Class 8 Science: Sample Paper Solutions - 2 | Sample Papers For Class 8 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Section - A |

|
| Section - B |

|
| Section - C |

|
| Section - D |

|
Time: 3 hrs
Total Marks: 80
General Instructions:
This question paper consists of 31 questions in total and all questions are compulsory.
- Questions 1-7 are multiple-choice questions and each carries 1 mark. Write the correct answer in your answer sheet.
- Questions 8-16 are very short-answer questions and carry 2 marks each.
- Questions 17-26 are short-answer questions and carry 3 marks each.
- Questions 27-31 are long-answer questions and each carries 5 marks.
Section - A
Q1. Which of the following is a non-renewable source of energy? (1 mark)
(a) Wind energy
(b) Solar energy
(c) Coal
(d) Hydro energy
Ans: (c)
Coal is a fossil fuel that takes millions of years to form. Once used, it cannot be replaced quickly, so it is non-renewable.
Q2. Which method is used to separate cream from milk? (1 mark)
(a) Sedimentation
(b) Filtration
(c) Centrifugation
(d) Evaporation
Ans: (c)
In centrifugation, milk is spun rapidly. The denser milk separates at the bottom, while the lighter cream collects at the top.
Q3. The outermost layer of a plant cell is: (1 mark)
(a) Nucleus
(b) Cytoplasm
(c) Cell wall
(d) Cell membrane
Ans: (c)
Plant cells have an extra outer covering called the cell wall, made of cellulose, which gives rigidity and support.
Q4. Which of the following is an example of non-contact force? (1 mark)
(a) Friction
(b) Muscular force
(c) Magnetic force
(d) Force of hand while pushing
Ans: (c)
A magnet can attract or repel objects without touching them, so it is a non-contact force.
Q5. Which gas is produced during photosynthesis? (1 mark)
(a) Carbon dioxide
(b) Oxygen
(c) Nitrogen
(d) Methane
Ans: (b)
In photosynthesis, plants use carbon dioxide and water in sunlight to produce glucose, releasing oxygen as a by-product.
Q6. Which of the following is a non-biodegradable material? (1 mark)
(a) Paper
(b) Glass
(c) Cotton
(d) Cow dung
Ans: (b)
Biodegradable materials decompose naturally, but glass does not decompose easily, so it is non-biodegradable.
Q7. The SI unit of pressure is: (1 mark)
(a) Newton
(b) Pascal
(c) Joule
(d) Watt
Ans: (b)
Pressure = Force/Area. Its SI unit is Pascal (Pa), where 1 Pascal = 1 Newton per square metre.
Section - B
Q8. Define aquifer. Why is it important? (2 mark)
Ans: An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing rock or soil that stores groundwater.
It is important because it provides water for drinking, irrigation, and other human needs.
Q9. Write two uses of convex mirrors. (2 mark)
Ans:
- Convex mirrors are used as rear-view mirrors in vehicles.
- They are used in shops and malls for security purposes.
Q10. Differentiate between herbivores and carnivores with one example each. (2 mark)
Ans:
- Herbivores: Animals that eat only plants.
Example: Cow.- Carnivores: Animals that eat other animals.
Example: Lion.
Q11. Why does a freely suspended magnet always rest in the north-south direction? (2 mark)
Ans: A freely suspended magnet always rests in the north-south direction because the earth itself behaves like a giant magnet, and its magnetic field aligns the magnet with the geographic north and south.
Q12. Name two diseases caused by viruses. (2 mark)
Ans:
- Common cold
- Polio
Q13. State two differences between metals and non-metals. (2 mark)
Ans:
- Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity, while non-metals are poor conductors.
- Metals are generally malleable and ductile, while non-metals are brittle.
Q14. What are two disadvantages of friction? (2 mark)
Ans:
- Friction causes wear and tear of moving parts of machines.
- It wastes energy in the form of heat.
Q15. Why do astronauts wear special space suits? (2 mark)
Ans: Astronauts wear special space suits to protect themselves from extreme temperatures, lack of air, and harmful radiation in space.
Q16. Define manures. Give one example. (2 mark)
Ans: Manures are natural substances obtained from the decomposition of plant and animal waste, which are added to the soil to increase its fertility.
Example: Cow dung manure.
Section - C
Q17. Explain sedimentation and decantation with examples. (3 mark)
Ans:
- Sedimentation: The process in which heavier particles in a liquid settle down at the bottom due to gravity. Example: Mud particles settling at the bottom of muddy water.
- Decantation: The process of carefully pouring out the clear liquid after sedimentation without disturbing the settled particles. Example: Clear water from muddy water is separated by decantation.
Q18. State differences between heat and temperature. Give examples. (3 mark)
Ans:
- Heat: It is a form of energy transferred between bodies due to a difference in temperature.
