Class 6 Geography Chapter 4 Notes - Maps
What is a Map?
A map is a representation or a drawing of the earth’s surface or part of it, drawn on a flat surface according to a scale.
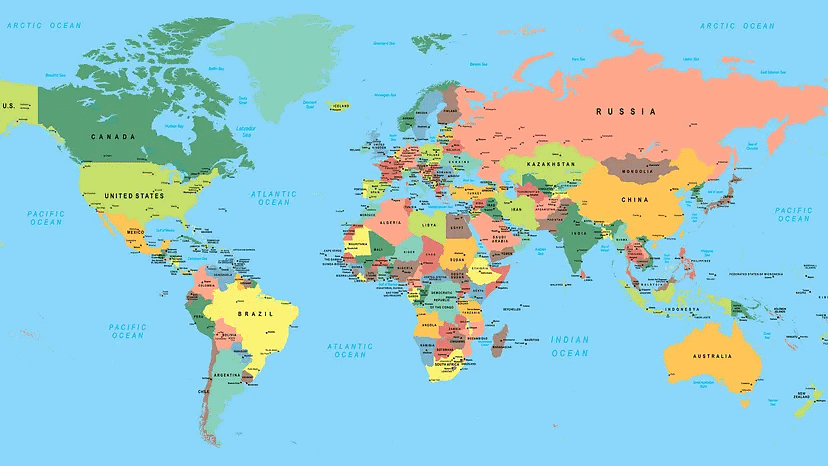 World Map
World Map
- Maps are helpful to us for various reasons.
- One type of map shows a small area with limited information, while another can contain as much data as a large book.
Types of Maps
Maps offer more information than a globe and come in different forms.
There are three three different types of maps:
- Physical Maps
- Political Maps
- Thematic Maps
Let's learn about them:
1. Physical Maps
Maps showing natural features of the earth, such as mountains, plateaus, plains, rivers, oceans, etc., are called physical or relief maps.
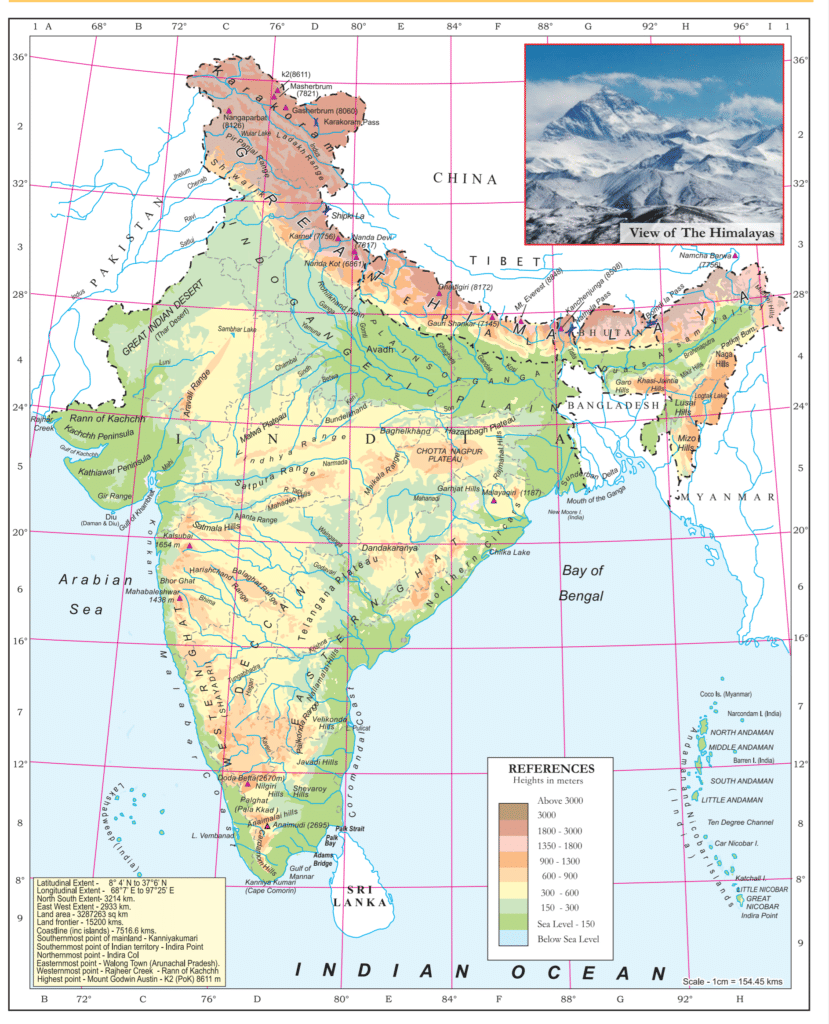 Physical Map of India representing Natural Features
Physical Map of India representing Natural Features
2. Political Maps
Maps showing cities, towns and villages, countries and states of the world with their boundaries are called political maps.
