Class 11 Economics Short Questions With Answers (Part - 1) - Introduction to Micro Economics
Q.1. Explain how scarcity and choice go together.
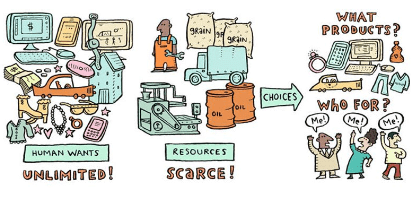 Human wants are unlimited but resources are scarce
Human wants are unlimited but resources are scarce
Ans. Scarcity and choice are closely linked concepts in economics, influencing human behaviour significantly.
- Resources are limited, forcing individuals to make choices about their use.
- Everyone, regardless of wealth, faces scarcity; even the richest must manage their time effectively.
- This relationship means that scarcity necessitates choice, as we cannot have everything we want.
Q.2. What gives rise to an economic problem?
Ans
- Scarcity of Resources: Limited availability of resources relative to unlimited wants and needs.
- Unlimited Wants and Needs: Human desires for goods and services are virtually limitless.
- Alternative Uses of Resources: Resources can be used in different ways, leading to opportunity costs and trade-offs.
Q.3. What is meant by the economic problem?
Ans. The economic problem arises from the limited availability of resources compared to our endless wants and needs. Key aspects include:
- Scarcity: Resources are finite while desires are infinite.
- Choice: Societies must decide how to allocate resources effectively among competing needs.
- Opportunity Cost: Choosing one option means forgoing another, highlighting the cost of decisions.
- Resource Allocation: This involves determining what to produce, how to produce it, and for whom.
Understanding these elements is crucial for grasping how economies function in terms of production, consumption, and distribution.
Q.4. Why is economic problem regarded as a problem of choice?
Ans.
Scarcity necessitates choice: Limited resources relative to unlimited wants require decisions on resource allocation.
Opportunity cost: Every choice involves trade-offs, meaning the value of the next best alternative is lost.
Trade-offs: Decision-making requires prioritizing among alternatives, considering benefits and costs.
Decision-making process: Options are assessed based on personal preferences and priorities.
Limited resources, unlimited wants: Inability to satisfy all desires necessitates choosing which to fulfill and which to forgo.
Q.5. Why do problems related to allocation of resources in an economy arise? Explain.
Ans.
- Scarcity: Resources are limited while wants are unlimited, leading to the need for efficient allocation.
- Competition: Individuals, firms, and governments compete for scarce resources, complicating allocation.
- Diverse Needs: Different sectors and individuals have varying needs, requiring prioritisation in allocation.
- Changing Demands: Economic conditions and consumer preferences evolve, necessitating adjustments in resource distribution.
- External Factors: Environmental constraints and global events can disrupt resource availability, adding to allocation challenges.
Q.6. What are the main tools of economic analysis?
Ans.
- Mathematical Models: Use equations to represent economic relationships and analyse data.
- Graphical Analysis: Visual tools like graphs to illustrate concepts such as supply and demand.
- Statistical Methods: Techniques to analyse economic data, identifying patterns and trends.
- Optimization Techniques: Methods to maximise or minimise economic objectives under constraints.
- Econometric Models: Combine economic theory with empirical data to estimate relationships and make predictions.
Q.7. What is positive economics?
Ans. Positive economics is a branch of economics that focuses on describing and explaining economic phenomena using factual data.
- Objective Analysis: It examines what is happening in the economy without making value judgments.
- Empirical Testing: This approach relies on evidence and observation to test economic theories.
- Predictive Power: The aim is to accurately predict economic outcomes based on observable data.
Q.8. What is normative economics?
Ans. Normative economics involves making value judgments about economic policies and outcomes. It focuses on what should be done in the economy based on subjective beliefs.
- Prescription: It recommends actions for economic improvement.
- Subjective Analysis: It includes opinions and moral principles in evaluating policies.
- Policy Recommendations: It guides how resources should be allocated.
- Value-Based: Normative statements reflect beliefs about fairness and social welfare.
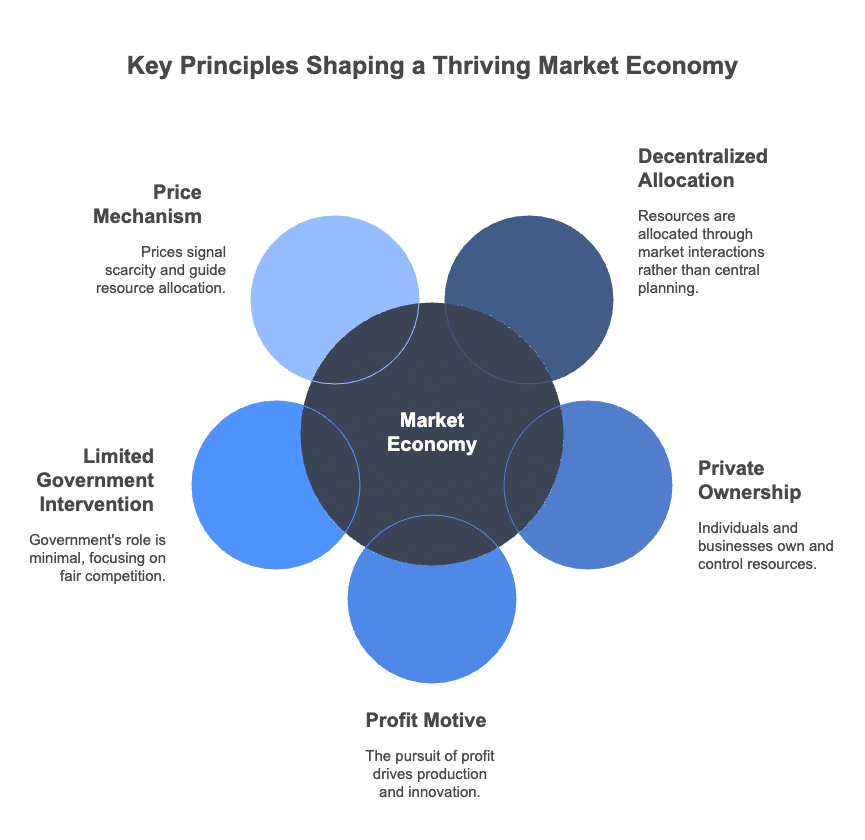
Q.9. What is a market economy?
Ans.
Decentralised Allocation: A market economy is characterized by decentralized decision-making, where resources are allocated through the interaction of supply and demand in markets.
Private Ownership: Most resources, such as land, labor, and capital, are owned and controlled by individuals and businesses rather than the government.
Profit Motive: Participants in a market economy are driven by the pursuit of profit, which serves as a key incentive for production and innovation.
Limited Government Intervention: Government intervention in a market economy is typically minimal, with regulations focused on ensuring fair competition and protecting property rights.
Price Mechanism: Prices play a crucial role in coordinating economic activities, signaling information about scarcity and guiding resource allocation decisions.
|
59 videos|222 docs|43 tests
|
FAQs on Class 11 Economics Short Questions With Answers (Part - 1) - Introduction to Micro Economics
| 1. What is microeconomics? |  |
| 2. What are the key concepts in microeconomics? |  |
| 3. How does microeconomics differ from macroeconomics? |  |
| 4. Why is microeconomics important? |  |
| 5. How does microeconomics relate to everyday life? |  |