Class 5 Maths Chapter 2 HOTS Questions - Chapter 2 - Shapes and Angles
Q1: In the given figure,
If ∠AOB=∠BOC=∠COD=38∘,
find reflex angle ∠AOC and reflex angle ∠AOD.
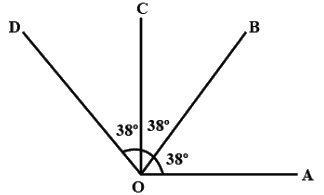 Sol: Given, ∠AOB = ∠BOC=∠COD = 38∘.
Sol: Given, ∠AOB = ∠BOC=∠COD = 38∘.
Now, ∠AOC = ∠AOB +∠BOC
= 38∘ + 38∘
= 76∘
⇒∠AOC = 76∘
Then, reflex angle ∠AOC = 360∘ − 76∘
= 284∘ .
Now, ∠AOD = AOB + ∠BOC + ∠COD
=38∘ + 38∘ + 38∘
=114∘
⇒∠AOD = 114∘ .
Then, reflex angle ∠AOD=360∘ − 114∘
=246∘ .
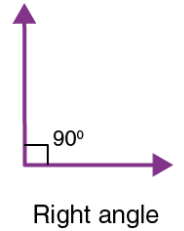
Q2: Look at the angle in the picture and choose the correct option

(a) Right angle
(b) Less than Right angle
(c) More than Right angle
(d) None of these
Ans: (a)
Sol: As evident from the picture in qn., it can be seen that the angle is less than 90∘ or right angle.
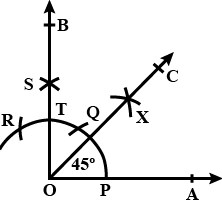
Q3: Construct the following angle with the help of ruler and compasses only: 45∘
Sol: To construct an angle of 45∘, construct an angle of 90∘ and bisect it.
⇒ Procedure to draw ∠90∘
Draw a ray OA.
With a convenient radius and centre at O, draw an arc cutting the ray OA at P.
With the same radius and centre at P, draw another arc, which cuts the first arc at Q.
With the same radius and centre at Q, draw another arc, which cuts the first arc at R.
With Q and R as centres and radius more than half of QR, which cuts each other at S.
Draw OS and extend it to B from the ray OB.
∠AOB is required angle of 90∘ .
After constructing the ∠AOB=90∘ , rays OA and OB intersect the arc at points P and T as shown in figure.
With P and T as centers and radius more than half of PT, draw two arcs, which cut each other at X.
Draw OX and extend it to C to form the ray OC.
∠AOC is the required angle of 45∘ .
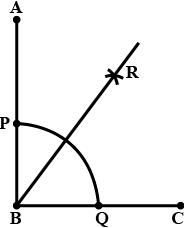
Q4: Using a protractor, draw a right angle and bisect it to get an angle of measure 45∘ .
Sol: We are asked to construct an angle of 90° using protractor and bisect it.
We will follow the following algorithm to construct this figure.
Steps of Construction
STEP1: Using the protractor, draw a right angle and label it as angle ABC.
STEP2: With centre as B, draw an arc of any radius, intersecting the ray BA at P and the ray BC at Q.
STEP3: With centre as P, and taking radius greater than half of PQ, draw an arc inside the angle ABC.
STEP4: With centre as Q, and taking the same radius, draw another arc, intersecting the previous arc at R.
STEP5: Draw the ray BR.
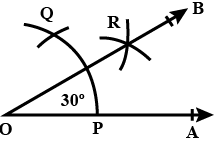
Q5: Construct the following angle with the help of ruler and compasses only: 30∘
Sol: Draw a ray OA.
With a convenient radius and centre at O, draw an arc, which cuts OA at P.
With the same radius and centre at P, draw an arc cutting the previous arc at Q.
Taking P and Q as centres and radius more than half of PQ, draw two arcs, which cuts each other at R.
Draw OR and extend it to B.
∠AOB is the required angle of 30∘.
Q6: Using a protractor, draw an angle of measure 72∘ . With this angle as given, draw angles of measure 36∘ and 54∘ .
Sol: Draw a ray OA.
With the help of a protractor, draw an angle ∠AOB of 72° .
With a convenient radius and centre at O, draw an arc cutting sides OA and OB at P and Q, respectively.
With P and Q as centres and radius more than half of PQ, draw two arcs cutting each other at R.
Join O and R and extend it to X.
OR intersects arc PQ at C.
With C and Q as centres and radius more than half of CQ, draw two arcs cutting each other at T.
Join O and T and extend it to Y.
Now, OX bisects ∠AOB
Therefore, ∠AOX=∠BOX= 72/2
= 36°
Again, OY bisects ∠BOX
Therefore, ∠XOY = ∠BOY= 36/2
= 18°
Therefore, ∠AOX is the required angle of 36° and ∠AOY=∠AOX + ∠XOY
= 36° + 18°
= 54°
The diagram is shown the above image.
Therefore, ∠AOY is the required angle of 54° .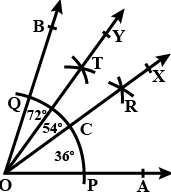
Q7: Construct the following angle with the help of ruler and compasses only:90°.
