Class 7 Civics Chapter 2 Notes - Role of the Government in Health
Introduction
In a democracy, people have the right to ask the government to take care of their needs and well-being. This includes making sure there are good schools, hospitals, jobs, homes, and basic services like roads and electricity. In this chapter, we will look closely at what "health" means and the challenges that come with it. By examining the different sections of this chapter, we can see how closely health is connected to what the government is supposed to do for its people.

What is Health?
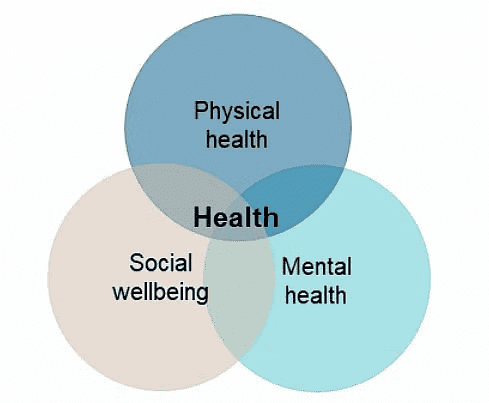
Health is a condition of complete physical, mental, and social well-being, not just the absence of disease or illness. It's important to consider various factors that influence our health. For instance, having access to clean drinking water or living in a clean environment can lead to better health. Conversely, insufficient food or overcrowded living conditions can make people more susceptible to illness. Health involves caring for one's body through proper nutrition, exercise, and hygiene, as well as having access to healthcare services when necessary. The state of our health also relies on basic facilities and social conditions, in addition to healthcare services.
Importance of Mental Well-being
We all desire to be active and feel good in whatever we do. Being dull, inactive, anxious, or fearful for long periods is not healthy. It's essential to be free from mental stress. All these different aspects of our lives contribute to our overall health. The Costa Rican government recognises that a healthy nation is vital for its development and places great emphasis on the well-being of its citizens. It provides essential services and amenities to all Costa Ricans, including:
- Safe drinking water
- Sanitation
- Nutrition
- Housing
Health education is also considered very important, and knowledge about health is a crucial part of education at all levels.
Healthcare in India
Let's look at some aspects of healthcare in India.
- To prevent and treat illnesses, we need appropriate healthcare facilities like health centres, hospitals, laboratories for testing, ambulance services, and blood banks. These facilities provide necessary care and services for patients.
- Running these facilities requires health workers such as nurses, doctors, and other professionals who can advise, diagnose, and treat illnesses.
- We also need medicines and equipment essential for treating patients.

- India has the largest number of medical colleges globally and is among the biggest producers of doctors, with over 30,000 new doctors qualifying each year.
- Additionally, India is the largest producer of medicine, aiding its healthcare system.
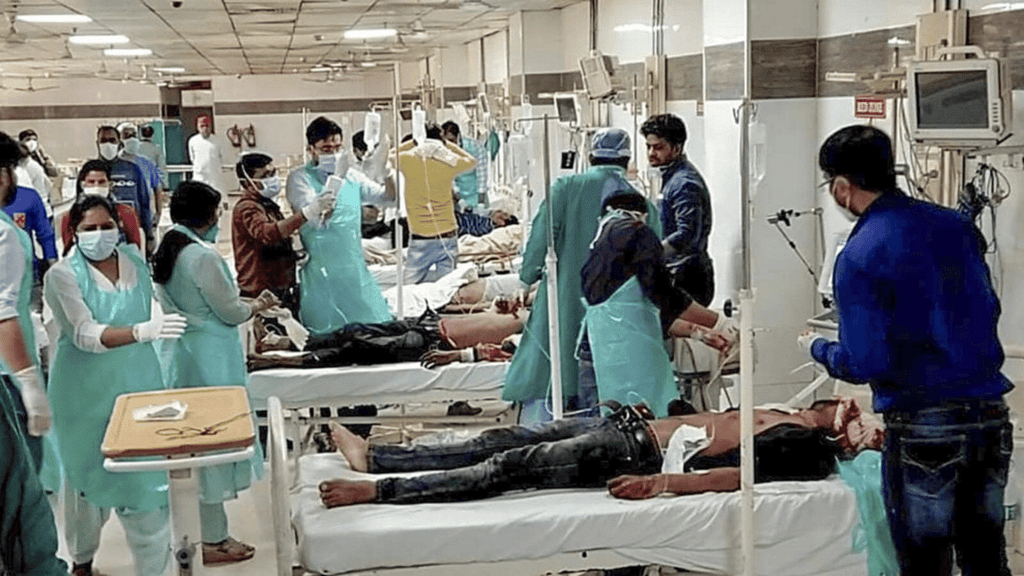
- However, it's noted that the health situation in our country is poor. Most doctors choose to work in urban areas, meaning rural people must travel long distances for treatments.
