Class 6 Science: Sample Paper Solutions - 2 | Sample Papers For Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Section - A |

|
| Section - B |

|
| Section - C |

|
| Section - D |

|
Time: 3 hrs
Total Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- This question paper consists of 34 questions in total and all questions are compulsory.
- Questions 1-7 are multiple-choice questions and carry 1 mark each. Write the correct answer in your answer sheet.
- Questions 8-17 are very short answer questions and carry 2 marks each.
- Questions 18-28 are short answer questions and carry 3 marks each.
- Questions 29-34 are long answer questions and carry 5 marks each.
Section - A
Q1. Which of these is a constellation? (1 Mark)
(a) Mars
(b) Orion
(c) Sun
(d) Moon
Ans: (b) Orion
Orion is a constellation because it’s a group of stars that make a pattern in the sky, not a single thing like Mars or the Sun!
Q2. Which process separates husk from grain? (1 Mark)
(a) Sieving
(b) Winnowing
(c) Filtration
(d) Evaporation
Ans: (b) Winnowing
Winnowing uses wind to blow light husk away from heavier grain—it’s perfect for that job!
Q3. Which vitamin helps in blood clotting? (1 Mark)
(a) Vitamin A
(b) Vitamin K
(c) Vitamin C
(d) Vitamin D
Ans: (b) Vitamin K
Vitamin K helps our blood clot so cuts stop bleeding—it’s like a superhero for healing!
Q4. Which of these has a tap root system? (1 Mark)
(a) Grass
(b) Wheat
(c) Mango
(d) Rice
Ans: (c) Mango
Mango trees have a tap root—one big root going deep, not like grass with lots of thin ones!
Q5. What type of motion does a spinning wheel show? (1 Mark)
(a) Linear
(b) Rotational
(c) Periodic
(d) Random
Ans: (b) Rotational
A spinning wheel turns around a center—that’s rotational motion, like a top spinning!
Q6. Which resource is essential for photosynthesis? (1 Mark)
(a) Coal
(b) Water
(c) Petroleum
(d) Iron
Ans: (b) Water
Plants need water for photosynthesis to make food—without it, they’d starve!
Q7. Which of these is a characteristic of living things? (1 Mark)
(a) Rusting
(b) Reproduction
(c) Melting
(d) Breaking
Ans: (b) Reproduction
Reproduction is something living things do—like birds having babies—but rusting isn’t alive!
Section - B
Q8. What is a hypothesis? Give an example.(2 Marks)
Ans: A hypothesis is an educated guess or a testable statement based on observations, which can be tested through experiments.
Example: "Plants grow taller when exposed to more sunlight."
To test this, you would place one plant in direct sunlight and the other in the shade and compare their growth over time. This allows us to find out whether the hypothesis is true or not.
Q9. Name two poles of a magnet and their interaction.(2 Marks)
Ans: The two poles of a magnet are the North pole and the South pole.
- When a North pole is brought near a South pole, they attract each other.
- When two North poles or two South poles are brought together, they repel each other.
Q10. How does temperature affect evaporation? (2 Marks)
Ans:
- Higher temperatures increase the rate of evaporation, as the heat gives water molecules more energy to escape into the air.
- Lower temperatures slow down evaporation because the water molecules have less energy to change into vapor.
Thus, evaporation occurs faster on hot days and slower on cold days.
Q11. What are two uses of stems in plants? (2 Marks)
Ans:
- Stems support the plant’s leaves, flowers, and fruits, helping them remain upright and exposed to sunlight for photosynthesis.
- They transport water, minerals, and nutrients from the roots to other parts of the plant, ensuring the plant stays healthy.
Q12. Name two renewable resources. (2 Marks)
Ans:
- Solar energy: This energy is derived from the Sun and is inexhaustible.
- Wind energy: Wind is used to generate power using windmills or turbines, and it is also renewable as the wind keeps blowing naturally.
