Class 10 Social Science: CBSE Sample Question Paper (2020-21) - 3 | Social Studies (SST) Class 10 PDF Download
Class - X
Social Science
TIME: 3 Hrs.
M.M: 80
General Instructions:
Read the following instructions very carefully and strictly follow them :
1. The question paper comprises five sections - A, B, C, D and E. There are 32 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
2. Section A - Question no. 1 to 16 are Objective Type Questions of 1 mark each.
3. Section B - Question no. 17 to 22 are Short Answer Type Questions, carrying 3 marks each. The answer to each question should not exceed 80 words.
4. Section C - Question no. 23 to 26 are Source Based Questions, carrying 4 marks each.
5. Section D - Question no. 27 to 31 are Long Answer Type Questions, carrying 5 marks each. The answer to each question should not exceed 120 words.
6. Section E - Question no. 32 is Map-Based, carrying 5 marks with two parts, 32.1 from History (2 marks) and 32.2 from Geography (3 marks).
7. There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in a few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions has to be attempted.
8. In addition to this, separate instructions are given with each section and question, wherever necessary.
Section A
Q.1. Which one of the following countries do not follow a dual or multi-party system? (1 marks)
(i) UK
(ii) China
(iii) India
(iv) USA
Ans. (ii) China
Explanation:
China follows a one-party system where only the Communist Party of China is allowed to rule. In India, a multi-party system is followed, where a number of parties, recognised as national parties contest for power while the UK and USA both follow the dual or biparty system where only two national parties are allowed to contest for power and the government is formed by one of the two.
Q.2. One way to find out if adults are undernourished is to calculate what nutrition scientists call body mass index (BMI). This is easy to calculate. Take the weight of the person in kg. Then take the height in metres. Divide the weight by the square of the height. If this figure is less than 18.5, then the person would be considered undernourished. However, if this BMI is more than 25, then the person is overweight.
After reading the source given above, mention one way to maintain a healthy BMI. (1 marks)
Ans. One way of maintaining a healthy/normal BMI is by taking a healthy diet that includes an appropriate amount of proteins, vitamins, carbohydrates and other nutrients.
Q.3. Quotas and taxes on imports are: (1 marks)
(i) Trade barriers
(ii) International agreements
(iii) Domestic revenue sources
(iv) All of the above
Ans. (i) Trade barriers
Explanation:
Governments can use trade barriers to increase or decrease (regulate) foreign trade. Since foreign trade is a source of foreign exchange, it is important to keep it profitable.
Q.4. ____________ crops are grown with the onset of monsoon in different parts of India. (1 marks)
Ans. Kharif crops
Explanation: Kharif crops are grown with the onset of monsoon in different parts of the country and these are harvested in September - October.
Q.5. ____________ is the main cause of land degradation in Punjab.
Ans. Over-irrigation
Explanation:
In states like Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra, overgrazing causes land degradation. In Punjab, Haryana, western Uttar Pradesh, over-irrigation is responsible for land degradation because waterlogging leads to an increase in the salinity and alkalinity of the soil, due to which the land becomes barren or loses its fertility.
Q.6. Which waterway connects the Brahmaputra River between Sadiya and Dhubri? (1 marks)
Ans. The waterway that connects the Brahmaputra River between Sadiya and Dhubri is National Waterway 2.
Q.7. How many zones are the Indian railways reorganised into?
Ans. The Indian railways is reorganised into 16 zones.
Q.8. The community government is elected by people belonging to one ___________ community. (1 marks)
Ans. Language
Explanation:
The concept of community government is prevalent in Belgium where people belonging to one language community: Dutch, French and German-speaking - no matter where they live-choose their government. This government has power regarding cultural, educational and language-related issues.
Q.9. ___________ is the system in which power is taken away from central and state governments and given to the local government.
Ans. Decentralisation
Explanation:
In terms of population, states in India are as large as the countries of Europe. For example - UP is bigger than Russia and Maharashtra is equal to Germany. This led to the introduction of the third tier of government called the local government. This was done to settle the issues and problems of our diverse and larger states which share power with their local bodies at village and town levels.
Q.10. Identify the name of the party from the symbol given in the picture. (1 marks)

Ans. The symbol represents the Communist Party of India (Marxist).
