Class 9 Economics Chapter 2 Extra Question Answers - People as Resource
Q41. Visit a nearby village or a slum area and write down a case study of a boy or girl of your age facing the same condition as Vilas or Sakal.
A typical case study can be written as follows. I visited my ancestral village and found some families in a similar plight to Vikas. One boy, Puran, who is 15 years old, works as a farm labourer. In fact, all his family members are farm labourers, as they are landless and uneducated. Since there is no secondary school in the village, Puran did not study beyond class five. He does not have enough clothes and whatever clothes he is wearing are also torn and worn out with use. He and his family members are undernourished. His father has already become a patient of tuberculosis and may not live long. He feels he will forever remain a poor person.
Q42. Based on the picture can you classify these activities into three sectors?

Activities into three sectors:
(i) The photo at the top is depicting agriculture, which is a Primary sector activity.
(ii) The photo in the middle is depicting manufacturing, which is a Secondary sector activity.
(iii) The photo at the bottom is depicting shipping, which is a Tertiary sector activity.
Q43. Say whether these activities are economic or non-economic activities.
(a) Vilas sells fish in the village market.
(b) Vilas cooks food for his family.
(c) Sakal works in a private firm.
(d) Sakal looks after his younger brother and sister.
(a) Economic activity.
(b) Non-economic activity.
(c) Economic activity.
(d) Non-economic activity.
Q44. What is the role of health in human capital formation?
Role of health in human capital formation are as follow:
- Only a healthy person can work efficiently and with full potential.
- A healthy person can work in a more effective manner.
- A healthy person can work in a productive way and in this way it can contribute better in the development of the economy of the country.
- The unhealthy person becomes a liability for the organization and country.
Thus for the development of human capital and country the health is the most important component.
Q45. In which field do you think India can build the maximum employment opportunity?
India can build the maximum employment opportunities in the agricultural sector and its based industries. Agriculture is the most labour absorbing sector of the economy. When the efficient and quality packaging happen with agricultural products then it can generate a lot of employment opportunities.
Q46. Can you suggest some measures in the education system to mitigate the problem of the educated unemployed?
Measures in the education system to mitigate the problem of the educated unemployed:
- Make education at the secondary level more career-oriented, which would endow individuals with not only education but also the requisite skills for gaining successful employment.
- Create a sort of screening process whereby each individual chooses subjects that suit his or her abilities.
- The introduction of newer subjects and fields of study at the school level should be accompanied by a growth of job opportunities in the sectors that would employ the students electing to study such subjects.
Q47. Can you imagine some village which initially had no job opportunities but later came up with many?
Rampur was a small village which initially depended on agriculture which was also dependent on rainfall:
(i) Then electricity reached the village and people could irrigate their fields and could grow 2 to 3 crops in a year and get work.
(ii) Some people set up small scale industries which could be run by electricity and provided employment to people.
(iii) A school was established and now the population started to become educated and as a result they could seek employment in and outside the village. The village became prosperous and soon had better health, education, transport and job facilities.
Q48. Which capital would you consider the best - land, labour, physical capital and human capital? Why?
- Human Capital is the best resource.
- Physical Capital and land resources need human capital to become useful, those resources cannot become useful on their own.
- Human capital utilises the land, labour and physical capital to achieve higher growth of the economy.
- The Green Revolution in India is an example of human capital having better knowledge which led to increased production and thereby helping to achieve self-sufficiency in the domain of agriculture in India.
- The IT revolution in India was led by the human capital. This goes on to prove the superiority of human capital resources over other types of resources.
- A country like Japan has very little resources, yet they are a very developed country, this is the result of investment on its people by Japan, through healthcare and education.
- These educated citizens of Japan made efficient utilization of other resources like capital and land.
- The investment in human capital is through healthcare, training and education.
- A healthier and educated person not only helps himself by earning higher incomes, but society also gains indirectly.
Q49. Why is human resource considered to be the best resource? Explain. Or Why is human resource superior to any other resource? Explain with the help of three arguments.
Human resource is considered to the best resource because
(i) It is a way of referring to country's working people in terms of their existing productive skills and abilities.
(ii) Looking at the population in form of human resource emphasises its ability to contribute to the creation of the Gross National Product.
(iii) When existing human resource is developed by becoming more educated and healthy, we call it 'human capital formation' that adds to the productive power of country just like 'physical capital' formation.
Q50. Why do educated parents invest more heavily in their children's education? Give three reasons.
Educated parents invest more heavily in their children's education because
(i) They know the value of education and understands that education is important for the development of children.
(ii) They usually plan their children’s education more efficiently as they are experienced and understand the process of development.
(iii) Educated parents know that intellectual and mental level of uneducated children is very low and they do not know anything about the world.
(iv) Analytical thinking of uneducated children is also very low.
Q51. What is meant by 'People as Resource'? Explain how is human resource different from other resources like land and physical capitals?
People as Resource is a way of referring to a country's working people in terms of their existing productive skills and abilities.
