Class 6 Science: Sample Paper Solutions - 1 | Sample Papers For Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Section - A |

|
| Section - B |

|
| Section - C |

|
| Section - D |

|
Time: 3 hrs
Total Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- This question paper consists of 34 questions in total and all questions are compulsory.
- Questions 1-7 are multiple-choice questions and carry 1 mark each. Write the correct answer in your answer sheet.
- Questions 8-17 are very short answer questions and carry 2 marks each.
- Questions 18-28 are short answer questions and carry 3 marks each.
- Questions 29-34 are long answer questions and carry 5 marks each.
Section - A
Q1. Which planet in our solar system takes the longest to complete one orbit around the Sun? (1 Mark)
(a) Earth
(b) Mars
(c) Jupiter
(d) Neptune
Ans: (d) Neptune
I know Neptune takes the longest because it’s so far from the Sun—about 165 years for one orbit, way more than Earth’s 1 year!
Q2. Which of these processes involves a change from gas to liquid? (1 Mark)
(a) Evaporation
(b) Condensation
(c) Melting
(d) Freezing
Ans: (b) Condensation
Condensation is when gas turns into liquid, like water vapour making droplets on a cold window.
Q3. Which nutrient deficiency causes night blindness? (1 Mark)
(a) Vitamin A
(b) Vitamin C
(c) Vitamin D
(d) Iron
Ans: (a) Vitamin A
Vitamin A keeps our eyes working, and without it, we can’t see well in the dark—that’s night blindness.
Q4. Which of the following conditions is NOT essential for the germination of a seed? (1 Mark)
(a) Air
(b) Sunlight
(c) Water
(d) Soil
Ans: (b) Sunlight
Sunlight is not essential for seed germination. Seeds generally require water, air, and suitable soil conditions for germination. After germination, sunlight is necessary for the further growth of the seedling
Q5. The SI unit of temperature is: (1 Mark)
(a) Celsius
(b) Fahrenheit
(c) Kelvin
(d) Gram
Ans: (c) Kelvin
Kelvin is the science unit for temperature, not Celsius, even though we use that a lot.
6. Which method separates a mixture of sand and iron filings? (1 Mark)
(a) Filtration
(b) Magnetic separation
(c) Sieving
(d) Decantation
Ans: (b) Magnetic separation
A magnet pulls out iron filings from sand because iron sticks to it.
7. Which of these is a non-renewable resource? (1 Mark)
(a) Solar energy
(b) Wind
(c) Coal
(d) Water
Ans: (c) Coal
Coal doesn’t come back fast—it’s non-renewable, unlike sunlight or wind.
Section - B
Q8. How does a cactus adapt to survive in a desert? (2 marks)
Ans: A cactus survives in the desert by having a thick, waxy coating on its stem, which prevents water from evapourating. This helps the cactus conserve water in the hot, dry climate. Additionally, it has spines instead of leaves. Spines reduce water loss as they minimize transpiration. The spines also protect the cactus from animals that might try to eat it, making it well-adapted to desert life.
Q9. What is the role of observation in scientific discovery? (2 marks)
Ans: Observation plays a crucial role in scientific discovery because it helps scientists notice patterns or unusual occurrences. For example, noticing that plants grow towards light can lead to questions about photosynthesis. Through careful observation, scientists ask more questions, form hypotheses, and design experiments to test their ideas, leading to new discoveries and better understanding of natural processes.
Q10. Name two properties of a magnet that distinguish it from other objects. (2 marks)
Ans:
Magnets attract certain materials, such as iron, steel, and nickel, while non-magnetic materials like wood or plastic do not respond to magnets.
Magnets have two distinct poles—north and south. These poles are where the magnetic force is the strongest, unlike non-magnetic objects which do not have poles or magnetic fields.
Q11. What happens to water when it reaches 100°C at standard pressure? (2 marks)
Ans: When water reaches 100°C at standard pressure, it starts to boil and turns into water vapour. The heat energy causes water molecules to move faster, and they break free from the liquid state, turning into gas. This is why steam rises from boiling water, as it changes from liquid to gas during the process of boiling.
Q12. Why do we use standard units like meters and seconds? (2 marks)
Ans: We use standard units like meters and seconds to ensure consistency and clear communication across different places. If everyone uses the same unit of measurement, such as meters for length and seconds for time, it helps avoid confusion. For example, saying "1 meter" means the same for everyone, regardless of location, making measurements accurate and universally understandable.
