Class 9 Geography Chapter 1 Extra Question Answers - India - Size and Location
Q1. What is the Easternmost longitude of India?
Ans: The Easternmost longitude of India is 97°25' E.
Q2. What is the longitude of the Westernmost point of India?
Ans: 68°7' East longitude.
Q3. Which Indian states have common frontiers with our neighboring country, Bhutan?
Ans: The states of West Bengal, Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, and Sikkim have common frontiers with Bhutan.
Q4. Name the countries sharing a land boundary with India.
Ans: The countries are Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, Myanmar, Nepal and Pakistan.
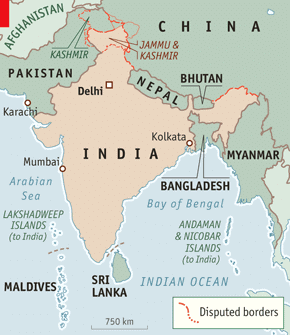 India's Neighbouring CountriesQ5. If you go to Silvassa, which union territory will you be in?
India's Neighbouring CountriesQ5. If you go to Silvassa, which union territory will you be in?
Ans: You will be in the union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli, as Silvassa is its capital.
Q6. What happened to the southernmost point of the Indian Union, Indira Point, in 2004?
Ans: Indira Point, the southernmost point of the Indian Union, got submerged under seawater during the 2004 tsunami.
Q7. Which Indian states border three countries?
Ans: The Indian states that border three countries are:
- Sikkim: Sikkim is a State in Northeast India. It is one of the fastest-growing, multiethnic, and multilingual Indian states. It borders Tibet in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Nepal in the west, and West Bengal in the south. Sikkim is also located close to India's Siliguri corridor, which is near Bangladesh.
- Arunachal Pradesh: Arunachal Pradesh, situated in the north-eastern part of India, is 83,743 sq km in area and has a long international border with Bhutan to the west (160 km), China to the north and north-east (1,080 km), and Myanmar to the east (440 km).
- Jammu and Kashmir: Jammu and Kashmir, formerly one of the largest princely states of India, is bounded to the east by the Indian union territory of Ladakh, to the south by the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab, to the southwest by Pakistan, and to the northwest by the Pakistani-administered portion of Kashmir.
Q8. Name the group of islands lying in the Arabian Sea.
Ans: The Lakshadweep islands lie in the Arabian Sea. 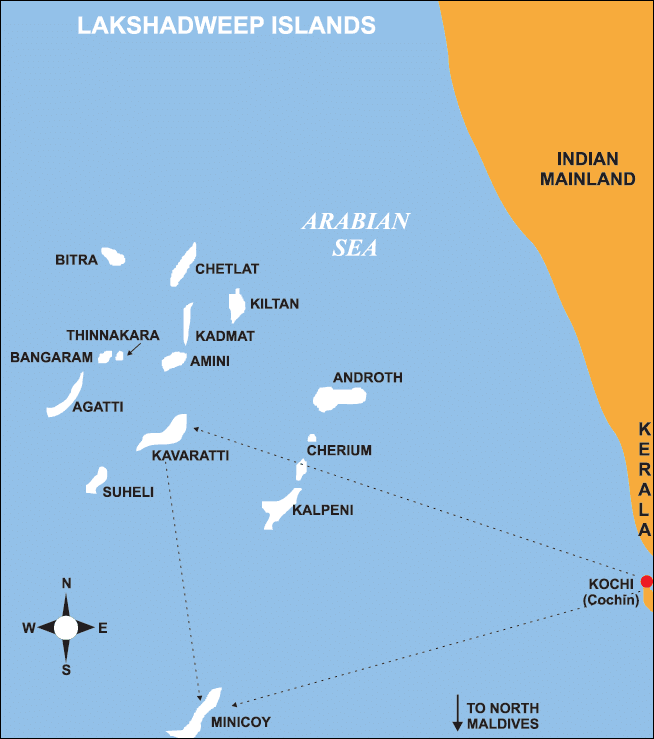 Lakshadweep Islands
Lakshadweep Islands
Q9. Why is there a time lag of two hours from Gujarat to Arunachal Pradesh?