Q.11.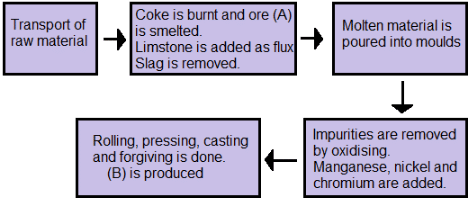
Based on this source, identify ore (A) used in the production process of the product (B) achieved as the final product. (1 marks)
Ans. (A) Iron ore
(B) Steel
Explanation: Iron ore, coking coal and limestone are required in the ratio of approximately 4:2:1 to produce steel. Manganese increases the strength, toughness and hardenability of steel. Chromium increases resistance and nickel is added to form corrosion-free and heat-resisting steel.
Q.12. What is the main purpose of the government behind setting up special economic zones in India? (1 marks)
Ans. The government’s main purpose behind setting up the Special Economic Zones (SEZs) is to attract foreign companies (multinational corporations) to invest in Indian companies and startups. This shall help us to build our credibility in the global market and expand our economy multi-folds.
Q.13. After primary and secondary, there is a third category of activities that falls under the tertiary sector and is different from the previous two. These are activities that help in the development of the primary and secondary sectors. Since these activities generate services rather than goods, the tertiary sector is also called the service sector. (1 marks)
Read the source above and identify which one of the following occupations cannot be classified under activities of the tertiary sector?
(i) Vegetable vendor
(ii) Basket weaver
(iii) Call centre employee
(iv) Courier
Ans. (ii) Basket weaver
Explanation:
A basket weaver does not provide a service to the consumers directly, he creates a product that is sold to the consumers. He makes a product from wood which is a secondary sector activity. All the other options of professionals are not involved in manufacturing any good, rather providing a service to increase consumer’s convenience.
Q.14. Suggest one way to prevent indiscriminate use of resources. (1 marks)
Ans. Resource planning accompanied with increased usage of renewable resources can save resources from diminishing.
OR
Define sheet erosion.
Ans. When surface water flows as a sheet over large areas down a slope without any obstruction in form of trees or plants, the topsoil is washed away. This is called sheet erosion.
Q.15. Correct the following statement and rewrite: (1 marks)
The Communist Party of India stands for the cause of reducing the interests and welfare of the Dalits and oppressed people.
Ans. The Bahujan Samaj Party of India stands for the cause of securing the interests and welfare of the Dalits and oppressed people.
Explanation:
The Communist Party of India was formed in 1925. It is an astringent observer and follower of Marxism-Leninism, secularism and democracy. It accepts parliamentary democracy as a means of promoting the interests of the working class, farmers and the poor.
The Bahujan Samaj Party was formed in 1984 under the leadership of Kanshi Ram. The party draws inspiration from the ideas and teachings of Sahu Maharaj, Mahatma Phule, Periyar Ramaswami Naicker and Babasaheb Ambedkar.
OR
Correct the following statement and rewrite: The parties that lose in the elections play the role of a political party.
Ans. The parties that lose in the elections play the role of the opposition party.
Q.16. What do you know about the Act of Union, 1707? (1 marks)
Ans. The Act of Union (1707) was signed between England and Scotland as a result of which the ‘United Kingdom of Great Britain’ came into being. After the Act was signed, England could impose its influence on Scotland.
Section B
Q.17. “British rule in India would have collapsed if Indians had not cooperated”. How did this statement help in starting a mass movement in India against British rule? (3 marks)
Ans. (i) Mahatma Gandhi declared that British rule was established in India with the cooperation of Indians and if Indians had refused to cooperate, British rule in India would have collapsed within a year.
(ii) He proposed that the movement should unfold in stages.
(iii) It should begin with the surrendering of titles that the government had awarded to the Indians.
(iv) A boycott of civil services, army, police, courts and legislative assemblies, schools and foreign goods would show their non-cooperation to the British empire.
(v) Gandhiji felt that in case the government used repression, a full civil disobedience campaign would be launched.
OR
Why did the Non- Cooperation Movement gradually slow down in the cities? Explain.
Ans. The Non- Cooperation Movement gradually slowed down the cities because:
(i) Khadi clothes were more expensive than mill clothes.
(ii) Poor people could not afford to buy it.
(iii) The boycott of British institutions posed a problem.
(iv) Students and teachers began trickling back to government schools.
(v) Lawyers joined back work in government courts.
