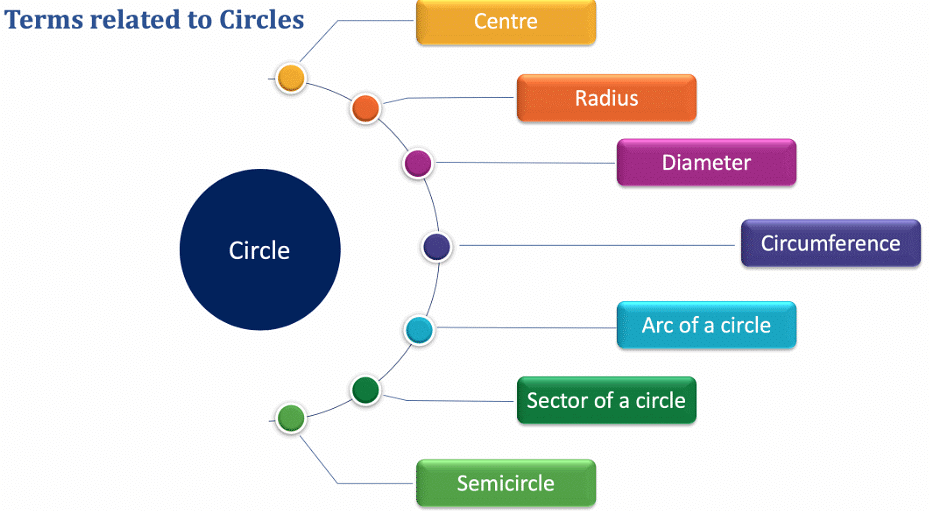
Terms related to Circles
 Center
Center
The fixed point in the circle is called the center.
- So, the set of points are at a fixed distance from the center of the circle.
Radius
- Radius is the fixed distance between the center and the set of points. It is denoted by “R”.
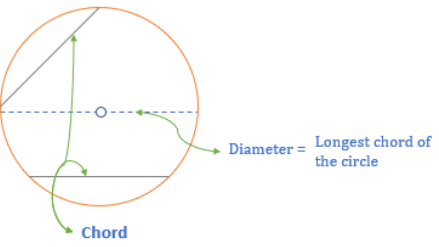
Diameter
- Diameter is a line segment, having boundary points of circles as the endpoints and passing through the center.
- So, logically a diameter can be broken into two parts:
- One part from one boundary point of the circle to the center
- And, the other part from the center to another boundary point.
- Hence, Diameter = Twice the length of the radius or “D = 2R”
Circumference
- It is the measure of the outside boundary of the circle.
- So, the length of the circle or the perimeter of the circle is called Circumference.
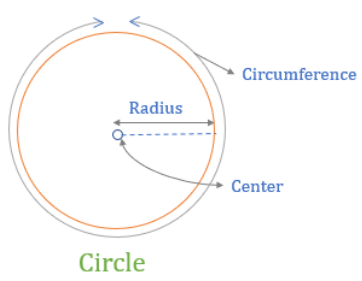
Arc of a circle
- The arc of a circle is a portion of the circumference.
- From any two-points that lie on the boundary of the circle, two arcs can be created: A Minor and a Major Arc.
- Minor arc: The shorter arc created by two points.
- Major Arc: The longer arc created by two points.
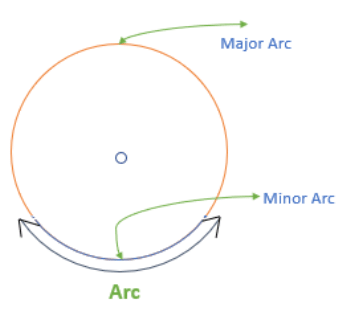 Sector of a circle:
Sector of a circle:
- A Sector is formed by joining the endpoints of an arc with the center.
- On joining the endpoints with the center, two sectors will be obtained: Minor and Major.
- By default, we only consider the Minor sector unless it is mentioned otherwise.
Semi-circle
- A semi-circle is half part of the circle or,
- A semi-circle is obtained when a circle is divided into two equal parts.
Important Properties of Circle – Lines
 Properties related to Lines in a Circle
Properties related to Lines in a Circle
Chord
- A chord is a line segment whose endpoints lie on the boundary of the circle.
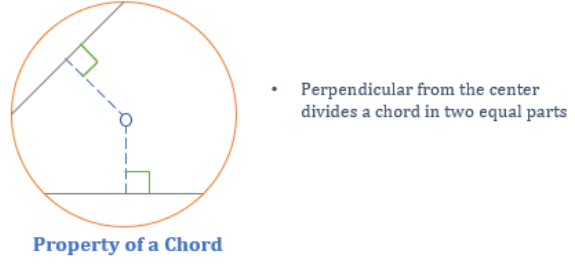
Properties of Chord
- Perpendicular dropped from the center divides a chord into two equal parts.
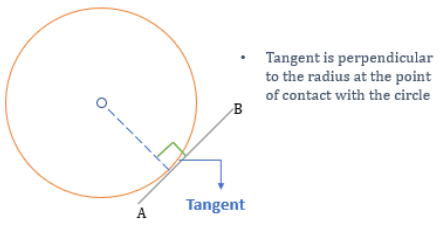
 Tangent
Tangent
- Tangent is a line that touches the circle at any point.
Properties of Tangent
- Radius is always perpendicular to the tangent at the point where it touches the circle.
Important Properties of Circle – Related to Angles
 Properties related to Angles in a circle
Properties related to Angles in a circle
Inscribed Angle
- An inscribed angle is the angle formed between two chords when they meet on the boundary of the circle.