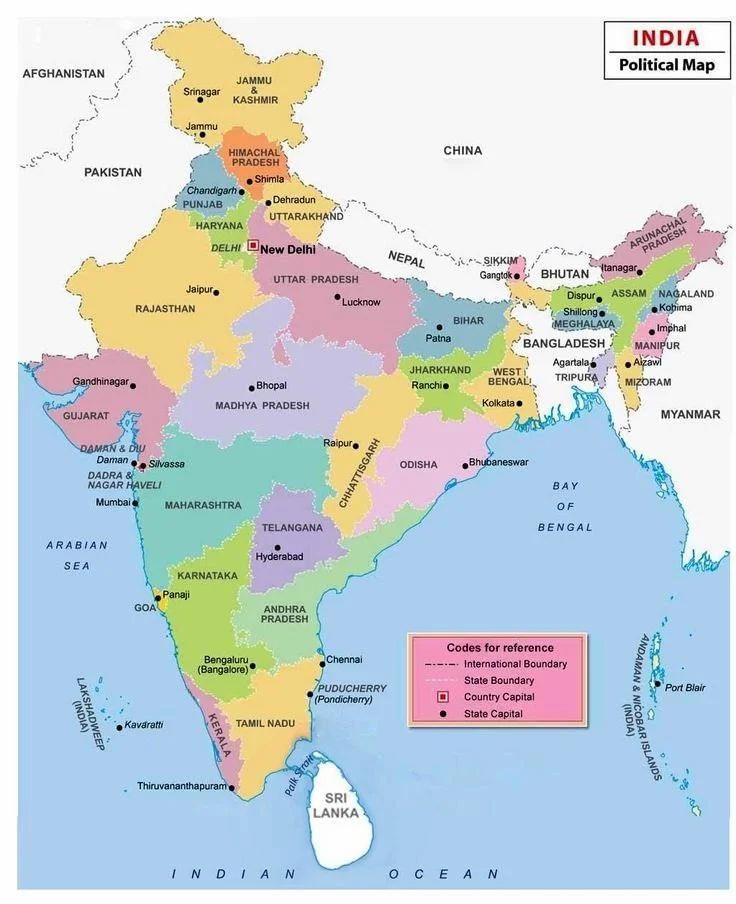 Political Map of India depictiong states and towns
Political Map of India depictiong states and towns
3. Thematic Maps
Some maps focus on specific information like rainfall maps, road maps, and maps of tourist places are called thematic maps. 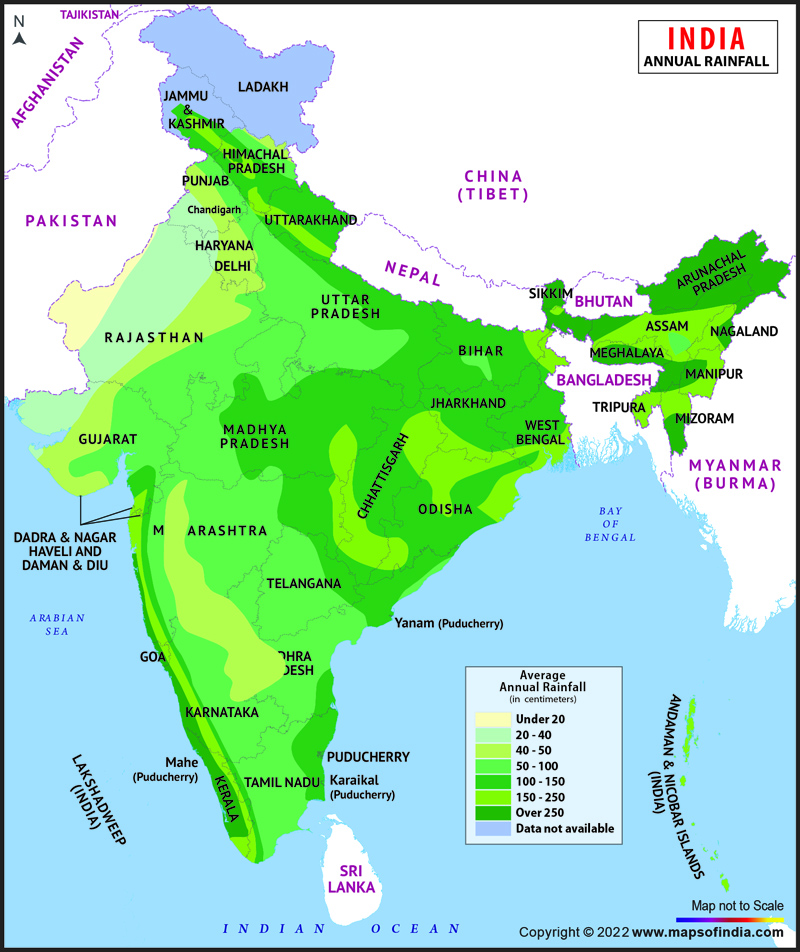 Thematic Map: Annual Rainfall
Thematic Map: Annual Rainfall
Components of Maps
There are three components of maps:
- Distance
- Direction
- Symbols
Let's learn about them:
1. Distance
- Distance is measured in terms of scale. Scale is the ratio between the actual distance on the ground and the distance shown on the map.

- Example: The distance between your school and your home is 10 km. If you represent this 10 km distance by 2 cm on a map, it means that 1 cm on the map corresponds to 5 km on the ground. The scale of your drawing would be 1cm = 5 km.