Q.18. How did the Balkan region become a source of nationalist tension in Europe after 1871? (3 marks)
Ans. (i) The Balkans was a region of geographical and ethnic variations comprising modern-day Romania, Bulgaria, Albania, Greece, Macedonia, Croatia, Bosnia-Herzegovina, Slovenia, Serbia and Montenegro.
(ii) The inhabitants of these regions were known as Slavs.
(iii) A large part of the Balkans was under the control of the Ottoman Empire.
(iv) As the different Slavic nationalities struggled to define their identity and independence, the Balkan area became an area of intense conflict.
(v) The Balkan states were fiercely jealous of each other and each hoped to gain more territory at the expense of others.
Q.19. What is pipeline transportation? Write two merits and demerits of the same. (3 marks)
Ans. Pipeline transport network is the new mode of transport these days. In the past, pipelines were used to transport water to cities and industries. Now, these are used for transporting crude oil, petroleum products and natural gas from oil and natural gas fields to refineries, fertiliser factories and big thermal power plants. Solids can also be transported through a pipeline when converted into a slurry.
Merits:
(i) Useful in transporting liquids and solid slurry from faraway locations.
(ii) Subsequent running costs after laying down the network are minimal.
Demerits:
(i) Initial cost of laying pipelines is high.
(ii) Pipelines can burst or can have leakage leading to wastage of valuable resources like water, mineral oil, etc.
Q.20. “Sharing of powers makes a country more powerful and united”. Do you agree with this statement and why? (3 marks)
Ans. Power sharing is desirable in democracy because :
(i) Prudential reasons:
(a) It helps to reduce the possibility of conflict between social groups Since social conflict often leads to violence and political instability.
(b) It is a good way to ensure the stability of political order.
(c) Imposing the will of the majority community, over others may look like an attractive option in the short run, but in the long run it undermines the unity of the nation.
(ii) Moral reasons:
(a) Power sharing is the very spirit of democracy. A democratic rule involves sharing power with those affected by its exercise and who have to live with its effect.
(b) People have the right to be consulted on how they are to be governed.
(c) A legitimate government is one where citizens through participation, acquire a stake in the system.
Q.21. Evaluate the role of MNCs in the economic development of a country.
Ans. Role of MNCs in economic development: (3 marks)
(i) MNCs place order for production with small producers.
(ii) MNCs are setting up partnerships with local companies.
(iii) They are interlinking the markets all over the world.
(iv) Any other relevant point.
Q.22. “A wide-ranging choice of goods are available in the Indian markets”. Support the statement with examples in the context of Globalization. (3 marks)
Ans. A wide-ranging choice of goods :
(i) We have a wide variety of goods and services before us in the market.
(ii) The latest models of digital cameras, mobile phones and televisions made by leading manufacturers of the world are available in the market.
(iii) Every season, new models of automobiles can be seen on Indian roads.
(iv) Today Indians are buying cars produced by nearly all the top companies in the world.
(v) A similar explosion of brands can be seen for many other goods.
OR
Enumerate any three features of Multinational Corporations.
Ans. Multinational Corporations (MNCs) are the companies that own or control the production of their goods in more than one country.
The main features of MNCs are :
(i) They set up their factories and offices in more than one country.
(ii) They set up their units where the cost of production is low and higher profits can be earned.
(iii) They set up their units where they can get cheap labour and other resources.