Ans: India extends about 30° in longitudinal extent, from Gujarat in the west to Arunachal Pradesh in the east. Since each degree of longitude corresponds to a time difference of 4 minutes, there is a total time lag of approximately 2 hours between these two places. To maintain a uniform time across the country, the Standard Meridian of India (82°30' E) is used as the reference for Indian Standard Time (IST).
Q10. What is the significance of India’s location in the Indian Ocean?
Ans: India's location in the Indian Ocean is strategically significant as it helps in establishing close trade and cultural connections with West Asia, Africa, and Europe from its western coast, and with Southeast and East Asia from its eastern coast. The Deccan Peninsula extends into the Indian Ocean, making India a central point for trans-Indian Ocean trade routes. This prominent position justifies naming the ocean after India.
Q11. Which countries are land neighbors of India?
Ans: China, Bhutan, Nepal, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Myanmar
Q12. Which union territory of India has the least area?
Ans: The union territory of Lakshadweep has an area of only 32 sq km, which is the least among all the union territories.
Q13. Which state of India has the least area?
Ans: The state of Goa has an area of 3702 sq km, which is the least among all the states (Delhi is considered a union territory, not a state).
Location of Goa in India
Q14. Why has 82°30' E been selected as the Standard Meridian of India?
Ans: India has a longitudinal extent of about 30°, which results in a time lag of nearly two hours between Arunachal Pradesh in the east and Gujarat in the west. To avoid confusion, the longitude 82°30' E, which passes through Mirzapur in Uttar Pradesh, has been selected as the Standard Meridian of India. This ensures a uniform time (Indian Standard Time) across the country.
Q15. What is the latitude of the Southernmost point on the Indian mainland?
Ans: The Southernmost point on the Indian mainland is Kanyakumari, at a latitude of 8°4' N.
Q16. Which union territory was converted into a state in 1987?
Ans: Goa was a union territory when it became independent from Portuguese rule in 1961. It was made into a state in 1987.
Q17. What is India’s rank in the world in terms of land area, and what is its total area?
Ans: India is the seventh-largest country in the world in terms of land area. It has a total area of 3.28 million square kilometers, which accounts for about 2.4% of the total geographical area of the world.
Q18. Was India's contact with the world first established by land routes or sea routes?
Ans: The land routes, because of the various passes across the mountains in the North, have provided passages to the ancient travelers, while the oceans restricted such interaction for a long time.
Q19. Which states of India does the Tropic of Cancer pass through?
Ans: The Tropic of Cancer passes through the states of Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Tripura and Mizoram. 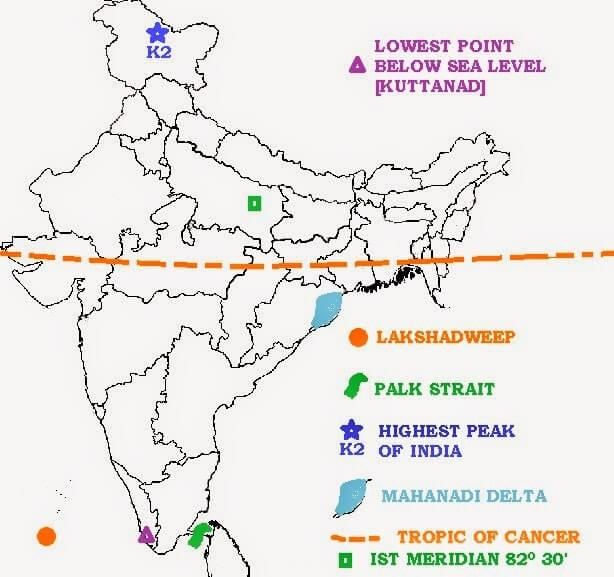 Tropic of CancerQ20. Which country has a common frontier with the four Indian states of Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal, and Sikkim?
Tropic of CancerQ20. Which country has a common frontier with the four Indian states of Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal, and Sikkim?
Ans: The country that has a common frontier with these Indian states is Nepal.
Q21. If you intended to visit Kavaratti during your summer vacations, which union territory of India will you be going to?
Ans: Kavaratti is the capital of the union territory of Lakshadweep.
Q22. In which year did the Indira Point get submerged under the seawater?
