Class 12 Geography Solved Paper (2017 Delhi Set-III) | Geography for Grade 12 PDF Download
Ques 1: Write any two features of rectangular rural settlement pattern in the world.
Ans: The features of rectangular rural settlements pattern are:
(i) Roads cut each other at right angles.
(ii) They are found in plains and valleys.
Ques 2: Which state of India has the highest percentage of population below poverty line?
Ans: Odisha (Orissa) is the state of India which has highest percentage of population below poverty line.
Ques 3: Which type of roads provides maximum links in India?
Ans: Rural roads and districts roads provide maximum links in India.
Ques 4: Explain any three points of distinction between 'Hamleted rural settlements' and 'Dispersed rural settlements of India'.
Ans:
S. No. | Hamleted Rural Settlement | Dispersed Rural Settlement |
1. | Compact settlement are normally found in fertile plains or river valleys. | Dispersed Settlement are normally found in mountainous highland ridges, forested areas and desert and semi desert. |
2. | Main occupation is agriculture. | Main occupation is cattle rearing, lumbering etc. |
3. | The houses are located adjacent to each other and from a compact block. They are comparatively small in size and provide less living space. | The houses are located at a distance from each other. They are comparatively bigger and provide more living space. |
4. | Fields in compact settlements are small. | Fields in dispersed settlements are large. |
5. | Streets are generally dirty due to lack of sanitation. | Dispersed settlement are normally neat and clean. |
6. | People live together and lead social life. | People lead isolated life since house are at a distance. |
Ques 5: Describe any five features of planation agriculture practised in different regions of the world.
Ans: Main features of plantation agriculture practiced in different regions in the world:
(i) Plantation agriculture was introduced in the tropical lands by Europeans and North Americans primarily in the colonies ruled by them.
(ii) Plantation crops are coffee, tea, banana, sugarcane, pine apples etc.
(iii) Estate for plantation are of very large size, sometimes running into the thousands of hectares.
(iv) It requires large capital investments, managerial and technical support and scientific method of cultivation.
(v) The labour are supplied by local peole at cheaper rates while technical and skilled assistance comes from tem-perate lands.
(vi) Cheap transport is required to link the estates with factories and markets for export of products.
Ques 6: Explain any five factors responsible for the development of 'Gujarat Industrial Region'.
Ans: Gujarat Industrial Region: The nucleus of this region lies between Ahmedabad-Vadodara as a result is also known as Ahmedabad-Vadodara Industrial region. The main features of growth of this region are:
(i) This region extends up to Valsad and Surat in the South and Jamnagar in the West.
(ii) This region is associated with cotton growing tracts with location of textile industries.
(iii) With discovery of oil and gas in Gulf of Khambat area led to the establishment of various oil refineries and petrochemicals around Ankleshwar, Vadodara and Jam Nagar.
(iv) Kandla port provides the basic infrastructure for import and exports.
(v) Developent of other heavy and basic chemicals, dyes, pesticides, engineering machinery, textile machinery, pharmaceuticals and dairy products have developed in this region.
(vi) Surat has best diamond cutting and processing units in the world.
(vii) Due to better roads and highways, transport facilities are available aplenty.
Ques 7: What is age structure? Interpret with example the triangular shaped age-sex pyramid.
Ans: Age structure is the number of people of different age group.
(i) Generally the population is categorised into three broad age groups:
(a) children,
(b) adults and
(c) aged.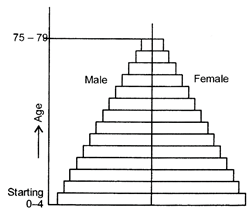 (ii) Most countries of Africa, Asia and Latin America have high birth rate and they have large size population in the lower age group. Countries having low birth rate and high life expectancy have more people in old age groups.
(ii) Most countries of Africa, Asia and Latin America have high birth rate and they have large size population in the lower age group. Countries having low birth rate and high life expectancy have more people in old age groups.
(iii) If we draw a triangular shaped pyramid having wide base and taper top this is a typical diagram to show age and sex structure of populations. The base and apex-represent younger and oldest age groups respectively.
(iv) This triangular pyramid is typical of less developed countries like Nigeria m Africa., Bangladesh, in Asia and Mexico in South -America.
(v) Wide base means high birth rates.
(vi) Tapered top indicates high death rates.
|
168 docs|32 tests
|
FAQs on Class 12 Geography Solved Paper (2017 Delhi Set-III) - Geography for Grade 12
| 1. What are the main topics covered in the Class 12 Geography Solved Paper (2017 Delhi Set-III) exam? |  |
| 2. How can I prepare effectively for the Class 12 Geography exam based on the 2017 Delhi Set-III paper? |  |
| 3. What are some useful tips for answering the map work questions in the Class 12 Geography Solved Paper (2017 Delhi Set-III) exam? |  |
| 4. Are there any specific chapters or topics from the Class 12 Geography syllabus that are frequently asked in the exam based on the 2017 Delhi Set-III paper? |  |
| 5. Can I rely solely on the Class 12 Geography Solved Paper (2017 Delhi Set-III) for my exam preparation? |  |
