Section C
23. Read the source given below and answer the following questions:
Like Germany, Italy too had a long history of political fragmentation. Italians were scattered over several dynastic states as well as the multi-national Habsburg Empire. During the middle of the nineteenth century, Italy was divided into seven states, of which only one, Sardinia-Piedmont, was ruled by an Italian princely house. The north was under Austrian Habsburgs, the centre was ruled by the Pope and the southern regions were under the domination of the Bourbon kings of Spain. Even the Italian language had not acquired one common form and still had many regional and local variations.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
23.1 During the mid- 19th century, Italy was divided into ________ states. (1 Mark)
(a) six
(b) seven
(c) eight
(d) nine
Ans. b
23.2 Which of the following part of Italy was ruled by an Italian princely house? (1 Mark)
(a) Rome
(b) Venetia
(c) Lombardy
(d) Sardinia-Piedmont
Ans. d
23.3 Who dominated the south regions of Italy? (1 Mark)
(a) Pope
(b) Bourbon Kings of Spain
(c) Austrian Habsburgs
(d) Bourbon Kings of France
Ans. d
23.4 Besides Italy, which of the following nation had a long history of political fragmentation? (1 Mark)
(a) Germany
(b) Britain
(c) USA
(d) Japan
Ans. a
24. Read the source given below and answer the following questions :
Tea cultivation is an example of plantation agriculture. It is also an important beverage crop introduced in India initiative by the British. Today, most of the tea plantations are owned by Indians. The tea plant grows well in tropical and sub-tropical climates endowed with deep and fertile well-drained soil, rich in humus and organic matter. Tea bushes require a warm and moist frost-free climate all through the year. Frequent showers evenly distributed over the year ensure continuous growth of tender leaves. Tea is a labour-intensive industry. It requires abundant, cheap and skilled labour. Tea is processed within the tea garden to restore its freshness. Major tea-producing states are Assam, hills of Darjeeling and Jalpaiguri districts, West Bengal, Tamil Nadu and Kerala. Apart from these, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Meghalaya, Andhra Pradesh and Tripura are also tea-producing states in the country. In 2015 India was the second-largest producer of tea after China.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
24.1 Who introduced tea cultivation in India? (1 Mark)
(a) German
(b) British
(c) French
(d) Dutch
Ans. b
24.2 Which of the following states is the largest producer of tea? (1 Mark)
(a) Assam
(b) West Bengal
(c) Uttarakhand
(d) Kerala
Ans. a
24.3 Tea bushes require ________ and moist frost-free climate all through the year. (1 Mark)
(a) cold
(b) warm
(c) moderate
(d) None of these
Ans. b
24.4 Which of the following countries was the largest producer of tea in 2015? (1 Mark)
(a) China
(b) India
(c) USA
(d) Sri Lanka
Ans. a
25. Read the source given below and answer the following questions:
What about subjects that do not fall in any of the three lists? Or subjects like computer software that came up after the constitution was made? According to our Constitution, the Union Government has the power to legislate on these 'residuary' subjects. We noted above that most federations that are formed by 'holding together' do not give equal power to their constituent units. Thus, all States in the Indian Union do not have identical powers. Some States enjoy a special status. Jammu and Kashmir have its own Constitution. Many provisions of the Indian Constitution are not applicable to this State without the approval of the State Assembly. Indians who are not permanent residents of this State cannot buy land or house here. Similar special provisions exist for some other States of India as well.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
25.1 Which of the following subjects comes under 'residuary' subjects? (1 Mark)
(a) Education
(b) Trade
(c) Banking
(d) Computer software
Ans. d
25.2 Which of the following states has its own Constitution? (1 Mark)
(a) Uttar Pradesh
(b) Jammu & Kashmir
(c) Andhra Pradesh
(d) Kerala
Ans. b
25.3 Who has the power to legislate on 'residuary' subjects? (1 Mark)
(a) Central Government
(b) State government
(c) Community government
(d) Local government
Ans. a
25.4 Indians who are not permanent residents of ________ cannot buy land or house here. (1 Mark)
(a) Kerala
(b) Assam
(c) Jammu & Kashmir
(d) Bihar
Ans. c
26. Read the source given below and answer the following questions :
Kanta works in an office. She attends her office from 9.30 a.m. to 5.30 p.m. She gets her salary regularly at the end of every month. In addition to the salary, she also gets provident fund as per the rules laid down by the government. She also gets medical and other allowances. Kanta does not go to the office on Sundays. This is a paid holiday. When she joined work, she was given an appointment letter stating all the terms and conditions of work.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
26.1 The passage given above relates to which of the following options? (1 Mark)
(a) Primary sector
(b) Organised sector
(c) Organised sector
(d) Secondary sector
Ans. b
26.2 When does Kanta not go to her office? (1 Mark)
(a) On Saturday
(b) On Monday
(c) On Sunday
(d) On Friday
Ans. c
26.3 Besides salary, Kanta gets __________ as per the rules laid down by the government. (1 Mark)
(a) provident fund
(b) emergency fund
(c) free meal
(d) house rent
Ans. a
26.4 What was Kanta given, when she joined work? (1 Mark)
(a) Appointment letter
(b) Advance salary
(c) Leave
(d) Gift
Ans. a
Section D
Q.27. Who had organized the Dalits into the 'Depressed Classes Association' in 1930? Describe his achievements. (5 marks)
Ans. Depressed Classes Association was organized by Dr B. R. Ambedkar in 1930.