Ans: 2004 was the year when Indira Point was submerged under seawater. It was situated on Great Nicobar Island in the Nicobar Islands, which are located in the eastern Indian Ocean at 6∘45′10′N and 93∘49′36′E.
Q23. Name the imaginary line in India along which time is taken as standard time.
Ans: Standard Meridian is the imaginary line in India along which time is taken as standard time.
Q24. What is the length of the Indian coastline?
Ans: The length of the Indian coastline is 7516.6 km.
Q25. What is the East-West extension of India in kilometers?
Ans: The distance of the East-West extension of India is 2933 km. East-west extension of India
East-west extension of India
Q26. What is India's position with respect to its area in the world?
Ans: India holds the 7th position in the world in terms of area. India's total landmass measures around 3.28 million sq. km.
Q27. Name the water bodies that separate Sri Lanka from India.
Ans: Palk Strait and the Gulf of Mannar are water bodies that separate Sri Lanka from India.
Q28. What is the length of the Indian land boundary?
Ans: The length of the Indian land boundary is 15200 km.
Q29. If you want to visit Lakshadweep during your winter holiday, which water body you have to cross?
Ans: We have to cross the Arabian Sea if we visit Lakshadweep.
Q30. How many countries in the world are larger than India in terms of land area? Name them according to their position.
Ans: There are six countries in the world larger than India. They are Russia, Canada, China, the United States of America, Brazil and Australia.
Q31. What is the North-South extension of India in kilometers?
Ans: The distance of the North-South extension of India is 3214 km.
Q32. Which latitudinal line divides India into approximately two equal parts?
Ans: The latitudinal line that divides India into two equal parts is the Tropic of Cancer.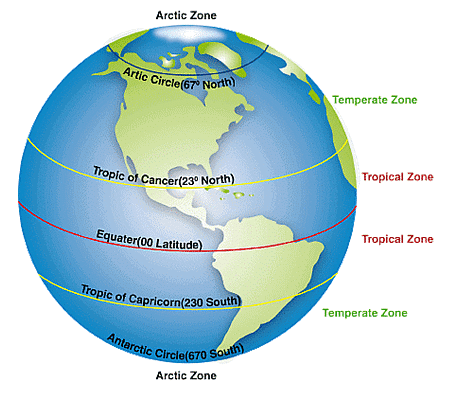
Q33. Why does the sun rise two hours earlier in Arunachal Pradesh as compared to Gujarat, but the watches show the same time?
Ans: Due to India's east-west longitudinal extent of about 30°, Arunachal Pradesh in the east experiences sunrise about two hours earlier than Gujarat in the west. However, the entire country follows Indian Standard Time (IST), which is based on the Standard Meridian at 82°30' E. This ensures that all watches in India show the same time despite the difference in actual sunrise and sunset timings.
Q34. Why days and nights are almost of equal duration at Kanyakumari?
Ans: The day and night are nearly of the same duration at the equator. As Kanyakumari is quite near the equator at 8°4'N, the difference between the day and night is hardly one hour, and therefore, the duration of day and night is hardly felt at Kanyakumari.
Q35. Which country shares the longest boundary with India?
Ans: Bangladesh shares the longest boundary with India. It is 4053 km long. 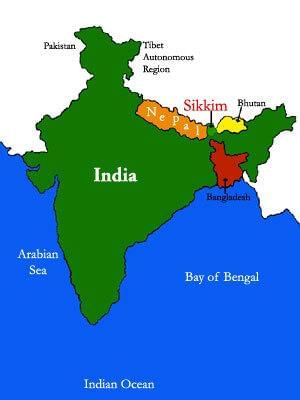 Bangladesh shares border with India
Bangladesh shares border with India
Q36. Which state has the longest coastline in India?
Ans: Gujarat has the longest coastline in India along its Kathiawar region. The length of the Gujarat coastline is about 1600 km, surrounded by the Arabian Sea.
Q37. Just before independence, how were the Provinces and states in India organized?
Ans: Just before independence in 1947, there were two types of states in India. The Provinces and the Princely states. Provinces were ruled directly by British officials who were appointed by the Viceroy. Princely states were ruled by local, hereditary rulers who acknowledged the sovereignty of the British in return for local autonomy. Examples of the rulers of Princely states are the Nizam of Hyderabad and Maharaja Hari Singh of Jammu and Kashmir.