Q13. How do birds adapt to flight? (2 Marks)
Ans:
- Birds have hollow bones which make them lighter, reducing the weight they need to carry while flying.
- Their feathers help with aerodynamics, allowing birds to lift off and glide smoothly through the air.
These adaptations enable birds to fly efficiently.
Q14. What is sedimentation? Give an example. (2 Marks)
Ans: Sedimentation is the process by which solid particles in a liquid settle down due to gravity.
Example: When muddy water is left undisturbed, the heavy mud particles settle at the bottom, and the clear water remains at the top.
This process is commonly used to separate solids from liquids.
Q15. What is the freezing point of water in Kelvin? (2 Marks)
Ans: The freezing point of water in the Kelvin scale is 273 K.
This is because the Kelvin scale starts at absolute zero (0 K), so the freezing point of water, which is 0°C, is represented as 273 K in this scale.
Q16. Name two types of motion with examples. (2 Marks)
Ans:
- Linear motion: Movement in a straight line, such as a car driving on a straight road.
- Rotational motion: Movement around an axis, like a spinning top or a rotating wheel.
These motions are observed in many everyday objects.
Q17. What is a satellite? Give an example. (2 Marks)
Ans: A satellite is an object that orbits a planet or a moon.
Example: The Moon is Earth's natural satellite, as it orbits around the Earth. Satellites can be natural (like the Moon) or man-made (such as communication satellites).
Section - C
Q18. Mention the methods that can be used for the separation of the following mixtures: (3 Marks)
(i) wheat, sugar and husk
(ii) rice, gram and iron fillings
(iii) sand, black gram (ura(d) and husk.
Ans: (i) Mixture of wheat, sugar and husk.
- For separating husk from the mixture, we should follow the winnowing method as husk is lighter than other two components.
- Wheat and sugar can be separated by sieving as they have different sizes.
(ii) Mixture of rice, gram and iron fillings.
- For separating iron fillings, we can use a magnet.
- Rice and gram can be separated either by sieving or by handpicking.
(iii) Mixture of sand, black gram (ura(d) and husk.
- For separating sand from the mixture, we can sieve the mixture.
- Black gram (ura(d)and husk can be separated by the method of winnowing.
Q19. Give two examples for each of the following motions: (3 Marks)
(i) Linear motion
(ii) Spinning motion
(iii) Oscillatory motion
(iv) Periodic motion
(y) Circular motion
Ans: (i) Linear motion: ((a) March-past of soldiers in a parade, ((b) Moving of bicycle on a straight road.
(ii) Spinning motion: ((a) Rotating fan, ((b) Wheel of sewing machine
(iii) Oscillatory motion: ((a) Pendulum of clock, ((b) Motion of a child on a swing.
(iv) Periodic motion: ((a) Pendulum of clock, ((b) Motion of a swing,((c) Heartbeat
(v) Circular motion: ((a) Rotation of fan, ((b) Bicycle wheel.
Q20. What are asteroids? Where are they found in the solar system? (3 Marks)
Ans: Asteroids are small, rocky objects that orbit the Sun, similar to planets but much smaller in size. They are mostly found in the asteroid belt, which lies between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.
Asteroids vary in size from tiny pebbles to large objects that are hundreds of kilometers wide. Some asteroids are considered leftover building blocks of the solar system, offering insight into the early solar system's formation.
Q21. How do roots help plants survive? (3 Marks)
Ans: Roots are essential for a plant’s survival.
- Anchoring the plant: Roots hold the plant firmly in the ground, preventing it from being uprooted by wind or water.
- Absorbing water and nutrients: Roots take up water and minerals from the soil and transport them to the rest of the plant.
- Storage: Roots also store food and water, like in carrots, ensuring the plant survives in tough conditions like droughts.
