Class 9 Geography Chapter 2 Extra Question Answers - Physical Features of India
1) What is the location of the Purvachal mountain range in India?
Ans: Purvachal range lies along the Eastern edge of India and forms the boundary with Myanmar. 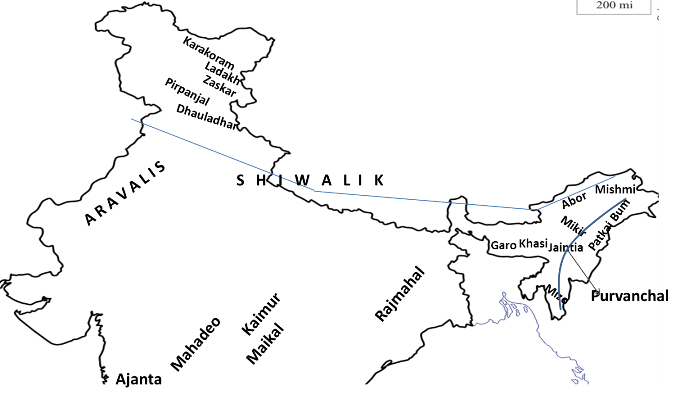 Purvanchal in east India2) 'Folding' and 'faulting' are the result of what geological actions?
Purvanchal in east India2) 'Folding' and 'faulting' are the result of what geological actions?
Ans:'Folding' and 'faulting' are the results of the movement of tectonic plates.
3) Why is the Himadri mountain range called by this name?
Ans: Himadri in Sanskrit means 'mountain top of snow' and this range is perpetually snowbound.
4) What is orographic rainfall?
Ans: This is rainfall caused when masses of air pushed by wind are forced up the side of elevated land formations like mountains. Orography is the study of the physical geography of mountains and mountain ranges.
5) Which island in the Lakshadweep group of islands has a bird sanctuary?
Ans: The bird sanctuary is located on Pitti Island.
6) Which variety of rock is used for making talcum powder?
Ans: Soapstone rock is used for the manufacture of talcum powder, as it is a very soft rock.  Soapstone rock7) What do we mean by the term Bhangar?
Soapstone rock7) What do we mean by the term Bhangar?
Ans: Bhangar is the older alluvial soil region lying above the flood plains and presenting a terrace-like feature.
8) Which two well-known rivers originate near the Mahadeo hills?
Ans: The rivers originating near the Mahadeo hills are the Narmada and the Son.
9) The Terai belt lies North of which belt?
Ans: The Terai belt lies North of the Bhangar belt.
10) What is the name of the part of the Himalayas lying between the Kali and the Tista rivers?
Ans: The part of the Himalayas lying between the Kali and the Tisca rivers is called Nepal Himalayas.
11) What is the location of the Satpura mountain range in comparison with the Aravali mountain range?
Ans: The Satpura range is to the South of the Aravali range.
12) What is the variation in height in the Shivalik mountain range?
Ans: The height of the Shivalik mountain range varies from 900 to 1100m.
13) Which area of India is a flat land of extensive alluvial deposits?
Ans: The Northern Plains is a flat land having extensive alluvial deposits from the rivers flowing in it.
14) Which major rivers of the Indian subcontinent flow into the Arabian Sea?
Ans: The major rivers of the Indian subcontinent flowing into the Arabian sea are Indus (with a delta) and the Narmada and Tapi (as estuaries).
15) Why do landslides occur frequently in the Shiwaliks?
Ans: The Shiwaliks are composed of unconsolidated sediments brought down by rivers from the main Himalayan ranges and thus are prone to landslides.
16) Arrange the given mountain peaks in order of height, starting from the lowest: Doda Betta, Kanchenjunga, Mahendragiri and Namcha Barwa.
Ans: The heights of the peaks are
1. Mahendragiri 1501 m (lowest)
2. Doda Betta 2637 m
3. Namcha Barwa 7756 m
4. Kanchenjunga 8598 m (highest)  Kanchenjunga peak17) What makes up the habitat in which coral polyps flourish?
Kanchenjunga peak17) What makes up the habitat in which coral polyps flourish?
Ans: The coral polyps flourish in a habitat consisting of shallow warm water which does not have mud. This kind of habitat is found in Lakshadweep.
18) The state of Meghalaya forms a part of which physiographic division of India?
Ans: Meghalaya is part of the Eastern extension of the Peninsular plateau.
19) Arrange the given ranges of the Himalayas starting from the Westernmost and moving Eastwards Assam Himalayas, Kumaon Himalayas, Nepal Himalayas and Punjab Himalayas.
Ans: The order is Punjab Himalayas (Westernmost), Kumaon Himalayas, Nepal Himalayas and Assam Himalayas (Easternmost).
20) Are the Aravali hills located in the Western Ghats or the Eastern Ghats?