Sol: Draw a ray OA.
With a convenient radius and centre at O, draw an arc cutting the ray OA at P.
With the same radius and centre at P, draw another arc, which cuts the first arc at Q.
With the same radius and centre at Q, draw another arc, which cuts the first arc at R.
With Q and R as centres and radius more than half of QR, which cuts each other at S.
Draw OS and extend it to B from the ray OB.
∠AOB is required angle of 90°.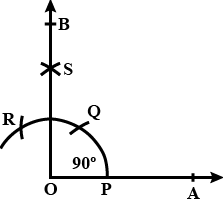
Q8: Name the angle formed at each corner of an envelope.
(a) Acute angle
(b) Obtuse angle
(c) Right angle
(d) Straight angle
Ans: (c)
Sol: The envelope is nothing but rectangular in shape
∴ Each corner angle of Envelope is 90°
i.e. right angle.
Q9: Give a definition for Perpendicular lines
Ans: Perpendicular lines: When a straight line set up on a straight line making a right angle with another line is called a perpendicular line.
Both the lines are perpendicular to each other.
Q10: What is the angle formed between the two hands of a clock at the time 3:00?
(a) Right
(b) Acute
(c) Obtuse
(d) Left
Ans: (a)
Sol: First, note that a clock is a circle made of 360 degrees and that each number represents an angle and the separation between them is 360/12=30. And at 3:00, the minute hand is on the 12 and the hour hand is on the 3.
The correct answer is 3 x 30 = 90 degrees.
At 3 o' clock the angle formed between the two hands of a clock is right angled.
Hence the correct answer is option A.
Q11: 179∘ is an example of
(a) obtuse angle.
(b) acute angle.
(c) right angle.
(d) None of the above
Ans: (a)
Sol: An obtuse angle is an angle which is more than 90∘ but less than 180∘ .
Hence 179∘ is an example of obtuse.
Hence Option A is correct.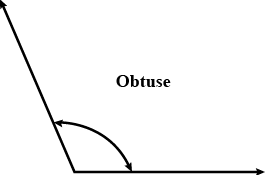
Q12: An angle which is more than 180∘ and less than 360∘ is called:
(a) btuse angle
(b) right angle
(c) reflex angle
(d) complete angle
Ans: (c)
Sol: By definition, we know, an angle which is more than 180o
180∘ and less than 360∘
360∘ is called reflex angle.
That is, an angle larger than a straight angle but less than 1 turn (between 180∘ and 360∘ ) are called reflex angle.
Therefore, option C is correct.
Q13: An angle that is 1∘ less than right angle is:
(a) Reflex angle
(b) Straight angle
(c) Obtuse angle
(d) Acute angle
Ans: (d)
Sol:
Right angle measures 90∘
1∘ less of right angle = 90∘ −1∘
= 89∘
Which is an acute angle.
Acute angle is the angle which is greater than 0o and less than 90∘ .
Obtuse angle is the angle which is greater than 90∘ and less than 180∘ .
Right angle is the angle which is equal to 90∘ .
Reflex angle is the angle which is greater than 180∘ and less than 360∘.
Q14: An angle which measures 180∘ is called_______angle.
(a) zero
(b) right
(c) straight
(d) acute
Ans: (c)
An angle which measures 180∘ is called a straight angle.
Q15: What is the angle between two hands of a clock when the time in the clock is 9′ O clock?
Sol: The time in the clock is 9′ O clock.
We can clearly see from the figure, angle between the hands is 90∘
when the time is 9′ o clock.
Hence, the angle is 90∘ or Right angle.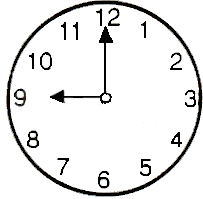
Q16: Identify the angles which are more than right angles and which are less than right angle?
Sol: Angles whose measure are less than 90∘ (right angle) are called as acute angles.
And the angles whose measure is more than 90∘ (right angle) are called as obtuse angles.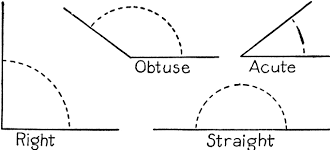
Q17: What is the measure of a right angle?
Ans: A right angle is an angle that measures exactly 90 degrees.
Q18: List ten situations where the angles made are right angles.
Ans: Step 1: To list down
(1) Ten situations where the angles made are right angles.
Step 2: Ten situations
Ten situations where the angles made are right angles are as follows:
Laptop screen, Refrigerator door, Table, Chair, Book, Box, 3 O'Clock Hands, Stairs, Set Square, the angle between the corner of walls.
Q19: Find five situations where obtuse angles are made.
Ans: Step 1: To find
(1) Five situations where obtuse angles are made
Step 2: Five situations
Obtuse angle examples are as follows:
The open book kept for reading, Wide open cupboard door, Rooftop, Clock showing 8 o’clock, the base of a Tripod.
Q20: Write down the measures of some acute angles.(give at least two examples)
Ans: An angle is said to be acute angle if it is lesser than 90∘
45∘ ,70∘ . are example of acute angle as it measure less than 90∘
|
31 videos|192 docs|41 tests
|





