Q22. Describe the differences between thermometers in terms of their use and range. (3 Marks)
Ans:
Clinical Thermometers Laboratory Thermometers 1. Clinical thermometers are designed specifically for measuring human body temperature. 1. Laboratory thermometers are used for a variety of scientific purposes. 2. They typically have a limited range, from around 35 °C to 42 °C, which is sufficient for detecting fevers and other health-related temperature variations. 2. Laboratory thermometers can measure a much wider range of temperatures, usually from-10 °C to 110 °C. 3. Clinical thermometers are used to take readings of body temperatures on Celsius or sometimes on Fahrenheit scale. 3. Laboratory thermometers are used to take readings of temperatures on Celsius scale or on Kelvin scale. 4. Clinical thermometers can be mercury thermometers, digital thermometers or non-contact infrared thermometers. 4. Laboratory thermometers use coloured alcohol or mercury as liquids that expand to show the temperatures readings.
Q23. (i) Which of the two- water in earthen pot or water in stainless steel pot will give cold water after being left for some time? Illustrate with another example.
(ii) How do the areas covered with concrete affect the availability of ground water? (3 Marks)
Ans: (i) Water in the earthen pot will be cold. It is because water from the surface of the earthen pot evaporates and imparts a cooling effect on water. On the other hand, water in stainless steel will not give cold water.
Another Example: We cool the surface of the roof or floor by sprinkling water over it. Surahi is also used for similar purpose.
(ii) Areas covered with concrete reduce the seepage of rain water into the ground and this reduces the availability of ground water.
Q24. How do animals depend on plants? (3 Marks)
Ans: Animals rely on plants in many ways:
For food: Herbivores eat plants for energy, such as cows eating grass or deer eating leaves.
For oxygen: Plants produce oxygen through photosynthesis, which animals need to breathe and survive.
For shelter: Plants, like trees, provide homes for many animals, such as birds nesting in branches or insects hiding under leaves.
Plants play an essential role in sustaining life on Earth by providing food, oxygen, and shelter.
Q25. What is rainwater harvesting? Describe the method of rainwater harvesting. (3 Marks)
Ans: Rainwater harvesting is the collection of rainwater and storing for future use. In this system rainwater in collected from the rooftops by means of pipes into storage tank for later use. Recycling water and water harvesting also help in saving water.
Methods of Rainwater Harvesting:
- Rooftop rainwater harvesting. In this system, the rainwater from the rooftop is collected in a storage tank, through pipes.
- Another method, a big pit is dug near house for collecting rainwater. This pit is filled with different layers of bricks, coarse gravels and sand or granite pieces.
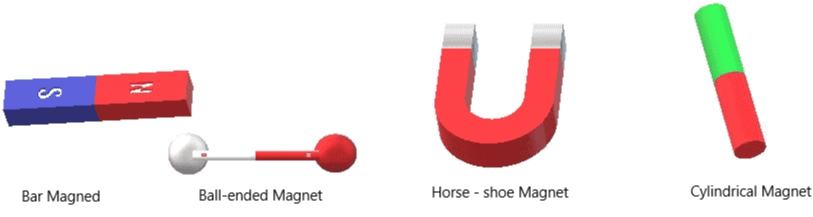
Q26.What are artificial magnets? Draw diagrams to show the different shapes of magnets. (3 Marks)
Ans: The magnets formed from the pieces of iron are called artificial magnets. The following are the different shapes of magnets:
Q27. Why is protein important? (3 Marks)
Ans: Protein is essential for the growth and maintenance of our body.
- Builds muscles: Protein is a key component of muscles, which help us move and stay strong.
- Repairs tissues: Protein helps repair damaged tissues in the body, such as when we get a cut or bruise.
- Makes enzymes: Enzymes are proteins that help digest food and regulate body functions.
Q28. How do planets differ from stars? (3 marks)
Ans: Planets and stars are very different:
- Stars emit light: Stars, like the Sun, produce their own light because they burn hot gases whereas Planets reflect light: Planets, like Earth, reflect light from stars but do not generate their own light.