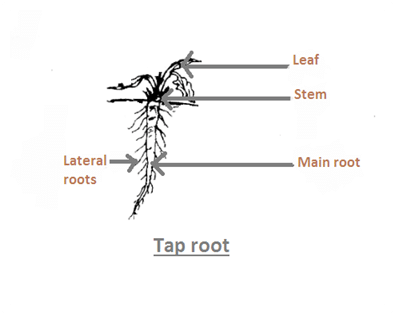
Q13. Draw a labelled diagram of a tap root system and name one plant with this root type. (2 marks)
Ans:
Plant with Tap Root System: Carrot
Carrots have a tap root system where the primary root grows deep into the soil. This allows the carrot to absorb water and nutrients efficiently. Additionally, the tap root of the carrot stores nutrients, which helps in the plant's growth
Q14. Name two methods to separate a mixture of salt and sand. (2 marks)
Ans:
Dissolution and Filtration: Add water to the mixture. The salt dissolves in the water, while the sand does not. Then, filter the mixture using filter paper. The sand is left behind, and the salty water passes through the paper.
Evaporation: After filtering the mixture, heat the salty water to evaporate the water. As the water turns into vapour, the salt is left behind as solid crystals.
Q15. What are two characteristics of living creatures? (2 marks)
Ans:
Growth: Living creatures grow and develop. For example, a baby grows into an adult, which is not seen in non-living things.
Response to stimuli: Living creatures respond to changes in their environment, like how a dog barks when it hears a sound or how plants bend towards light.
Q16. Why is air considered a natural resource? (2 marks)
Ans: Air is a natural resource because it provides oxygen necessary for breathing and survival. It also enables wind, which can be used for generating electricity through windmills. Additionally, air carries water vapour for rainfall and helps in the dispersal of seeds, playing a crucial role in sustaining life and the environment.
Q17. What is the primary source of energy for Earth’s climate system? (2 marks)
Ans: The Sun is the primary source of energy for Earth's climate system. It provides the heat that warms the Earth's surface, causing air to move, forming winds and clouds. This leads to weather patterns and the water cycle, maintaining the climate and supporting life. Without the Sun’s energy, Earth would be cold and lifeless.
Section - C
Q18. Explain how sedimentation and decantation together can purify muddy water. (3 marks)
Ans:
Sedimentation: First, when muddy water is left undisturbed, gravity causes the heavier particles of mud to settle at the bottom. As a result, the water at the top becomes clearer.
Decantation: After sedimentation, the clear water is carefully poured into another container without disturbing the settled mud. This method helps separate the solid particles from the liquid, making the water cleaner.
Both steps together help purify the water, making it suitable for various uses, including washing or further purification for drinking.
Q19. How do poles of a magnet interact with each other? (3 marks)
Ans:
Like poles repel: When two like poles (north-north or south-south) are brought close together, they repel each other. This is known as repulsion, and you can feel the force pushing them apart.
Opposite poles attract: When a north pole is brought near a south pole, they attract each other and stick together, a process called attraction.
Magnetic force: The strongest magnetic forces are found at the poles, not at the center of the magnet. This is why magnets are useful for navigation, like in compasses, where the poles help point towards the Earth’s magnetic north.
Q20. Why is measurement of motion important in daily life? (3 marks)
Ans:
Ensuring safety: Measuring motion helps us track the speed of vehicles, ensuring that drivers follow speed limits to prevent accidents.
Time management: It also helps in planning and managing time effectively, such as calculating how long it will take to reach a destination.
Everyday use: Motion measurement is important in daily tasks like cycling, where we need to measure the motion of the wheels to ensure they roll smoothly, preventing accidents and improving efficiency.
Q21. What happens to an object’s state when its temperature drops below its freezing point? (3 marks)
Ans: When the temperature of a liquid drops below its freezing point, it undergoes the following changes:
Change of state: The liquid turns into a solid, like water turning into ice at 0°C.
Particle movement: The particles of the liquid slow down and pack closely together, making the substance solid.
Heat release: As the liquid freezes, it releases heat, which is why you can feel warmth if you touch a freezing object. This process is called latent heat of fusion.