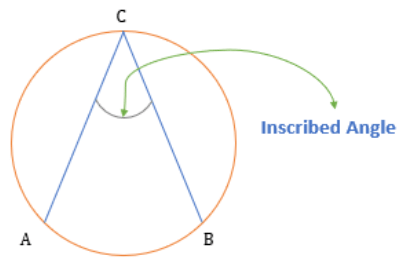
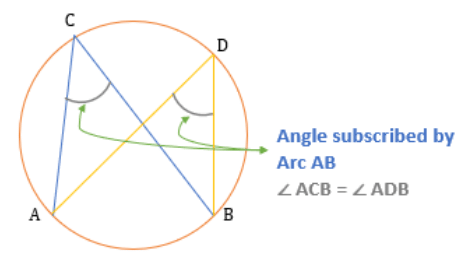
Properties of Inscribed Angles
- Angles formed by the same arc on the circumference of the circle is always equal.
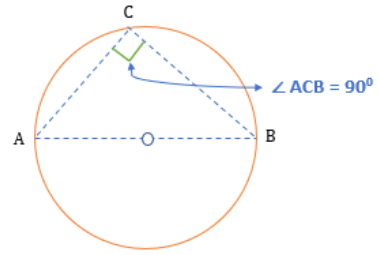
 The angle in a semi-circle is always 90°.
The angle in a semi-circle is always 90°.
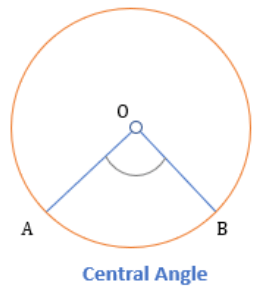
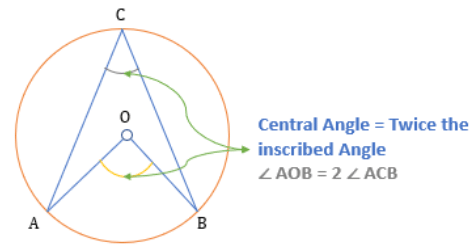
Central Angle
- A central angle is the angle formed when two-line segments meet such that one of the endpoints of both the line segment is at the center and another is at the boundary of the circle.
 Property of Central Angles
Property of Central Angles
- An angle formed by an arc at the center is twice the inscribed angle formed by the same arc.
Important Circle Formulas: Area and Perimeter
The following are some mathematical formulae that will help you calculate the area and perimeter/circumference of a circle.
Perimeter:
- Perimeter or the Circumference of the circle = 2 × π × R.
- Length of an Arc = (Central angle made by the arc/360°) × 2 × π × R.
Area:
- Area of the circle = π × R²
- Area of the sector =(Central angle made by the sector/360°) × π × R².
Example of Application of the properties
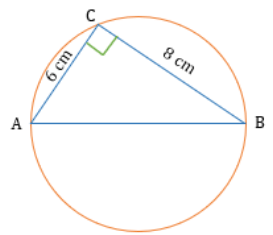
Example 1: The lengths of two sides in a right-angle triangle other than hypotenuse are 6 cm and 8 cm. If this right-angle triangle is inscribed in a circle, then what is the area of the circle?
(a) 5 π
(b) 10 π
(c) 15 π
(d) 20 π
(e) 25 π
Correct answer is option (e)
Step 1: Given
- The lengths of two sides other than hypotenuse of a right triangle are 6 cm and 8 cm.
- This triangle is inscribed in a circle.
Step 2: To find
- Area of the circle.
Step 3: Approach and Working out
- Let us draw the diagrammatic representation.
By applying the property that the angle in a semi-circle is 90º, we can say that AB is the diameter of the circle.
- And, once we find the length of the diameter, we can find the radius, and then we can find the area of the circle as well.
Applying Pythagoras theorem in △ ABC,
- AB² = AC² + BC²
- AB² = 6² + 8² = 36 +64 = 100
- AB = 10 cm
Since AB is the diameter, AB = 2R = 10
- Hence, R = 5 cm.
Area of the circle = π × R²= π × 5² = 25 π.
Hence, the correct answer is option E.
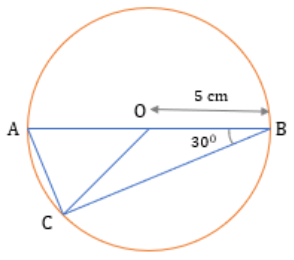
Example 2: In the diagram given below, O is the center of the circle. If OB = 5 cm and ∠ABC = 300 then what the length of the arc AC?
(a) 5π/6
(b) 5π/3
(c) 5π/2
(d) 5π
(e) 10π
Correct answer is option (b)
Step 1: Given
- OB = 5 cm
- ∠ABC = 30°
Step 2: To find
- Length of the arc
Step 3: Approach and Working out
- Length of the arc = (Central angle made by the arc/360°) × 2 × π × R.
To find the length of the arc, we need the value of two variable, the center angle made by the arc and the radius.
- We are already given radius as OB = 5cm
- We need to find the ∠AOC
On visualizing the diagram, the inscribed angle by the arc AC is ∠ABC, and the center angle by arc AC is ∠AOC.
- Hence, we can apply the property that the angle made at the center by an arc is twice the inscribed angle formed by the same arc.
- Thus, ∠AOC = 2 × ∠ABC = 2 × 30° = 60°
Now, we know the central angle formed by the arc as well.
- Hence, length of the arc AC =(Central angle made by the arc/360°) × 2 × π × R.
- =(60°/360°) × 2 × π × 5.
- =(1/6) × 2 × π × 5.
- =(5π/3) cm
Thus, the correct answer is option B.
|
433 videos|220 docs|166 tests
|