- Despite an increase in healthcare facilities, almost two million cases of malaria are reported annually, and there has been no decrease in tuberculosis cases.
- We are unable to provide clean drinking water for everyone. 21 percent of all communicable diseases are waterborne. Additionally, half of all children in India suffer from undernourishment.
- To tackle these challenges, the healthcare system possesses the knowledge and experience needed for effective implementation.
Role of government
According to our Constitution, the government has the primary duty to ensure the welfare of the people and provide healthcare facilities for all. The government's role in health is crucial for the well-being of its citizens and includes several key responsibilities:
- Health system strengthening.
- Regulation and enforcement in public health.
- Health promotion.
- Human resource development and capacity building.
- Public health policy.
- Scope for further action in the health sector.
Cost of Cure
- This section talks about the financial challenges people face when trying to get healthcare. It points out that treatments, hospital visits, and medications can be quite costly, particularly for low-income families.
- Many individuals find private healthcare unaffordable, leading them to depend on public health services, which may not always be sufficiently equipped.
- It stresses the need for government support in making healthcare affordable and accessible for everyone. The Constitution states that it is the government's main responsibility to look after the welfare of the people and provide healthcare services to reduce the financial burden on those seeking medical help.
- A study revealed that 40 percent of people admitted to hospitals for illness or injury have to borrow money or sell belongings to cover their medical costs.
- Those who are poor often suffer from malnutrition, which greatly affects their health and raises their medical expenses.
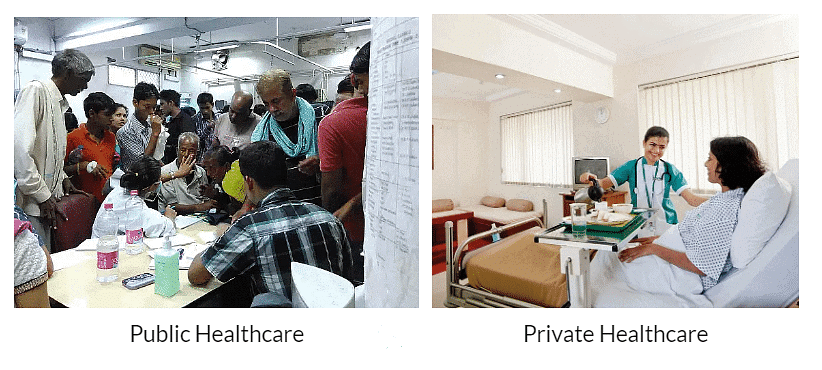
Public and Private Healthcare
The health care facilities are divided into two categories: 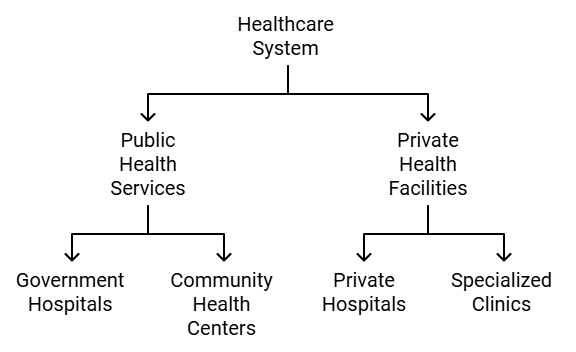
- Public Health Services
- Private Health Facilities
Public Health Services
The public health service consists of a network of health centres and hospitals managed by the government. These facilities are connected to ensure that both rural and urban areas receive care, addressing a wide range of health issues, from common ailments to specialised services.