Q22. How do animals in cold climates survive? (3 marks)
Ans:
Thick fur or fat: Animals in cold climates, like polar bears, have thick layers of fat (blubber) and fur to insulate their bodies and retain heat.
Hibernation: Some animals, like bears, hibernate during the cold months. They sleep through the winter, conserving energy when food is scarce.
Physical adaptations: Animals like Arctic foxes have small ears and shorter legs to reduce heat loss, helping them conserve warmth in extremely cold temperatures.
These adaptations enable animals to survive and thrive in harsh, freezing environments.
Q23. Why do we need a balanced diet? (3 marks)
Ans: A balanced diet is important because it provides all the essential nutrients needed for growth, energy, and overall health:
Energy: It provides energy from carbohydrates and fats, enabling us to stay active throughout the day, like when playing sports or studying.
Growth: Proteins and minerals in a balanced diet help in the growth and repair of body tissues, such as the calcium in milk, which strengthens bones.
Prevention of diseases: Vitamins and minerals from fruits and vegetables help strengthen the immune system and prevent diseases like scurvy (due to lack of Vitamin (c), ensuring good health.
Q24: Briefly describe the life cycle of a mosquito. (3 marks)
Ans: The mosquito life cycle includes four stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult.
Egg Stage: Female mosquitoes lay eggs on water surfaces. Eggs must be in water to hatch, leading to the larval stage.
Larva Stage: Larvae live in water, feeding on microorganisms and growing until they become pupae. They must surface to breathe air.
Pupa Stage: The mosquito transforms inside the pupal case, not eating but still moving. This stage prepares it to become an adult.
Adult Stage: The adult mosquito emerges, with females seeking blood to produce eggs and males feeding on nectar. This final stage is crucial for reproduction and disease transmission.
Q25. How do constellations help us? (3 marks)
Ans:
- Navigation: Constellations help in navigation by guiding travelers, such as the North Star in Ursa Major, which points to the north.
- Timekeeping: Constellations can also indicate seasons. For example, the appearance of Orion in the night sky signals the arrival of winter, which helps farmers know when to plant or harvest crops.
- Astronomy: Constellations are used by scientists to study the stars and learn about the universe’s structure and behavior.
Q26. What are the characteristics of living creatures that distinguish them from non-living things? (3 marks)
Ans: Living creatures have several key characteristics that distinguish them from non-living things:
- Reproduction: Living things reproduce to create offspring, ensuring the survival of their species. For example, animals give birth to young ones.
- Energy requirements: Living creatures need energy to survive. Humans and animals consume food, while plants use sunlight to make their own food through photosynthesis.
- Growth and movement: Living organisms grow and change over time. Plants grow toward sunlight, and animals grow from babies into adults. Non-living things, like a rock, do not grow or move on their own.
Q27. Why should we conserve water? (3 marks)
Ans: Water conservation is crucial for several reasons:
- Essential for life: Water is needed by all living organisms, including humans, animals, and plants. Without it, life cannot be sustained.
- Scarcity of freshwater: Freshwater is limited, as most of Earth's water is salty, and we risk depleting the available freshwater supplies if we waste it.
- Agriculture: Water is vital for growing crops. Without sufficient water, crops like rice cannot grow, which would lead to food shortages.
Q28. How does asking questions lead to scientific discoveries? (3 marks)
Ans: Asking questions is a fundamental part of scientific discovery because it sparks curiosity and leads to investigations. For example, asking "Why do leaves fall?" can lead to studies about plant growth and changes in seasons.
- Observations: Questions help scientists observe natural phenomena, like how water boils, and then experiment to understand the reasons behind them.
- Testing and discovery: Once questions are formed, experiments are conducted to test ideas and hypotheses, leading to new knowledge and discoveries about the world.
Section - D
Q29. (a) What is the water cycle?
(b) Explain three stages with examples.
(c) Why is it important? (5 marks)
Ans: (a) The water cycle is the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the Earth's surface. It moves from water bodies to the atmosphere and back, providing fresh water to the environment.
(b) Three stages of the water cycle:
Evapouration: Water from rivers, lakes, and oceans changes into vapour due to the Sun’s heat. For example, water in a puddle evapourates when exposed to sunlight.
Condensation: The water vapour cools down as it rises, forming clouds. For example, when you breathe on a cold glass, you see fog form on the surface.
