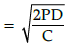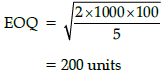Class 12 Entrepreneurship: CBSE Sample Question Paper- Term II (2021-22)- 1 | Sample Papers for Class 12 Commerce PDF Download
Class - XII
Time: 120 Minutes
Max. Marks: 35
General Instructions:
- The paper is divided into 3 Sections.
- Section-wise overall choice is given to the students.
- Section A (2 markers) has 6 questions. Attempt any 4 out of 6.
- Section B (3 markers) has 5 questions. Attempt any 4 out of 5.
- Section C (5 markers) has 4 questions. Attempt any 3 out of 4.
Section - A
Q.1. Pink & Blue Store sells 1000 insulated water bottles annually. Demand for the product is uniform. Purchase cost per bottle is ₹ 50. Holding cost per annum is 10% of purchase cost. Ordering cost is ₹ 100 per order. Calculate the Economic Ordering Quantity for bottles.
Economic Ordering Quantity
Thus as : Annual demand (D) = 1,000 bottles
Order cost (P) = ₹ 100
Annual carrying cost of 1 unit (C/i) = 10% × ₹ 50 = ₹ 5
Q.2. Identify and explain the method of raising additional finance from existing shareholders by offering securities to them on pro-rata basis.
Rights issue is a method of raising additional finance from existing shareholders by offering securities to them on pro-rata basis i.e. giving them a right to a certain number of shares in proportion to the shares they are holding. Normally, through a circular, rights issues are proposed to the existing shareholders and in case they are not willing to subscribe, they can renounce the same in favour of another person. This method of issuing securities is considered to be inexpensive as it does not require any brokers, agents, underwriters, prospectus or enlistment, etc.
Q.3. ‘Winber Motors Ltd.’ was a car dealer. It took over a car manufacturing plant ‘Speed Cart & Co., and started a new business in the name of ‘Unique Cart Ltd.’ to synergize and capture a major share of the market and to maximize their profits. Like their competitors, they decided to sell their cars through company appointed dealers (retailers) in various parts of the country. This type of distribution network will enable the company to retain control over the distribution process. Identify and give the meaning of this type of enterprise growth opportunity.
Acquisition: Acquisition is a corporate action in which a company buys most,if not all, of the target company's ownership stakes in order to assume control of the target firm. Acquisitions are often made as part of a company's growth strategy whereby it is more beneficial to take over an existing firm's operations and niche compared to expanding on its own. Acquisitions are often paid in cash, the acquiring company's stock or a combination of both. An acquisition, also known as a takeover, is buying of one company (the target) by another.
Q.4. Evaluate the pricing strategy which permits different rates to be extended to different customers for the same goods or services.
Variable price method: Variable pricing is a marketing approach that permits different rates to be extended to different customers for the same goods or services. The approach is often employed in cultures where dickering over the price of goods is considered the norm, or potential buyers are allowed to participate in a bidding situation, such as in an auction. Even in countries where fixed pricing is the standard, variable pricing may come into play when the customer is committing to the purchase of large volumes of goods or services. When this is the case, the customer must usually comply with specific criteria in order to enjoy pricing that varies from the standard cost.
Q.5. What is product franchise business opportunity? How is it different from manufacturing franchise opportunity?
In product franchise business opportunity manufacturers use the product franchise to govern how a retailer distributes his products. The manufacturer grants a store owner the authority to distribute goods by the manufacturer and allows the owner to use the name and trade mark owned by the manufacturer. The store owner must pay a fee or purchase a minimum inventory of stock in return for these rights. Some tire stores are good examples of this type of franchise. Whereas manufacturing franchise opportunity provides an organization with the right to manufacture a product and sell it to the public, using the franchisor's name and trademark. This type of franchise is found most often in the food and beverage industry. Most bottlers of soft drinks receive a franchise from a company and must use its ingredients to produce, bottle and distribute the soft drinks.
Q.6. Enlist any four objectives of advertising.