Example: Heat flows from hot tea to a steel spoon.- Temperature: It is the degree of hotness or coldness of a body.
Example: A thermometer measures the temperature of boiling water.
Q19. Why is water called a universal solvent? Explain with an example. (3 mark)
Ans: Water is called a universal solvent because it can dissolve a large number of substances.
Example: Salt or sugar dissolves easily in water.
Q20. Explain the process of photosynthesis with a word equation. (3 mark)
Ans: Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants prepare food using carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll.
Word equation:
Carbon dioxide + Water → Glucose + Oxygen
(in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll)
Q21. How are earthquakes measured? What are their effects? (3 mark)
Ans:
- Earthquakes are measured using an instrument called a seismograph and their strength is expressed on the Richter scale.
- Effects: They cause damage to buildings, loss of life, landslides, floods, and changes in land surface.
Q22. Describe the structure and function of the human heart. (3 mark)
Ans:
- Structure: The human heart is a muscular organ with four chambers – two atria (upper chambers) and two ventricles (lower chambers). Valves are present to prevent backflow of blood.
- Function: The heart pumps oxygen-rich blood to the body and oxygen-poor blood to the lungs. It maintains continuous circulation of blood.
Q23. Give reasons: (3 mark)
(a) We should not waste paper.
Ans: Paper is made from trees. Wasting paper means cutting more trees, which leads to deforestation and environmental problems.
(b) Plastic bags should be banned.
Ans: Plastic bags are non-biodegradable. They pollute soil, choke drains, and harm animals when swallowed.
Q24. What is a constellation? Explain with two examples. (3 mark)
Ans: A constellation is a group of stars that appear to form a recognizable pattern in the night sky.
Examples:
- Orion – looks like a hunter.
- Ursa Major – also called the Great Bear or Big Dipper.
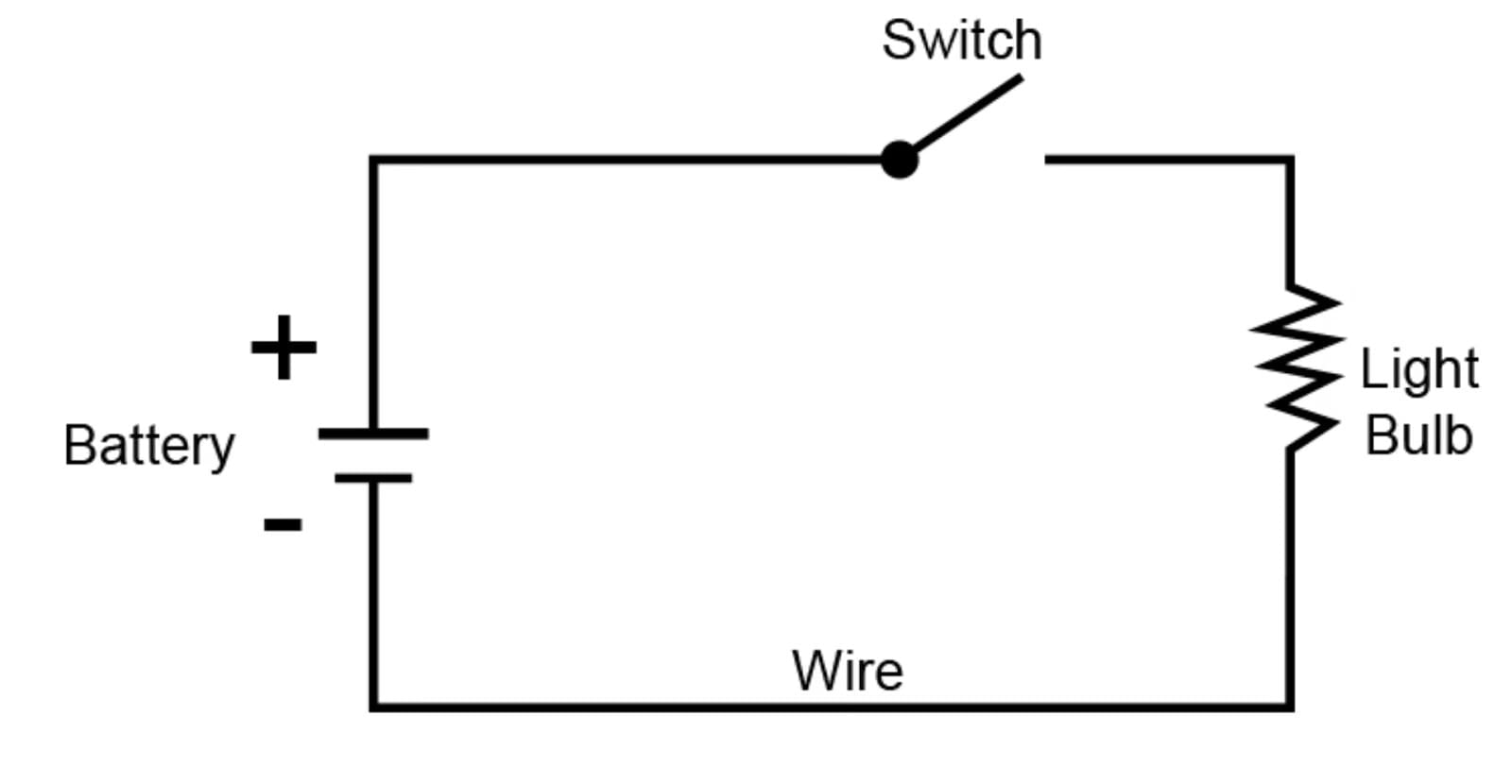
Q25. How does a simple electric circuit work? Draw a labelled diagram. (3 mark)
Ans:
- A simple electric circuit consists of a cell, wires, a switch, and a bulb.