- If you know the scale, you can calculate the distance between any two places on a map.
Small-Scale and Large-Scale Maps
- Small Scale Map: When large areas like continents or countries are to be shown on paper, then we use a small scale. It is called a small-scale map. Their scale covers a large distance on a small scale. For example, 100 km is shown in 1 cm. These maps have less information about the places shown on the map.
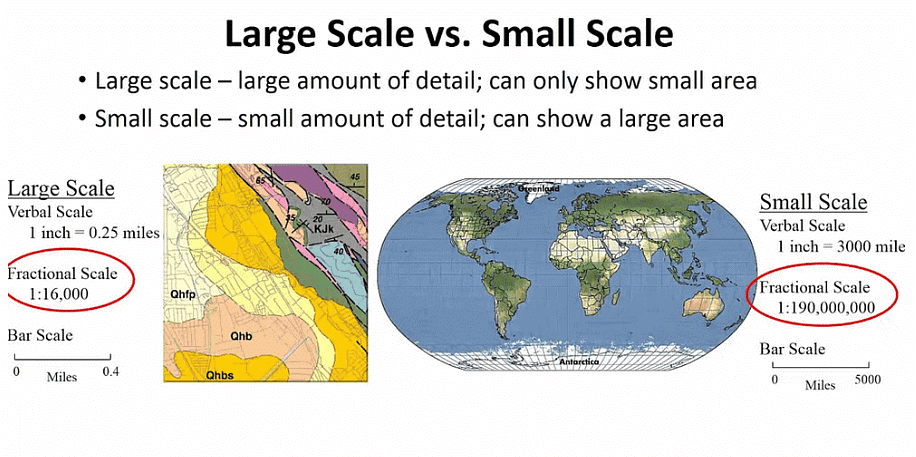 Large Scale vs. Small Scale Maps
Large Scale vs. Small Scale Maps - Large Scale Map: When a small area like your village or town is to be shown on paper, then we use a large scale that is 5 cm. It is called a large-scale map. These maps generally show detailed information, including roads and buildings present in a village or town.