The objective of advertising is to increase profit by increasing sales. Advertising aims to:
(i) Make business and product name familiar to the public.
(ii) Create goodwill and build a favourable image.
(iii) Educate and inform the public.
(iv) Offer specific products or services.
(v) Attract customers to find out more about your product or service.
Section - B
Q.7.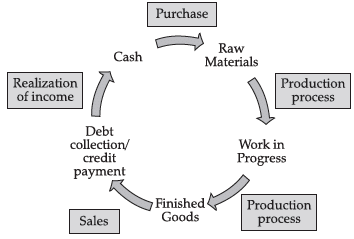
(i) Identify the type of diagram represented above.
(i) The diagram represents Operating cycle or the cash conversion cycle (CCC).
(ii) Analyse why different products will have different operating cycles.
(ii) Different products will have different operating cycles. If the conversion takes longer time
then the cycle will be longer. For trading, where there is no manufacturing (or conversion), the operating cycle will be shorter. Longer the operating cycle, working capital quantum is more; shorter the cycle, less working capital is needed.
Q.8. Calculate working capital of Raja & Co. which has the following items in its Balance sheet:
Stock — ₹ 50,000;
Trade creditors – ₹ 32,000;
Debtors – ₹ 75,000;
Cash – ₹ 1,00,000;
Dividend payable – ₹ 50,000;
Tax – ₹ 44,000;
Short term loan – ₹ 61,000;
Short term investments – ₹ 76,000.
Calculate gross and net working capital.
Total Current Assets = Debtors + Stock + Cash + Short term investment
Total Current Assets = (₹ 75000 + ₹ 50,000 + ₹ 1,00000 + ₹ 76,000)
Total Current Assets = ₹ 3,01,000
Total Current Liabilities = Sundry Creditors + Dividend Payable + Tax + Short Term loan)
Total Current Liabilities = (₹ 32,000 + ₹ 50,000 + ₹ 44,000 + ₹ 61,000) = ₹ 1,87,000
Gross Working Capital = Total Current Assets
Gross Working Capital = Total Current Assets = ₹ 3,01,000
Net Working Capital = Total Current Assets – Total Current Liabilities
= ₹ 3,01,000 – ₹ 1,87,000 = ₹ 1,14,000
Thus, Gross Working Capital = ₹ 3,01,000
Net Working Assets = ₹ 1,14,000
Q.9. What are the qualities of a good brand name?
A good brand name should basically possess qualities of distinctiveness. It should have the capability to stand out amongst a host of competing names. Thus, in selecting a brand name, entrepreneur should ask himself/herself what he/she wants to achieve from it. While selecting a brand name, entrepreneur should choose a name which is:
(i) Short, simple and easy to pronounce.
(ii) Noticeable, easy to recognize and remember.
(iii) Pleasing, impressive when uttered.
(iv) Neither obscene, negative, offensive or vulgar.
(v) Adaptable to packaging, labelling requirements, to different advertising media and languages.
(vi) Linked to product, symbolically eye catching.
(vii) Contemporary, capable of being registered and protected legally.
Q.10. Explain in brief the three ways in which an organisation can expand externally.
The three ways in which an organisation can expand externally are:
(i) Franchising: Franchising is as "an arrangement whereby the manufacturer or sole distributor of a trade marked product or service gives exclusive rights of local distribution to independent retailers in return for their payment of royalties and conformance to standardized operating procedures". The person offering the franchise is known as the franchisor. The franchisee is the person who purchases the franchise and is given the opportunity to enter a new business with a better chance to success than if he or she were to start a new business from scratch. Foundation of this relationship is the Franchise Agreement. A franchise agreement is the legal document that binds the franchisor and franchisee together.
(ii) Mergers: A merger is a combination of two companies into one larger company. This action involves stock swap or cash payment to the target. In merger, the acquiring company takes over the assets and liabilities of the merged company. All the combining companies are dissolved and only the new entity continues to operate. In general, when the combination involves firms that are of similar size, the term, consolidation, is applied. When the two firms differ significantly by size, the term merger is used. Merger commonly takes two forms. In the first form amalgamation, two entities combine together and form a new entity, extinguishing both the existing entities. In the second form absorption, one entity gets absorbed into another.