- At the village level, health centres are staffed by a nurse and a village health worker. They are trained to handle common illnesses and operate under the guidance of doctors at the Primary Health Care (PHC). Each centre serves multiple villages in rural areas.
- At the district level, a District Hospital oversees all health centres.
- Major cities have several government hospitals, including specialised facilities.
The term 'public' health service is used for several reasons:
- The government has established hospitals and health centres for everyone, fulfilling its promise to provide healthcare to all citizens.
- The medical services are offered at a low cost to ensure that even those with limited means can access treatment.
- The funds to operate these services come from the taxes paid by the public, which contributes to keeping the costs low.
Public health services aim to prevent the spread of diseases like TB, malaria, jaundice, cholera, diarrhoea, chikungunya, and others. The government must protect every individual's right to life. According to our Constitution, it is the government's primary duty to promote the welfare of the people and provide healthcare facilities for all.
- A variety of private health facilities exist in our country.
Private Health Facilities
- A wide range of private health facilities exist in our country.
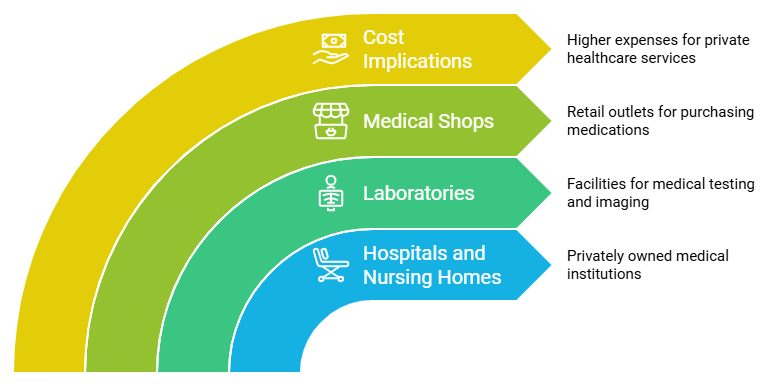 Private Health Facilities
Private Health Facilities
- Hospitals and nursing homes are privately owned, meaning they are not run by the government.
- There are many laboratories that perform tests and provide services such as X-rays and ultrasounds.
- Additionally, there are medical shops where we can purchase medicines.
- In contrast to public health services, patients in private facilities must pay significantly more for each service they receive.
Healthcare and Equality: Is Adequate healthcare available to all?

- India has experienced significant growth in private healthcare services compared to public systems. However, a major issue is that urban areas benefit more from these private services than rural ones.
- Private healthcare facilities are run by organisations, leading to high costs that many cannot afford. Those from lower economic backgrounds often have to borrow money for private healthcare.
- Some private services promote unethical practices to maximise profit. Cheaper alternatives may be overlooked; for instance, some doctors prescribe unnecessary medicines or injections when affordable oral treatments exist.
- Data shows that only 20% of the population can afford all the necessary medicines during illness.