Ans: The Aravali hills are neither in the Eastern nor in the Western Ghats, but are located North of both on the Peninsular plateau.
21) Which of the two has a higher average height, the Eastern Ghats or the Western Ghats?
Ans: The average height of the Western Ghats is 900 to 1600 m, whereas the average height of the Eastern Ghats is only about 600 m. Thus the Western Ghats are higher.
22) What is the Southern part of the Western coastal plains known as?
Ans: This is known as Malabar (mostly in Kerala).
23) In which mountain range is the Khyber Pass located?
Ans: The Khyber Pass is located in the Sulaiman Range (Afghanistan-Pakistan border).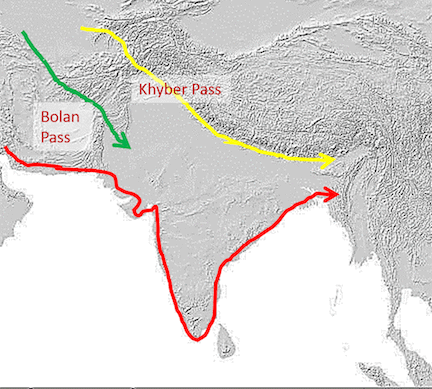 Khyber pass 24) What is the highest peak in the Eastern Ghats and what is its height?
Khyber pass 24) What is the highest peak in the Eastern Ghats and what is its height?
Ans: Mahendragiri at a height of 1501 m is the highest peak in the Eastern Ghats.
25) What do you understand by the term "Peninsula"?
Ans: The Peninsula is a landmass that is bounded by the sea on three sides.
26) What is the name of the Western coastal strip that lies in the South of Goa?
Ans: Konkan Region.
27) Name the oldest part of the Indian landmass.
Ans: The Peninsular Plateau is the oldest landmass of India.
28) Name the hills that lie at the junction of Western and Eastern Ghats.
Ans: The Nilgiri hills in Tamil Nadu lie at the junction of the Eastern and the Western Ghats.
29) What is the name of the wet and swampy belt of the Northern region?
Ans: The wet, swampy and marshy belt of the Northern plains is known as terai.
30) What is the name of the part of the Northern plain formed by older alluvium?
Ans: The part of the Northern plains formed of older alluvium is called the Bhangar.
31) Name the Indian state where Kanchenjunga is located.
Ans: Kanchenjunga is located in the Indian state of Sikkim.
32) Which part of the Indian coastal plain is known as Northern Circ00ar?
Ans: The Northern part of the Eastern coastal plains is known as Northern Circar.
33) Name the highest peak which lies in the Western Ghats.
Ans: Anai Mudi is the highest peak in the Western Ghats. Its height is 2695 metres.
34) Which island of India has the only active volcano in India?
Ans: India's only active volcano is found on Barren island in the Andaman and Nicobar group of islands.
35) Make a comparison between the Shiwaliks and Himachal Himalayas based on the following
(i) Composition
(ii) Age
(iii) Altitude
Ans: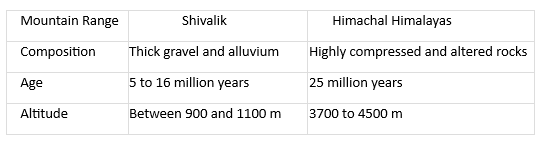
36) Give a description of the Shivalik.
Ans: The Shiwaliks are the outermost range of the Himalayas. Their altitude varies from 900 to 1100 m and the length of the range is about 2400 km from Jammu and Kashmir to Arunachal Pradesh. The width of this range varies from 10 to 50 km. It is composed of thick gravel and alluvium brought down by rivers.
37) Compare the features of the Western Ghats with those of the Eastern Ghats in tabular form.
Ans: 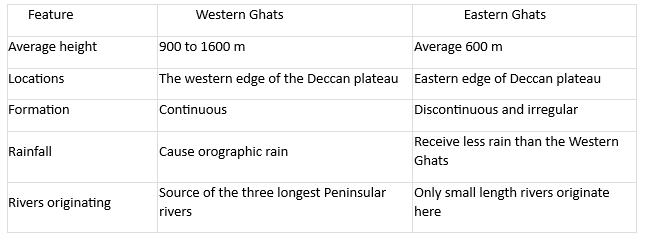
38) How were the Northern plains formed?
Ans: The Northern plains have been formed by three major river systems, namely the Indus, the Ganga and the Brahmaputra, along with their tributaries. These plains are formed of alluvial soil. The deposition of alluvium in a vast basin lying at the foothills of the Himalayas over millions of years formed these fertile plains. With a rich soil cover combined with an adequate water supply and favourable climate, it is agriculturally a very productive part of India.
39) Assume that you have recently travelled in the Indian desert. Describe the desert to a person not living in India.