2. Direction
- Most maps have a north arrow (N) indicating the north direction (north line).
- There are four major directions: North, South, East and West. They are called cardinal points.
 Four Cardinal Points
Four Cardinal Points - The other four intermediate directions are northeast (NE), southeast (SE), southwest (SW) and northwest (NW).
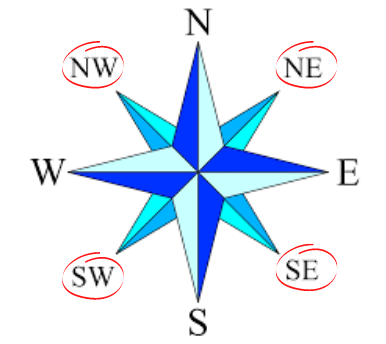 Four Intermediate Directions
Four Intermediate Directions
What is a Compass?
We can find out the direction of a place with the help of a compass. It is an instrument used to find out main directions. Its magnetic needle always points towards north-south direction. Compass helps determine directions accurately.
Compass
3. Symbols
- It is not possible to draw on a map the actual shape and size of different features such as buildings, roads, etc.
- So, they are shown by using certain letters, shades, colours, pictures and lines.
- These symbols give a lot of information in a limited space.
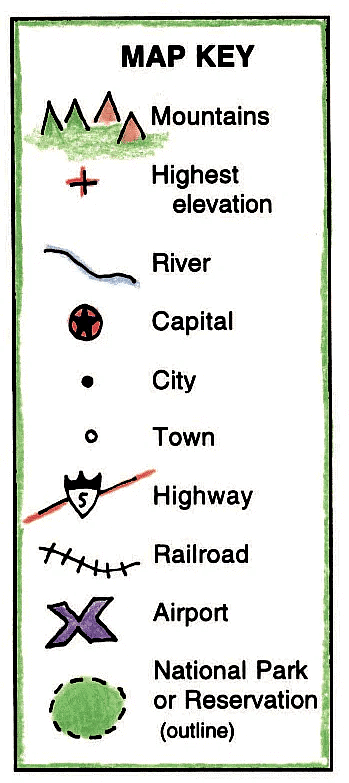 Symbols
Symbols - Maps have a universal language that can be understood by all. There is an international agreement regarding the use of these symbols. These are called conventional symbols.
- Various colours are used for the same purpose. For example, blue is generally used to show water bodies, brown is used for mountains, yellow is used for plateaus, and green is used for plains.
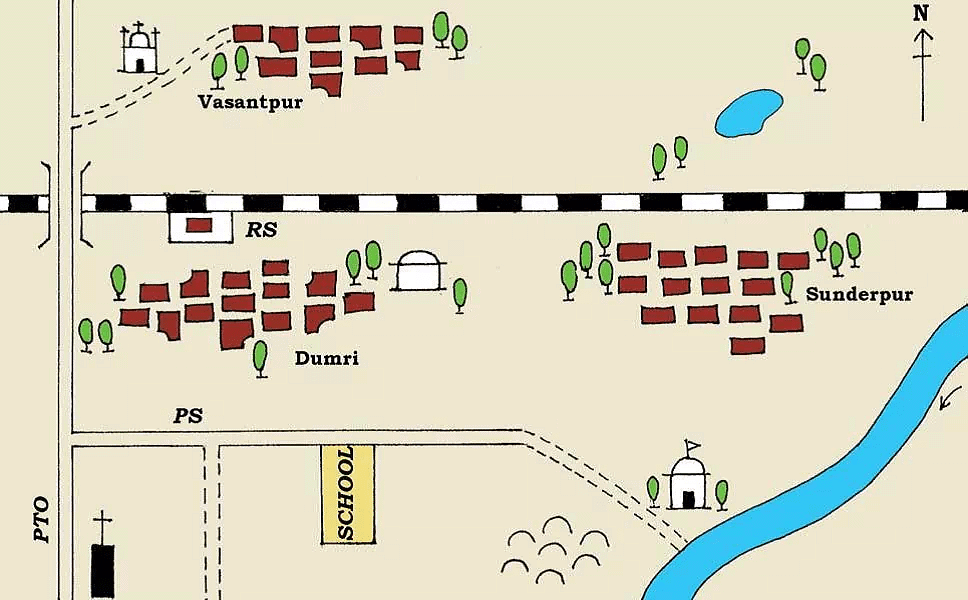 Representation of a small part of an area in the form of a map
Representation of a small part of an area in the form of a map
What is a Sketch?