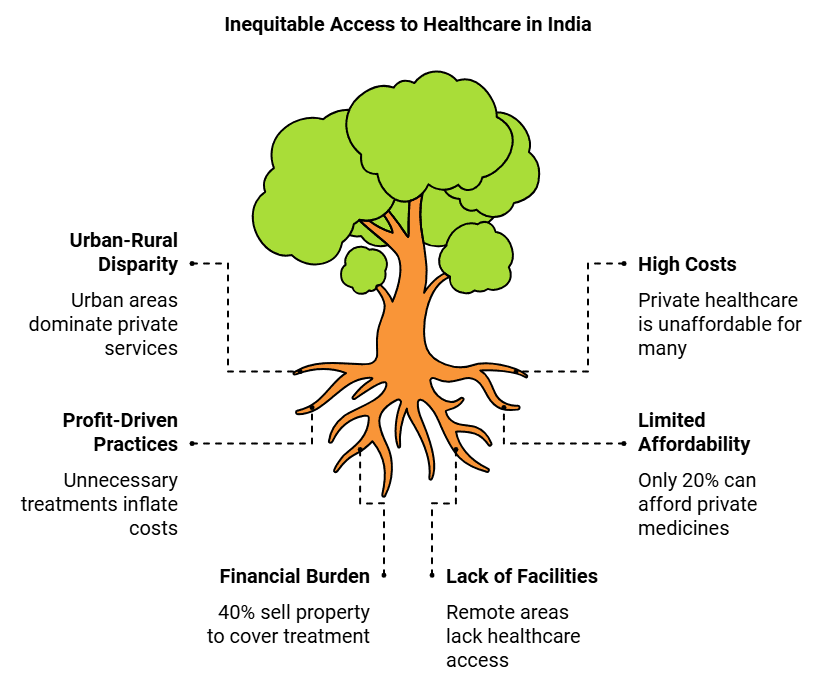
- The expenses for treatment in private hospitals can lead to financial hardship. A survey revealed that 40% of those admitted to hospitals for injuries or illnesses have to borrow money or sell belongings to cover treatment costs.
- For poor individuals, this situation can cause stress and worry.
- Those living in poverty often face undernutrition. They do not have sufficient food, clean housing, or hygienic conditions. As a result, poorer people are more susceptible to illness, and they find it impossible to afford treatment in the private sector.
- Another concern is the lack of well-functioning health centres in remote areas, making it difficult for tribal and rural communities to access healthcare services (both public and private). According to UNICEF, more than a million children die each year in India from preventable infections.
What can be done?
The government is responsible for offering quality healthcare services to all citizens, particularly the poor and disadvantaged. However, health is influenced not only by healthcare services but also by basic amenities and social conditions. Therefore, it is crucial to improve both areas to enhance the overall health of the population. Here are two examples to illustrate this point.
1) The Kerala Experience
- In 1996, the Kerala government allocated a significant amount of its total budget to local panchayats, empowering them to plan according to their needs.
- This allowed villages to effectively plan for essential services like water, food, women's development, and education. Consequently, water supply schemes were monitored, and the functioning of schools and anganwadis was ensured, while addressing specific village issues.
- Improvements were made through a broader strategy that included community participation and planning.
- Despite these initiatives, challenges such as a shortage of medicines, insufficient hospital beds, and a lack of doctors remained, which still need addressing.

It is vital to acknowledge that the government must protect the Right to Life of every individual, which is a crucial aspect of its healthcare responsibilities.
Furthermore, the paradox in India’s healthcare system reveals that despite progress, adequate healthcare facilities are not accessible to everyone.
2) The Costa Rican Approach
- Costa Rica is regarded as one of the healthiest countries in Central America.
- The primary reason for this can be traced back to the Costa Rican Constitution.
- Years ago, Costa Rica chose not to maintain an army, allowing the government to allocate funds towards health, education, and essential services for its citizens.
- The government believes that a nation's health is crucial for its progress and prioritises the well-being of its population.
- Basic services and facilities are provided to all Costa Ricans, including safe drinking water, sanitation, nutrition, and housing.
- Health education is also highly valued, and health awareness is a key part of education at every level.
FAQ's
Q.1 What is a ‘District hospital’?
Ans. A district hospital is typically its region's major healthcare facility, with many intensive care beds. It comes under the Secondary Level of Care.
Q.2 Where is 'Costa Rica' located?
Ans. Costa Rica is a republic in Central America on the Isthmus of Panama. It borders the Pacific Ocean and the Caribbean Sea.
Q.3 What are the functions of a ‘Primary health center’?
Ans. 1. Medical care
2. Maternal-child health care
3. Safe water supply
4. Prevention of local endemics
|
63 videos|371 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Civics Chapter 2 Notes - Role of the Government in Health
| 1. What is the definition of health? |  |
| 2. How is healthcare structured in India? |  |
| 3. What are the differences between public and private healthcare in India? |  |
| 4. Is adequate healthcare accessible to all sections of society in India? |  |
| 5. What role does the government play in healthcare? |  |

