(iii) Acquisitions: A corporate action in which a company buys most, if not all, of the targetcompany's ownership stakes in order to assume control of the target firm. Acquisitions are
often made as part of a company's growth strategy whereby it is more beneficial to take over
an existing firm's operations and niche compared to expanding on its own. Acquisitions are
often paid in cash, the acquiring company's stock or a combination of both. An acquisition, also known as a takeover, is the buying of one company (the target) by another.
Q.11. Identify the technique of sales promotion used in the below given situations.
(i) Monica took her sister Poonam for shopping to ‘Diva’ to buy her a dress on the occasion of her birthday. She was delighted when on payment for the dress, she got a discount voucher to get 20% off for a meal of ₹ 500 or above at a famous eating joint.
(i) Useable benefits is the technique of sales promotion used by the company in the given
situation. Under this method, coupons are distributed among the consumers on behalf of the
producer. Coupon is a kind of certificate telling that the product mentioned therein can be
obtained at special discount. It means that if a customer has a coupon of some product he will
get the discount mentioned therein whenever he buys it. Possession of a coupon motivates the consumer to buy the product, even when he has no need of it.
(ii) Tanu took her friend Veena for shopping to ‘Mega Stores’ to buy her a hand bag for her birthday. She was delighted when on payment of the hand bag she got a wallet along with the hand bag free of cost.
(ii) Product combination is the technique of sales promotion used by the company in the given situation. Under this method, along with the main product some other product is offered to the customer as a gift, say offer of a pack of ½ kg of rice with the purchase of a bag of Aatta (wheat flour), or ‘Get 128 KB Memory Card Free with a Digicam’ or Buy a TV of 25+ and Get a Vacuum Cleaner Free’ or ‘100 gm Bottle of Sauce Free with 1 kg Detergent.’
(iii) An Air Purifier company is engaged in manufacturing of air conditioners and desert coolers. The company offers a wide range of products to meet the requirements of people from varied income groups. Recently the company has developed a new product, an air purifier that improves the quality of air by filtering out all allergens and microbes. The company introduced the product on two variants namely ‘Puro Tech’ and ‘Puro Tech Premium’. In order to persuade people to buy the product it is offering easy payment options in equal monthly installments for different time periods. Moreover, every buyer will be offered ‘scratch a card’ option to win instant gifts like decorative items, T-shirts, etc.
(iii) Instant draws and assured gifts is the technique of sales promotion used by the company in the given situation. Under this method, a customer is asked to scratch a card on the purchase of a product and the name of the product is inscribed thereupon which is immediately offered to the customer as a gift. For example, on buying a car when the card is scratched such gifts are offered – TV, Refrigerator, Computer, Mixer, Dinner Set, Wristwatch, T-shirt, Iron Press, etc.
Section - C
Q.12. Who are Angel Investors? State any four features of Angel Investors.
Business angel or informal investor or an angel investor, is an affluent individual who provides capital for a business start-up and early-stage companies usually in exchange for convertible debt or ownership equity.
Four features of Angel Investors are:
(i) Most angel investors are current or retired executives, business owners or high net worth individuals who have the knowledge, expertise, and funds that help start-ups match up to industry standards.
(ii) As angel investors bear extremely high risk and are usually subject to dilution from future investment rounds. They expect a very high return on investment.
(iii) Apart from investing funds, most angels provide proactive advice, guidance, industry connections and mentoring start-ups in its early days.
(iv) Their objective is to create great companies by providing value creation, and simultaneously helping investors realize a high return on investments.
(v) They have a sharp inclination to keep abreast of current developments in a particular business arena, mentoring another generation of entrepreneurs by making use of their vast experience.