Human resource is different from other resources in many senses. Human resources need education, training and healthcare to develop. On the other hand, land and physical capital need money and physical inputs to develop. Land and physical capital are useless without human resources.
Q52. What is meant by economic activities and how are these classified? Give one example of each. Or Distinguish between market and non-market activities with three points of distinction, Or What are the two types of economic activities? State two characteristics of each.
An economic activity is an activity of providing, making, buying, or selling of commodities or services by people to satisfy their day-to-day needs of life. Economic activities include any activity that deals with the manufacturing, distributing, or utilising of products or services.
Activities that involve money, or the exchange of products or services, are economic activities.
The three types of economic activities are as follows:
- Business: This economic activity provides goods and services to satisfy human needs on a daily basis with the aim of earning profits.
- Profession: It can also be defined as an occupation or a professional job that offers specialised services in return for professional charges.
- Employment:This activity is based on a contract between the company and the employee. Here, the employee performs duties for the company, and is paid (with wages or a salary) in return.
Or
The activities which focus on the production of goods and services and add value to the national income are referred to as economic activities. It has two parts - the market and non-market activities.Or
Economic activities are those activities which add value to the national income.
Economic activities have two parts:
(i) Market activities.
(ii) Non-market activities.
Market activities:
(i) These are the activities performed for payment or profit.
(ii) They include production of goods and services.
Non-market activities:
(i) These involve production for self-consumption.
(ii) It includes consumption of primary production and production of fixed assets.
Q53. Explain the four requirements for the production of goods and services. What are the items that come under physical capital ?
The four main requirements for the production of goods and services are
- The first requirement is land and other natural resources.
- The second is labour i.e., people who carry out the work for production.
- The third is physical capital i.e., varieties of inputs that are required for production such as fixed capital (Building, equipment, machinery and tools, etc.) and working capital (cash, raw materials, etc).
- The fourth requirement is human capital, which may include technology, qualified manpower, etc. The items under physical capital are fixed capital and working capital.
Q54. What are the two types of unemployment found in rural areas? How does unemployment affect the overall growth of an economy? Explain by giving four points.
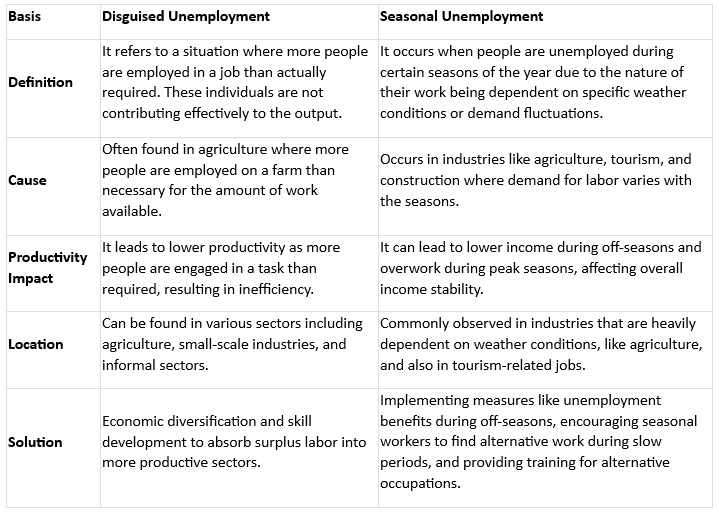
Two types of unemployment found in rural areas are
- Seasonal Unemployment Agriculture being a seasonal activity, most of the labour is required during sowing and harvesting. At other times the labour is unemployed.
- Disguised Unemployment This occurs when all the members of a family of a small farmer are working in the fields, but all may not be required. For instance, the farmer may require only five labourers for the work, but because eight are available, all are working. Actually they are working at less than full productivity. Unemployment affects the overall growth of an economy as
i) it is a wastage of manpower resource.
ii) it increases the economic overload.
iii) it tends to increase the number of dependent population.
iv) increase in unemployment is an indicator of a depressed economy.
Q55. Why are women employed in low paid work?
Education is one of the major determinants of the earning of an individual in the market. As a majority of the women in India have lesser education and lesser skill training than men due to traditional reasons, they are paid less than men or are employed in low paid work. Another reason is that jobs involving physical labour are entrusted to men only due to their physique; here women cannot do as much physical work as men. Women also generally have an additional responsibility of bringing up their family and children and so they cannot be as regular as men in their duties. So, they are often given non-critical and low paid duties.
Q56. Why is educated unemployment, a peculiar problem of India ?
Educated unemployment is a peculiar problem of urban India. This is the situation wherein a number of youth with matriculation, graduation and post graduation degrees are not able to find suitable jobs. The education system is such that even after about 18 years of education, a person is practically 'unskilled'. So, a large number of unskilled educated youth get churned out of educational institutions year after year, but only a fraction of them are able to find suitable jobs. Among the remaining, some remain unemployed while others get employed in activities that are not as per their potential, i.e., they are underemployed. In effect, it is wastage of the resources spent on educating them.