Precipitation: The water in the clouds falls back to the Earth as rain, snow, or hail. For example, when clouds become heavy, they release water as rain.
(c) The water cycle is important because it ensures the continuous movement and renewal of water, which is necessary for all living organisms. It helps maintain weather patterns, supports plant growth, and replenishes groundwater resources.
Q30. (a) What are natural resources?
(b) Differentiate between renewable and non-renewable resources with examples.
(c) Draw a diagram showing one resource cycle. (5 marks)
Ans: (a) Natural resources are substances or materials provided by nature that are used to meet the needs of living organisms. Examples include air, water, soil, minerals, and plants.
(b) Difference between renewable and non-renewable resources:
Renewable resources: These are resources that can be replenished naturally in a short time. Examples include sunlight, wind, and water.
Non-renewable resources: These are resources that cannot be replaced quickly and take millions of years to form. Examples include coal, oil, and natural gas.
(c)
Water Cycle
Q31. (a) What is adaptation?
(b) Explain two animal adaptations with examples.
(c) How do these help survival? (5 marks)
Ans: (a) Adaptation refers to the special characteristics or behaviors that organisms develop over time to survive in their specific environment.
(b) Two animal adaptations:
Camels: Camels have humps that store fat, not water, which they use for energy when food is scarce in the desert.
Penguins: Penguins have a thick layer of blubber beneath their skin, helping them stay warm in cold Antarctic waters.
(c) These adaptations help survival by enabling the animals to thrive in extreme environments. Camels can survive long periods without food and water, while penguins can withstand freezing temperatures and swim efficiently in icy waters.
Q32. (a) What is rotational motion?
(b) Differentiate it from linear motion with examples.
(c) Draw an object showing rotational motion. (5 marks)
Ans: (a) Rotational motion is the motion of an object around a central point or axis. It occurs when an object spins or rotates, like a wheel turning around its center.
(b) Difference between rotational and linear motion:
Rotational motion: The object moves in a circular path around an axis. Example: A spinning top or a Ferris wheel.
Linear motion: The object moves along a straight line. Example: A car moving along a road.
(c)
Spinning Top
Q33. (a) What are deficiency diseases?
(b) Name two with their causes and symptoms.
(c) How can they be prevented? (5 marks)
Ans: (a) Deficiency diseases are illnesses caused by the lack of essential nutrients in the body. These nutrients could be vitamins, minerals, or other essential substances.
(b) Two deficiency diseases:
Scurvy: Caused by a lack of Vitamin C, leading to symptoms like bleeding gums, weakness, and joint pain.
Rickets: Caused by a lack of Vitamin D, leading to symptoms like soft bones, bone pain, and leg deformities in children.
(c) These diseases can be prevented by consuming a balanced diet that includes all essential nutrients. Eating fruits rich in Vitamin C (like oranges) can prevent scurvy, while drinking milk and getting sunlight can prevent rickets by providing Vitamin D.
Q34. (a) What is the solar system?
(b) Name its components and explain two.
(c) Draw a labelled diagram of the solar system. (5 marks)
Ans: (a) The solar system is a collection of celestial objects that includes the Sun and all the objects that revolve around it, such as planets, moons, asteroids, comets, and other space debris. These objects are held together by the Sun's gravitational pull. The solar system is the region in space where the Sun's gravitational influence dominates.
(b) (i) Planets: Planets are large, nearly spherical objects that revolve around the Sun. There are eight planets in the solar system: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. These planets are classified into two categories:
Inner planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars) are smaller, rocky, and have solid surfaces.
Outer planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune) are larger, gaseous, and have rings made of dust and rocky materials.
(ii) Moons: Moons are natural satellites that orbit planets. For example, Earth has one moon, while Jupiter and Saturn have many moons. Moons can vary greatly in size and characteristics, and they are often studied to understand planetary systems.
(c)
Solar System
FAQs on Class 6 Science: Sample Paper Solutions - 1 - Sample Papers For Class 6
| 1. What topics are typically covered in the Class 6 Science syllabus? |  |
| 2. How can I effectively prepare for the Class 6 Science exam? |  |
| 3. What types of questions can I expect in the Class 6 Science exam? |  |
| 4. Are there any recommended books for Class 6 Science preparation? |  |
| 5. How important are practicals in the Class 6 Science curriculum? |  |