Q38. What is the strategic significance of India's location in Asia?
Ans: The Indian landmass has a central location between East and West Asia. The trans-Indian Ocean routes, which connect the countries of Europe in the West and the countries of East Asia, provide a strategic central location to India. 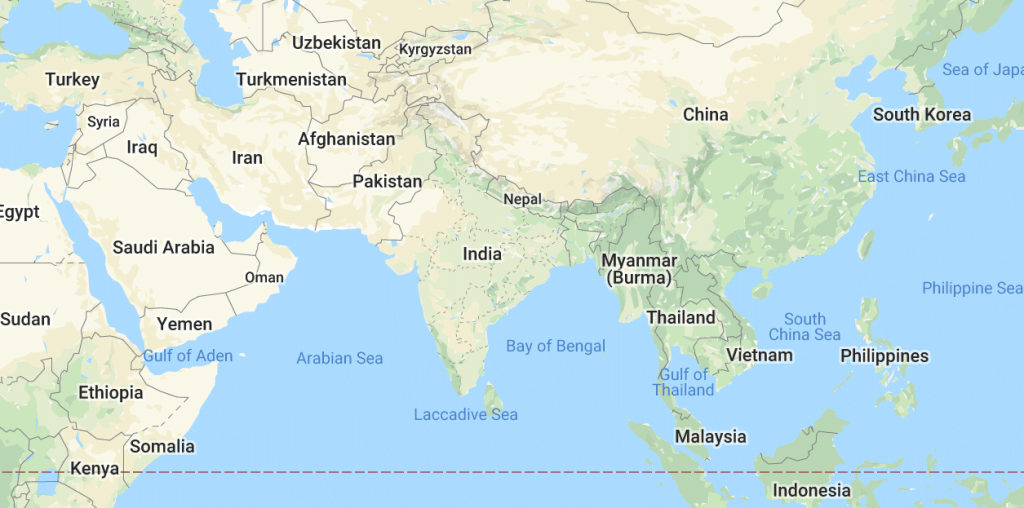 Location of India in AsiaThe various passes across the mountains in the North have provided passages to the ancient travelers. These routes have contributed to the exchange of ideas and commodities since ancient times. Thus, India is very strategically located.
Location of India in AsiaThe various passes across the mountains in the North have provided passages to the ancient travelers. These routes have contributed to the exchange of ideas and commodities since ancient times. Thus, India is very strategically located.
Q39. How does India's longitudinal extent affect time, and how is a uniform time maintained across the country?
Ans: India's longitudinal extent is about 30°, which creates a time difference of nearly two hours between Arunachal Pradesh in the east and Gujarat in the west. To maintain a uniform time across the country, 82°30' E longitude, passing through Mirzapur in Uttar Pradesh, has been chosen as the Standard Meridian of India. The local time at this meridian is taken as Indian Standard Time (IST) for the entire country.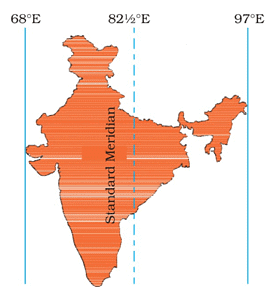 Indian Standard Time
Indian Standard Time
Q40. Why is the difference between day and night durations not felt at Kanyakumari but not so in Kashmir?
Ans: Since the axis of rotation of the Earth is tilted at 23.5° to the perpendicular, the circle of illumination of the Earth varies from summer to winter. At the equator, it does not cause any time difference between day and night throughout the year, but North or South of it, the durations vary. Kanyakumari is close to the equator, while Kashmir is far away. So, this difference is felt in Kashmir in winter or summer but not in Kanyakumari.
|
55 videos|635 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Geography Chapter 1 Extra Question Answers - India - Size and Location
| 1. What is the geographical size of India compared to other countries? |  |
| 2. What are the neighboring countries of India? |  |
| 3. How does India's location affect its climate? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of India's location in terms of trade? |  |
| 5. How does India's topography vary across different regions? |  |

