- When the switch is closed, electric current flows from the cell through the wires and the bulb, making the bulb glow.
Q26. How does the use of fossil fuels affect the environment? (3 mark)
Ans:
- Burning of fossil fuels releases carbon dioxide, leading to global warming.
- It produces harmful gases like sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, causing air pollution and acid rain.
- Excessive use depletes natural reserves, leading to energy crises.
Section - D
Q27. (a) Define agriculture. (5 mark)
(b) Explain two modern methods of irrigation with examples.
(c) State their advantages.
Ans: (a) Agriculture: The practice of cultivating soil, growing crops, and rearing animals to provide food and other products for human use.
(b) Modern methods of irrigation:
- Sprinkler system: Water is sprayed through pipes with rotating nozzles, like artificial rain.
Example: Used in sandy soil.- Drip irrigation: Water is delivered drop by drop near the roots of plants.
Example: Used in fruit and vegetable farms.(c) Advantages:
- Save water compared to traditional methods.
- Provide uniform distribution of water, increasing crop yield.
Q28. (a) Define reflection of sound. (5 mark)
(b) Explain echo with conditions for its formation.
(c) Mention two applications of echo in daily life.
Ans: (a) Reflection of sound: The bouncing back of sound waves from a surface is called reflection of sound.
(b)
- Echo: An echo is the repetition of sound caused by its reflection from a distant surface.
- Condition: The reflecting surface must be at least 17 m away from the source of sound for humans to hear an echo.
(c) Applications:
- SONAR is used in ships and submarines to measure depth of seas.
- Bats use echoes to locate obstacles and prey.
Q29. (a) What is global warming? (5 mark)
(b) Mention three harmful effects of global warming.
(c) Suggest two ways to control it.
Ans: (a) Global warming: The gradual increase in the average temperature of the Earth due to the excessive accumulation of greenhouse gases like CO2 in the atmosphere.
(b) Harmful effects:
- Melting of glaciers causing rise in sea levels.
- Increased frequency of extreme weather events like storms and droughts.
- Loss of biodiversity due to habitat destruction.
(c) Ways to control:
- Reduce the use of fossil fuels and adopt renewable energy.
- Plant more trees to absorb excess CO2.
Q30. (a) What are simple pendulums? (5 mark)
(b) Derive the relation between time period and length.
(c) Explain one daily-life application of pendulum.
Ans: (a) Simple pendulum: A simple pendulum consists of a small bob (mass) suspended from a fixed support by a light string, free to swing back and forth.
(b) Relation between time period and length:
The time period (T) of a pendulum depends on its length (L) and acceleration due to gravity (g):
T = 2π √(L / g)
(c) Application: Pendulums are used in pendulum clocks to keep time.
Q31. (a) Define synthetic fibres. (5 mark)
(b) Mention two advantages and two disadvantages of synthetic fibres.
(c) Give two examples of synthetic fibres and their uses.
Ans: (a) Synthetic fibres: Man-made fibres produced from chemical substances are called synthetic fibres.
(b) Advantages:
- Strong, durable, and wrinkle-resistant.
- Dry quickly and are less expensive.
Disadvantages:
- Do not absorb sweat, making them uncomfortable in hot weather.
- Catch fire easily and melt on heating.
(c) Examples and uses:
- Nylon: Used in ropes, parachutes, and fishing nets.
- Polyester: Used in making clothes, bottles, and bedsheets.
FAQs on Class 8 Science: Sample Paper Solutions - 2 - Sample Papers For Class 8
| 1. What are the main topics covered in Class 8 Science? |  |
| 2. How can students effectively prepare for Class 8 Science exams? |  |
| 3. What types of questions are commonly asked in Class 8 Science exams? |  |
| 4. How important are practical experiments in Class 8 Science? |  |
| 5. What resources can students use to enhance their understanding of Class 8 Science topics? |  |