- A sketch is a drawing mainly based on memory and spot observation and not to scale.
- Sometimes, a rough drawing of an area is required to show where a particular place is located with respect to other places.
 Sketch
Sketch - Such a rough drawing is drawn without scale and is called a sketch map.
What is a Plan?
- A plan is a drawing of a small area on a large scale.
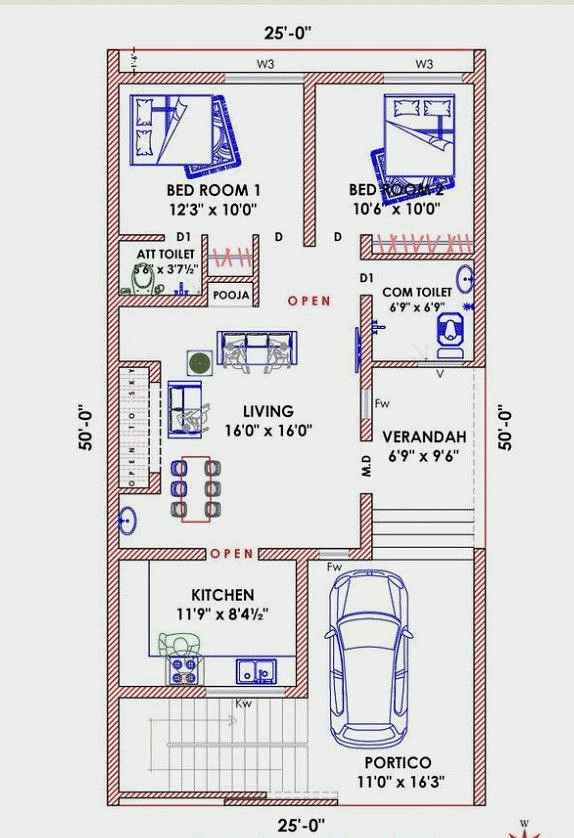 Plan
Plan - A large-scale map gives a lot of information, but there are certain things which we may sometimes want to know, for example, the length and breadth of a room, which can’t be shown on a map. At that time, we can refer to drawings drawn to a scale called a plan.
Important Questions
Ques 1: What is a ‘Thematic map’?
A thematic map provides a specific type of information such as distribution of population, location of industries, distribution of soils, climatic conditions and air and railway routes within a specific region.
Ques 2: What are the uses of ‘Maps’?
- General reference: Maps are like cool guides that show a bit of everything in a place—where things are, like countries and cities.
- Topographical: When you want to know about mountains, rivers, or other nature stuff in a place, maps can help you explore them.
- Navigational Uses: Imagine maps as magical tools to find your way! They help you figure out where you are and where you want to go, just like a treasure map but for real places.
Ques 3: How do symbols help in map reading?
Symbols are used to analyze maps. Buildings, bridges, railway lines, roads, and other features are difficult to depict on maps. As a result, symbols are employed. Letters, hues, colors, drawings, and dotted lines on a map are all examples of symbols.
Ques 4: What do you mean by the term ‘the scale of the map’?
The scale of the map is the ratio between the actual distance on the ground and the distance shown on the map. There are two types of maps based on scale: Large scale maps and small scale maps.
Ques 5: How are maps more helpful than a globe?
A map is a representation or a drawing of the earth’s surface or a part of it drawn on a flat surface according to a scale. It is impossible to flatten a round shape and scale it. Therefore, maps are more helpful than a globe.
FAQs on Class 6 Geography Chapter 4 Notes - Maps
| 1. What is a map? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of maps? |  |
| 3. What are the key components of a map? |  |
| 4. How is a sketch different from a map? |  |
| 5. Why are thematic maps important? |  |






