Achievements:
(i) Dr B. R. Ambedkar raised the demand for a separate electorate for Dalits.
(ii) British government conceded Ambedkar's demand for separate electorates for Dalits.
(iii) The depressed classes got reservation of seats in provincial and Central Legislative Councils.
(iv) Ambedkar accepted Gandhiji's position and as the result, Poona Pact was signed.
(v) Any other relevant point.
Detailed Answer:
Dr B. R. Ambedkar had organized the Dalits into the "Depressed Classes Association" in 1930. Following were his achievements :
(i) Dr B. R. Ambedkar organized the Dalits into the Depressed Classes Association because he wanted Dalits to get a share in the political power.
(ii) He clashed with Gandhiji in the Second Round Table Conference. He demanded a separate electorate for the Dalits.
(iii) He signed the Poona Pact with Gandhiji and got a reservation of seats for the Dalits in legislatures.
OR
Explain with examples the role of Industrialists in the freedom struggle of India.
Ans. (i) They lent their support to Congress in protest against the colonial policies that restricted indigenous business enterprises.
(ii) They also gave financial assistance and refused to buy or sell foreign goods. They formed associations like the Indian Industrial and Commercial Congress in 1920 and FICCI in 1927.
(iii) They viewed Swaraj as freedom from the domination of the market by foreign goods but withdrew their support when the Second Round Table Conference failed.
(iv) They were also concerned about the rise of the socialist ideology in Congress.
(v) Purshottamdas Thakurdas and G.D. Birla attacked colonial control over the Indian economy.
Q.28. Describe the role of technology in promoting the globalization process. (5 marks)
Ans. Technology in promoting globalization process.
Rapid improvement in technology has stimulated the globalization process.
(i) This has made much faster delivery of goods across long distances possible at lower costs.
(ii) Even more remarkable have been the developments in information and communication technology.
(iii) Technology in the areas of telecommunications, computers, the Internet has been changing rapidly.
(iv) Telecommunication facilities (telegraph, telephone including mobile phones, fax) are used to contact one another around the world, to access information instantly, and to communicate from remote areas.
(v) This has been facilitated by satellite communication devices.
Q.29. Name the national political party which gets inspiration from India’s ancient culture and values. Mention four features of that party. (5 marks)
Ans. 'Bharatiya Janata Party' (BJP) gets inspiration from India's ancient culture and values.
Four important features:
(i) Cultural nationalism or 'Hindutva' is an important element in its conception of Indian nationhood and politics.
(ii) The party wants full territorial and political integration of Jammu and Kashmir with India.
(iii) A uniform civil code for all people living in the country irrespective of religion and a ban on religious conversions.
(iv) Its support base increased substantially in the 1990s.
Q.30. “Democracy has failed to reduce economic inequality and poverty ”. Do you agree? Give arguments in support of your answer. (5 marks)
Ans. In actual life, democracies do not appear to be reducing inequalities.
(i) The poor constitute a large proportion of our voters and no party likes to lose their votes, yet democratically elected governments have not addressed the question of poverty as one would have expected them to.
(ii) The people in several poor countries are now dependent on rich countries even for food supplies.
Arguments in support:
(i) It enhances the dignity of the individuals.
(ii) It improves the quality of decision-making.
(iii) It provides a method to resolve conflicts.
OR
“Democracy stands much superior to any other form of government in promoting dignity and freedom of the individual”. Justify this statement.
Ans. Democracy stands much superior to any other form of government in promoting dignity and freedom of the individual -
(i) Every individual wants to receive respect from fellow beings.
(ii) The passion for respect and freedom is the basis of democracy.
(iii) Democracy in India has strengthened the claims of the disadvantaged and discriminated groups for equal status and equal opportunities.
(iv) It provides methods to resolve conflicts.
(v) Any other relevant point.
Q.31. Explain any five factors that are responsible for the concentration of iron and steel industries mainly in the Chhota Nagpur Plateau region. (5 marks)
Ans. Concentration of iron and steel industries in Chhota Nagpur Plateau Region:
(i) High-grade raw material in proximity.
(ii) Availability of labour.
(iii) Raw materials, as well as finished goods, are heavy and bulky containing heavy transport cost.
(iv) Road and rail transport facilities are available.