Q.13. ‘Ganpati Steel Ltd.’ is a large and creditworthy company manufacturing steel for the Indian market. It now wants to cater to the Asian market and decides to invest in new hi-tech machines. Since the investment is large, it requires long-term finance. The company decided to raise funds through the capital market.
40% of the funds will be raised directly from the public through the issue of prospectus. 40% of the shares will be directly sold to a limited number of sophisticated investors. 20% of the shares will be offered to the employees.
Identify the methods of flotation of new issues used by the company. Also state one benefit of each method. The issue was very well accepted by the investors. Mr. Raman, an investor could not get shares allotted when the offer was made to the public. He wishes to invest in the company. State the option available to him now and how will it benefit Raman?
40% of the funds will be raised directly from the public through the issue of prospectus - IPO. The primary advantage an entrepreneur stands to gain by going public is access to capital.
40% of the shares will be directly sold to a limited number of sophisticated investors - Private
Placement. This method is useful at times when the company does not wish to disclose information to the open market.
20% of the shares will be offered to the employees - Offer to employees - Benefit: Higher efficiency Raman can go to the Secondary market/ Stock exchange and buy shares. Benefit – This market imparts liquidity to the long term securities held by investors by providing an auction market for these securities.
Q.14. Read the following article from a business newspaper and answer the following questions:
“Fone India Ltd. is the second largest mobile network operator in India by subscriber base, after Virel.
Huber Evel Ltd (HEL) was another leading mobile operator in India. In the year 2007, Fone India Ltd., acquired 52 % stake in HEL. Fone India’s main motive in going for the deal was its strategy of expanding into emerging and high growth markets which will lead to improved profitability in the business.”
(i) Quoting the lines from the passage identify and explain reasons for taking up a stake by Fone India Ltd.,
(i) “deal was its strategy of expanding into emerging and high growth markets”: Entry into new markets: a company can enter the market avoiding too much competition.
“lead to improved profitability in the business”—Improved profitability: The acquisition will
lead to increased profits for the firm.
(ii) Also explain any three reasons apart from the one identified in part (i).
(ii)
(a) Synergy: Synergy between the participating firms determines the increase in value of thecombined entity.
(b) Acquiring new technology: By buying another company with unique technology, the
buying company can maintain or develop a competitive edge.
(c) Acquiring a competency: To acquire a competency or capability that they do not have.
(d) Access to funds: The newly acquired company can be cash rich which will help both the
firms.
(e) Tax benefits: If a loss making company is being acquired, it can lead to reduction in tax
liabilities.
Q.15. Explain the factors affecting channels of distribution with relation to market considerations.
(i) Number of buyers: If the number of buyers is large then it is better to take the services of middlemen for the distribution of the goods. On the contrary, the distribution should be done by the manufacturer directly if the number of buyers is less.
(ii) Types of buyers: Buyers can be of two types: General Buyers and Industrial Buyers. If more buyers of the product belong to the general category then there can be more middlemen. But in the case of industrial buyers there can be less middlemen.
(iii) Buying habits: A manufacturer should take the services of middlemen if his financial position does not permit him to sell goods on credit to those consumers who are in the habit of purchasing goods on credit.
(iv) Buying quantity: It is useful for the manufacturer to rely on the services of middlemen if the goods are bought in smaller quantities.
(v) Size of market: If the market area of the product is scattered fairly, then the producer must take the help of middlemen.
|
130 docs|5 tests
|
FAQs on Class 12 Entrepreneurship: CBSE Sample Question Paper- Term II (2021-22)- 1 - Sample Papers for Class 12 Commerce
| 1. What is the syllabus for Class 12 Entrepreneurship exam? |  |
| 2. How many marks are allotted for the Class 12 Entrepreneurship exam? |  |
| 3. What is the duration of the Class 12 Entrepreneurship exam? |  |
| 4. Are there any sample question papers available for the Class 12 Entrepreneurship exam? |  |
| 5. What are some important topics to focus on for the Class 12 Entrepreneurship exam? |  |