Ans: The desert in India lies to the West of the Aravali Hills in the states of Rajasthan and Gujarat. In India, it covers an area of more than 250000 square km. It has an arid climate with an annual rainfall of less than 150 mm. It is a sandy plain with very little vegetation. Barchans (crescent-shaped dunes) cover larger areas, but longitudinal dunes become more prominent near the Indo-Pakistan boundary.
40) What are the differences between the Central Highland and Deccan Plateau?
Ans: 
41) Find out the names of the glaciers and passes that lie in the Great Himalayas.
Ans: The names of the glaciers that lie in the Great Himalayas are
(a) Siachen Glacier-Jammu and Kashmir
(b) Godwin Glacier-Jammu and Kashmir
(c) Gangotri Glacier-Uttarakhand
(d) Yamunotri Glacier-Uttarakhand Passes that lie in the Great Himalayas Himachal Pradesh Rohtang Pass, Karakoram Pass, Rupin Pass Sikkim Nathu La, Jelep La Uttarakhand Mana Pass
42) Name the three major divisions of the Himalayas from North to South.
Ans: The three major divisions of the Himalayas from North to South are as follow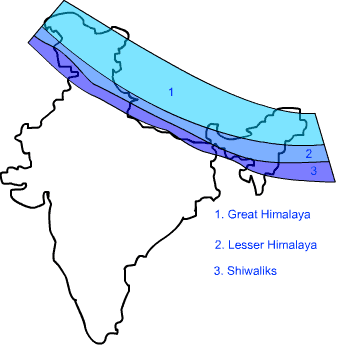 Fig: Three major divisions of Himalayas(a) The Great or Inner Himalayas or the Himadri It is a continuous range consisting of the highest peaks.
Fig: Three major divisions of Himalayas(a) The Great or Inner Himalayas or the Himadri It is a continuous range consisting of the highest peaks.
(b) Himachal or Lesser Himalayas The range lying to the South of the Himadri is known as Himachal or Lesser Himalayas.
(c) Shiwaliks The outermost range of the Himalayas is known as the Shiwaliks. These are the foothill ranges and represent the Southernmost division of the Himalayas.
43) In Lakshadweep, there is a bird sanctuary on Pitti island. This island is uninhabited. Should some people be allowed to live on Pitti island? If they are allowed, what can be the harmful effects?
Ans: Humans should not be allowed to inhabit Pitti island, as this will affect the breeding of the birds on it, as the presence of humans along with their activities will disturb them and the birds may move elsewhere. The harmful effects of human activity are
(i) Pollution of freshwater sources on the island due to human activity. The birds will not get clean water to drink.
(ii) Hunting of birds for food by the humans will not allow the birds to stay on the island.
44) In India, the Northern mountains are the major sources of water and forest wealth. What negative effects can result from uncontrolled exploitation of water and forest resources of the mountains?
Ans: Biodiversity will be affected on a large scale if there is uncontrolled exploitation of water and forest resources. Animals will lose their natural habitat and climatic changes will occur after a few years. So, the use of natural resources of the mountains should be done with care so that the ecology is not seriously disturbed. Only a very limited amount of water and forest reserves should be used. Trees can be freshly planted to replace the forests being exploited.
45) Describe any three features of the Shivalik range. Or Name the outermost range of the Himalayas. Write any two characteristics of it.
Ans: The outermost range of the Himalayas are known as Shivalik. Following are the main features of Shiwaliks range
(i) The height of Shiwaliks range varies between 900 and 1100 metres.
(ii) They are composed of unconsolidated sediments brought down by rivers from the main Himalayan ranges.
(iii) These valleys are covered with thick gravel and alluvium.
46) State any three difference between the Himadri range and Shiwalik range? Or Describe any three features of Himadri.
Ans: The differences between Himadri and Shiwalik ranges are:
47) What do you understand by Duns? Where are they situated in our country?
Ans: The longitudinal valley lying between the lesser Himalayas and Shiwaliks are known as Duns. Dehra Dun, Kotii Dun and Patii Dun are some of the well-known Duns. They are covered with thick deposits of gravel and alluvium.
48) Write any three differences between Bhangar and Khadar.
Ans: 
|
55 videos|525 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Geography Chapter 2 Extra Question Answers - Physical Features of India
| 1. भारत की भौगोलिक विशेषताएँ क्या हैं ? |  |
| 2. भारत में प्रमुख पर्वत श्रृंखलाएँ कौन सी हैं ? |  |
| 3. भारत की प्रमुख नदियाँ कौन सी हैं ? |  |
| 4. भारत का जलवायु प्रकार क्या है ? |  |
| 5. भारत के भूगोल का आर्थिक महत्व क्या है ? |  |






