- Planets orbit stars: Planets revolve around stars (like Earth orbits the Sun) whereas Stars stay in one place : Stars do not orbit other objects.
- Stars are much hotter: Stars are extremely hot and generate energy through nuclear fusion whereas Planets have cooler surfaces : do not produce energy as star does.
Section - D
Q29. Discuss the importance of conserving natural resources and suggest practical ways to conserve both renewable and non-renewable resources. (5 marks)
Ans: Conserving natural resources is crucial for maintaining ecological balance, ensuring sustainable development and preserving the environment for future generations. Overuse or depletion of resources can lead to environmental degradation, loss of biodiversity and scarcity of essential resources.
Practical ways to conserve renewable resources:
- Water conservation: Use water-saving fixtures, fix leaks and adopt practices like rainwater harvesting.
- Forest conservation: Support afforestation projects, avoid deforestation and use resources like paper and wood sustainably.
- Energy conservation: Utilise renewable energy sources like solar panels and wind turbines and reduce energy consumption through efficient appliances.
Practical ways to conserve non-renewable resources:
- Reduce fossil fuel use: Opt for alternative energy sources such as electric vehicles and public transport instead of personal cars.
- Recycling and Reuse: Recycle materials like metals, plastics and glass to reduce the need for new raw materials.
- Sustainable practices: Encourage industries to adopt sustainable practices and technologies that minimise the extraction and use of non-renewable resources.
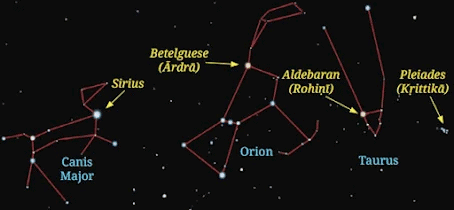
Q30. (a) What are constellations?
(b) Explain two with their uses.
(c) Draw one constellation. (5 marks)
Ans: (a) Constellations are patterns formed by groups of stars in the sky. These patterns have been identified by humans for centuries and often represent animals, objects, or characters from stories. They are used to navigate the night sky and help astronomers identify specific stars.
(b) Two constellations and their uses:
Orion: Orion is one of the most recognizable constellations. It looks like a hunter, with a belt of three stars. It is important for navigation in the winter months, as it helps people in the Northern Hemisphere identify the season and locate other stars.
Ursa Major: Also known as the Big Dipper, this constellation resembles a bear. It is used to find the North Star (Polaris), which helps navigators and sailors find direction, especially at night.
(c)
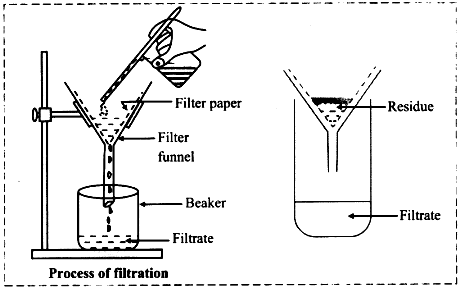
Q31. (a) What is separation?
(b) Explain two methods with examples.
(c) Draw a filtration setup. (5 marks)
Ans: (a) Separation is the process of dividing mixtures into their individual components based on their physical properties, such as size, shape, or solubility. This is done to obtain pure substances or to remove unwanted particles.
(b) Two methods of separation:
Filtration: This method separates solid particles from a liquid by passing the mixture through a filter. For example, filtering tea removes tea leaves from the liquid.
Evaporation: This method is used to separate a dissolved solid from a liquid. For example, when seawater is heated, the water evaporates, leaving salt behind as crystals.
(c)
Q32. (a) What are states of water?
(b) Explain changes between them.
(c) Suggest possible reasons explaining’the appearance of water droplets on the outer surface of the glass tumbler containing lemonade. (5 marks)
Ans: (a) Water exists in three states: Solid (ice), Liquid (water) and Gas (steam or vapour)
(b) Changes between states of water:
Melting: When ice is heated, it turns into liquid water as the molecules gain energy and start to move faster, breaking the bonds that hold them in a solid state.