Q57. What are the objectives of India's national policy on health? Suggest two ways in which the policy objectives can be met.
The objectives of the national health policy (2002) are as follow
- Enhancing the contribution of Private sector in providing health service for people who can afford to pay.
- Giving primacy for prevention and first line curative initiative.
- Emphasising rational use of drugs.
- Increasing access to tried systems of traditional medicine.
Some of the policy objectives can be met through the following methods.
- Increasing the number of trained nurses or midwives to one per village.
- Making available generic medicines (instead of branded medicines) at all government dispensaries. There are many other methods for fulfilling the other policy objectives.
Q58. What is the mid-day meal scheme? Explain its purpose.
The Mid-day meal scheme was started to provide a cooked Mid-day meal on every school day with nutritional content of 450 calories, 12 gms proteins and other micro nutrients to all children studying in classes I to VIII in government, local body and government aided schools, etc. The basic purpose of this scheme was to improve enrollment, retention and attendance of the children in school and simultaneously improving nutritional levels among them. This encouraged poor children, belonging to disadvantaged sections, to attend school more regularly and help them concentrate on classroom activities. An additional purpose was to provide nutritional support to children of primary classes in drought affected areas during summer vacation.
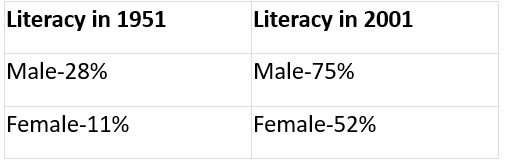
Q59. Study the graph and answer the following questions.
(a) Has the literacy rates of the population increased since 1951 ?
(b) In which year, India has the highest literacy rates?
(c) Why literacy rate is high among the males of India?
(d) Why are women less educated than men?
(e) How would you calculate literacy rate in India?
Yes, the literacy rates of the population have increased since 1951 as shown below.
Q60. What do you understand by 'people as a resource'?
'People as a resource' is a way of referring to a country's working people in terms of their existing productive skills and abilities. Because the humans contribute to GDP, they are also considered as a resource.
Q61. What is the difference between disguised unemployment and seasonal unemployment?
Q62. "Sakal was meritorious and interested in studies from the beginning. After sometime he got a job in a private firm..... His boss acknowledged his services and rewarded him with a promotion." "Vilas's father Mahesh was a fisherman, who passed away when he was only two years old. His mother Geeta sold fish to earn money to feed the family. She could earn only Rs. 20 to 30 a day by selling fish. Vilas......was not interested in studies. He helped his mother in cooking and also looked after his younger brother Mohan. After his mother died, Vilas, too, was forced to sell fish in the same village. He, like his mother, earned only a meagre income." Sakal and Vilas are friends. What has Vilas not got which Sakal had? Is it possible for Vilas to improve his financial position now? If so how? Explain in about 120 words.
Answer: Vilas has not received the same educational opportunities and job prospects that Sakal had. Sakal's merit and interest in studies led to him securing a job in a private firm and subsequently earning a promotion. In contrast, Vilas faced a disadvantaged upbringing, with his family struggling to make ends meet through low-income activities like selling fish. Vilas did not have the chance to pursue education and career advancement as Sakal did.
However, it is possible for Vilas to improve his financial position at this point in his life. He can consider the following steps:
- Education: Vilas could explore opportunities for adult education or vocational training programs to acquire new skills and qualifications that would make him eligible for better job prospects.
- Entrepreneurship: With his experience in the fishing industry, Vilas could explore the possibility of starting a small business related to fisheries or any other local venture. This could potentially increase his income.
- Government Support: He could inquire about government welfare programs, scholarships, or subsidies for adult learners or individuals looking to start their own businesses.
- Financial Planning: Vilas should focus on efficient financial management and savings to gradually improve his financial stability over time.
While Vilas faced initial challenges, with determination and the right support, he can work towards a better financial future and break the cycle of meager income.
Q63. How is human resources different from other resources like land and physical capital?
Human resource is different from other resources in many senses. Human resources need education, training and healthcare to develop. On the other hand, land and physical capital need money and physical inputs to develop. Land and physical capital are useless without human resources.
Q64. The quality of a population depends on which factors?
The quality of a population depends on literacy, skill development, life expectancy and health.
Q65. Distinguish between physical and human capital.
Physical capital includes the variety of inputs required at all stages of a production activity. This includes fixed capital and working capital in the form of machinery, land and building, raw materials, cash in hand, etc. In contrast, human capital is the stock of competencies, knowledge, social and personality attributes, including creativity, embodied in the ability to perform labour so as to produce economic value. Here, it refers to the persons performing the economic activity like labourers, knowledge persons and others involved in the activity.
|
56 videos|439 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Economics Chapter 2 Extra Question Answers - People as Resource
| 1. What is meant by 'People as Resource'? |  |
| 2. How does education impact human capital? |  |
| 3. Why is health considered a vital component of human resources? |  |
| 4. What are the benefits of viewing people as resources in economic planning? |  |
| 5. How can governments enhance the quality of human resources? |  |