Class 12 Economics Solved Paper (2012 Outside Delhi Set-II) | Additional Study Material for Commerce PDF Download
Ques 1: Explain the central problem of 'how to produce'.
Ans: A number of methods are available to a producer for producing a good. First a producer decides how he should combined all factors in producing a commodity. A producer will use that combination or technique of production where the cost is minimum. This is the central problem of how to produce in an economy.
Ques 2: A farmer takes a farm on rent and carries on farming with the help of family members. Identify explicit and implicit costs from this information. Explain.
Ans:
(i) In the given example, the farmer carries on farming with the help of family members. If these members had worked elsewhere they would have earned wages.
Therefore, the imputed expenditure incurred on the wages of family members is implicit cost.
(ii) The farmer takes the farm on rent. Therefore, the expenditure incurred on rent (input) is explicit cost.
Ques 3: Define a budget line. When can it shift to the right?
Ans:
A budget line graphically shows the many combinations of two goods which a consumer can buy, given his entire income and the prices of the two goods. A budget line, as shown in the diagram is a straight line having a negative slope.
There will be a shift in the budget line towards right when:
(1) Income of the consumer increases, prices of both the goods given, as shown in Diagram (i)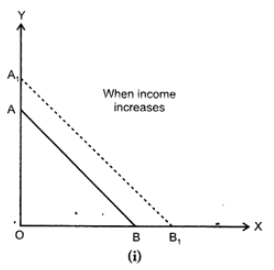
(2) Price of either of the two commodities or of both of commodities fall, as shown in Diagram (ii). 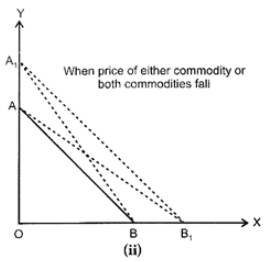
Ques 4: A consumer buys 14 units of a good at a price of Rs. 8 per unit. At price Rs. 7 per unit he spends Rs. 98 on the good. Calculate price elasticity of demand by the percentage method. Comment upon the shape of demand curve based on this information.
Ans:
Price (Rs.) | Q (Units) | Total Expenditure (Rs.) |
8 | 14 | 112 |
7 | 14 | 98 |
P = 8, P1= 7, = 14, Q1= 14
ΔP =78=1,ΔQ=1414=0
Therefore, the shape of demand curve will be perfectly inelastic.
Ques 5:
Find Gross Value Added at Factor Cost: | ||
(i) | Unit of output sold | 2,000 |
(ii) | Price per unit of output (Rs) | 20 |
(iii) | Depreciation (Rs) | 2,000 |
(iv) | Change in stock (Rs) | (-) 500 |
(v) | Intermediate costs (Rs) | 15,000 |
(vi) | Subsidy (Rs) | 3,000 |
Ans:
Gross Value Added at Factor Cost
= (Units of output sold × Price per unit of output) + Change in stock - Intermediate costs + Subsidy
= [(i) × (ii)] + (iv) - (v) - (vi)
=(2,000× 20)+(−500)−15,000+3,000
=40,000+3,000−15,500=Rs. 27,500
Ques 6: Find National Income from the following:
Autonomous Consumption = Rs. 100
Marginal propensity to consume = 0.60
Investment = Rs. 200
Ans: Given: Autonomous Consumption (a) = 100
MPC (b) = 0.60
Investment (I) = 200
∴ Income (Y)=a+bY+I
=100+0.6Y+200
⇒ (Y−0.6)=100+200=300
⇒ Y (0.4) = 300
⇒ Y = 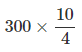
∴ Y=Rs. 750
Therefore National Income is Rs 750.
Ques 7: Giving reason, explain how should the following be treated while estimating national income:
(i) Expenditure on free services provided by government.
(ii) Payment of interest by a government firm.
Ans:
(i) It should be included because it is a government final consumption expenditure.
(ii) It should not be included because it is an intermediate cost.
Ques 8:
Find out (a) National Income | ||
(Rs. crore) | ||
(i) | Net imports | (-)10 |
(ii) | Net domestic fixed capital formation | 100 |
(iii) | Private final consumption expenditure | 600 |
(iv) | Consumption of fixed capital | 60 |
(v) | Change in stocks | (-)50 |
(vi) | Government final consumption expenditure | 200 |
(vii) | Net factor income to abroad | 20 |
(viii) | Net current transfers to abroad | 30 |
(ix) | Net indirect tax | 70 |
(x) | Factor income from abroad | 10 |
Ans:
(a) National Income
= Private final consumption expenditure + Government final consumption expenditure + [Net domestic fixed capital formation + Change in stocks] - Net imports - Net factor income to abroad - Net indirect tax
= (iii) + (vi) + [(ii) + (v)] - (i) - (vii) - (ix)
=600+200+[100+(−50)]1−(−10)−20−70
=800+100−50+10−90=910−140= Rs 770 crores
|
4 videos|168 docs
|
