Boiling: When liquid water is heated to 100°C, it changes to steam (gas) as the molecules gain enough energy to escape from the liquid and spread out into the air.
Freezing: When liquid water is cooled, it forms solid ice as the molecules lose energy and arrange themselves into a fixed pattern.
(c) Water does not come out from the glass tumbler. Water in the air deposits on the outer surface of the glass tumbler. This is due to condensation.
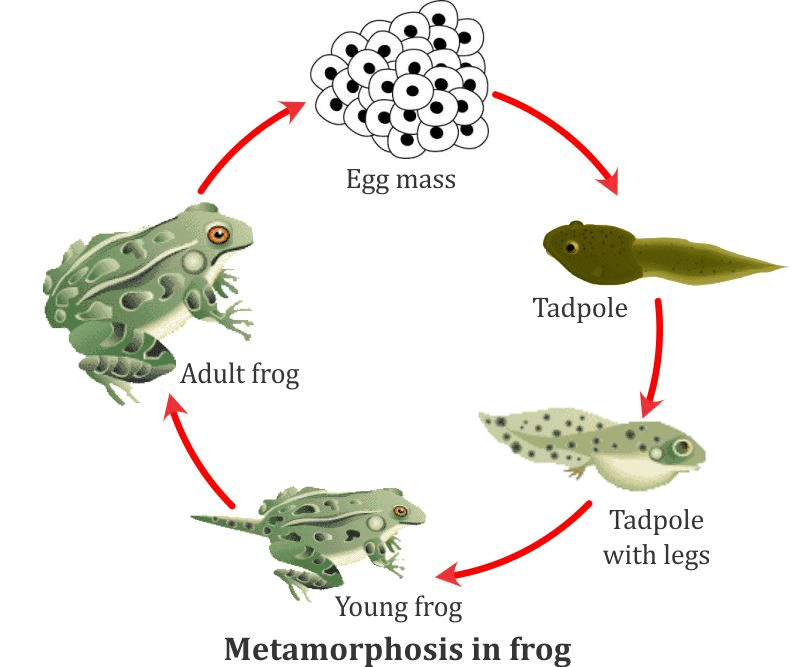
Q33. Explain the life cycle of a frog. (5 marks)
Ans:
- The life cycle of a frog begins with a fertilized egg.
- The fertilized egg develops into a tadpole.
- The fertilized egg and tadpole stages are found in the water in the spring.
- The tadpole develops into an immature froglet, then it is transformed via the process of metamorphosis into an adult frog.
- The tail is absorbed and the external gills are replaced by lungs.
- The adult frog lives on land and in the water and breathes air.
Q34. (a) What is motion?
(b) Explain two types with examples.
(c) Why measure it? (5 marks)
Ans: (a) Motion is the change in position of an object with respect to time. It is the movement of an object from one place to another.
(b) Two types of motion:
Linear motion: This is the motion of an object along a straight line. For example, a car moving on a straight road is an example of linear motion.
Periodic motion: This type of motion repeats at regular intervals. An example is a pendulum in a clock, swinging back and forth.
(c) Measuring motion is important because:
It helps us calculate speed (distance traveled in a given time).
It helps in designing machines and systems, such as calculating the rotation speed of a fan.
It provides us with useful information for safety and navigation, like determining how fast vehicles should travel on roads.
FAQs on Class 6 Science: Sample Paper Solutions - 2 - Sample Papers For Class 6
| 1. What are the main topics covered in Class 6 Science? |  |
| 2. How can students prepare effectively for their Class 6 Science exam? |  |
| 3. What types of questions can students expect in a Class 6 Science exam? |  |
| 4. Are there any recommended resources for Class 6 Science students? |  |
| 5. How important is practical work in Class 6 Science? |  |