(v) Vast growth potential in the home market.
(vi) Low-cost iron ore.
Detailed Answer:
The factors responsible for the concentration of iron and steel industries in and around the 'Chhota Nagpur Plateau Region' are as follows :
(i) Low cost of iron ore. Iron mines are located in nearby areas.
(ii) High-grade raw materials in proximity and other bulky raw materials like coking coal, limestone are also available in proximity.
(iii) From the adjoining areas of Bihar, Jharkhand and Odisha, cheap labour is available in abundance.
(iv) This region is well connected with roadways and railways that help in the swift movement of raw materials and finished goods to the industry and market areas, respectively.
(v) Kolkata is a well-developed port that is near to this area.
OR
How can the industrial pollution of freshwater be reduced? Explain various ways.
Ans. Control of industrial pollution of freshwater:
(i) Minimizing the use of water for processing by reusing.
(ii) Harvesting of rainwater to meet the water requirement.
(iii) Treating hot water and effluents before releasing them in rivers and ponds.
(iv) Regulation of the use of groundwater by industries.
(v) Installing water treatment plants at the industrial sites for recycling.
(vi) Any other relevant points to be explained.
Detailed Answer:
After Independence, the number of industries has been increasing at a rapid pace and this has become a reason for pressure on existing fresh water resources. Freshwater is almost limited, though renewable in India, but overexploitation and mismanagement of this resource by industries are aggravating the water stress day-by-day.
(i) Industries, especially heavy industries, use a huge amount of fresh water for industrial purpose and pollute and waste such water.
(ii) These industries, for their energy requirements, depend on hydroelectric projects and this electricity is generated through the construction of dams in the rivers' upstream. So, the river almost dries up in the lower stream areas.
(iii) Again, industries dump the chemical waste in the rivers, lakes, etc., which then consequently pollutes the water dangerously for human survival. These also contaminate the groundwater through seepage of industrial wastes. So, the increasing number of industries exerts pressure on existing fresh water resources.
Section E
Map-Based Questions
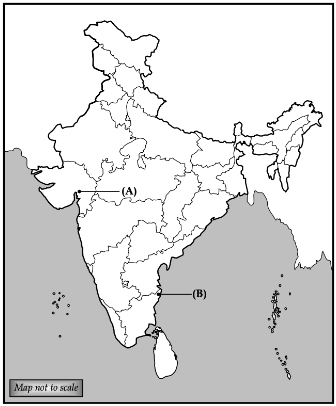
Q.32.
(i) Two places (A) and (B) are marked on the given political outline map of India. Identify them and write their correct names on the lines drawn near them.
(A) The place which is known for Peasant Satyagraha. (1 Mark)
(B) The place where the Congress Session was held in 1927. (1 Mark)
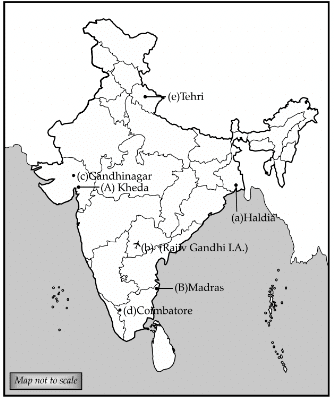
(ii) On the same outline map of India, locate and label any three of the following with appropriate symbols:
(a) Haldia: Major Seaport
(b) Rajiv Gandhi: International Airport
(c) Gandhinagar: Software Technology Park
(d) Coimbatore: Cotton Textile Industry
(e) Tehri: Dam (3 Mark)
 Ans. (i) & (ii)
Ans. (i) & (ii)
|
66 videos|614 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Social Science: CBSE Sample Question Paper (2020-21) - 3 - Social Studies (SST) Class 10
| 1. What is the format of the CBSE Sample Question Paper for Class 10 Social Science (2020-21)? |  |
| 2. How can I prepare for the Class 10 Social Science exam based on the CBSE Sample Question Paper? |  |
| 3. Are the questions in the CBSE Sample Question Paper for Class 10 Social Science aligned with the actual exam? |  |
| 4. Can I rely solely on the CBSE Sample Question Paper to prepare for the Class 10 Social Science exam? |  |
| 5. How can I effectively utilize the CBSE Sample Question Paper for Class 10 Social Science to improve my performance in the exam? |  |
















