Ques 1: Who collected the tax called Tithe' from the French peasants?
Ans: The tax called 'Tithes' were collected by the Church.
Ques 2: Eighteenth century France saw the emergence of a new social group known as ............
Ans: The new social group was known as the middle class.
Ques 3: In which group of hemispheres is India located?
Ans: India is located in the Eastern and Northern hemisphere. This can be seen by the latitudinal and longitudinal extent of India, where 'E' for East and 'N' for North are mentioned.
Ques 4: Which is the best way to establish democracy in a country?
Ans: The best way to establish democracy in a country is by getting voluntary support by the majority of the people.
Ques 5: Which international organisation is responsible for maintaining peace and security among countries of the world?
Ans: The UN Security Council is responsible for maintaining peace and security among countries of the world.
Ques 6: Out of Maulana Abdul Kalam Azad, Mahatma Gandhi, Dr. Rajendra Prasad and Durgaba Deshmukh, who was not a member of the Constituent Assembly?
Ans: Mahatma Gandhi was not a member of the Constituent Assembly.
Ques 7: When large and medium farmers sell their surplus produce in the market, what are the purposes to which they use this income?
Ans: A part of the earnings is saved and kept as capital for the next season. Thus, they are able to arrange for the capital for farming from their own savings. Some farmers also use the savings to buy cattle, trucks, or in other non-agricultural activities.
Ques 8: How will you define the life expectancy of a new-born baby?
Ans: Life expectancy is defined as the average length of life a new born baby will live.
Ques 9: Evaluate the differences between physical and human capital.
Ans: Physical capital includes the variety of inputs required in production activity. This includes fixed capital and working capital like machinery, land and building, raw materials, cash in hand etc., In contrast, human capital is the stock of competencies, knowledge, social and personality attributes, including creativity, embodied in the ability to perform labour so as to produce economic value. Here 'labour' refers to the persons performing the economic activity like laborers, knowledge persons and others involved in the activity.
Ques 10: Describe in brief the impact of the French Revolution on France.
Ans: (i) France became a republic and absolute monarchy came to an end.
(ii) The Declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen, which was the outcome of the French Revolution, granted equality and freedom of speech.
(iii) The Revolution supported the cause of the masses, abolished the idea of divine right and feudal privileges, slavery and censorship, as well as upholding merit as the basis of social up gradation.
Ques 11: Explain any three main features of Stalin's collectivization programme.
OR
Explain any three effects of Nazism on the school system.
Ans: Three main features of Stalin's collectivization program me were
(i) All the peasants were forced to cultivate in collective farms (Kolkhoz). This meant that all private agricultural landholdings were abolished and all such land belonged to the state.
(ii) The bulk of implements were transferred to the ownership of collective farms and peasants were sent there for work.
(iii) The Kolkhoz profit was shared between the peasants after giving the state its share.
OR
The effects of Nazism on the school system were
(i) All schools were cleansed and purified. This meant that teachers who were Jews or seen as 'politically unreliable' were dismissed.
(ii) Initially children were segregated: Germans and Jews could not sit together or play together. Subsequently, 'undesirable children' -Jews, the physically handicapped and Gypsies were thrown out of schools.
(iii) Good' German children were subjected to a process of Nazi schooling, a prolonged period of ideological training.
Ques 12: What were the causes of the revolutionary disturbances in Russia in 1905?
OR
Explain three reasons why Nazism became popular in Germany during the 1930s.
Ans: The causes of the revolutionary disturbances in Russia in 1905 were
(i) Due to Russia's defeat in the Russo-Japanese War in 1904, prices of essential goods rose dramatically, so that real wages declined by 20 per cent.
(ii) At the Putlog Iron Works, dismissal of some workers caused a strike.
(iii) During the subsequent events, a procession of workers was attacked by police in which 100 workers died. This was known as 'Bloody Sunday'.
OR
Nazism became popular because
(i) The Germans felt disgraced and humiliated after losing the first World War, as they were forced to pay reparations for it which ruined them economically.
(ii) Consequently they were impressed by Hitler's oratory that he would restore Germany to its former glory.
(iii) Political parties like the Communists, Socialists, Democrats etc were not united. There were conflicts between them and the government became weak. The Nazi Party took advantage of the situation and captured power.
Ques 13: Give the reasons for selecting longitude 82°30' as the Standard Meridian of India.
Ans: The longitudinal extent of the Indian mainland is about 30°. Thus, from Gujarat to Arunachal Pradesh there is a time difference of almost two hours. So the local time along the Standard Meridian of India (82°30'E) passing close to Mirzapur (in Uttar Pradesh) is taken as the Indian Standard Time. This is near to the centre of the country and also an exact multiple of a half hour related to Greenwich in England, which is at 0° longitude.
Ques 14: Make a comparison between the Shiwaliks and Himachal Himalayas based on the following
(i) Composition
(ii) Age
(iii) Altitude
Ans:
| Mountain Range | Shiwaliks | Himachal Himalayas |
| Composition | Thick gravel and alluvium | Highly compressed and altered rocks |
| Age | 5 to 16 million years | 25 million years |
| Altitude | Between 900 and 1100 m | 3700 to 4500 m |
Ques 15: List the differences between glaciers and rivers. Which glacier in Uttarakhand gives rise to a famous river?
Ans:
| Feature | Glaciers | Rivers |
| Composition and speed | They are composed of ice moving at a very slow speed | They are composed of water flowing at a faster speed. |
| Location | These are found either on show-capped mountains or in higher latitudes. | These are found from mountain tops to the oceans and at all latitudes |
| Dimensions | They are wide and deep, filling a whole valley | They are shallower and confined to a narrower channel |
The glacier is Gangotri and it gives rise to the river Ganga through its tributary, the Bhagirathi.
Ques 16: What freedoms are usually taken away when a democracy is overthrown by the military?
Ans: Freedoms taken away include the following
(i) The Military can do according to its wishes and no one can question them. The freedom of the people to choose their own leader is taken away.
(ii) The government can torture, put in prison and even kill people who oppose it.
(iii) People are denied the freedom of speech. They are not allowed the freedom of expressing displeasure at any of the government policies which they don't like.
Ques 17: Explain the meaning of the statement, "Democracy enhances the dignity of the citizens".
Ans: Democracy is based on the principle of political equality, on recognizing that the poorest and the least educated have the same status as the rich and the educated. People are not subjects of a ruler, they are the rulers themselves. Even if they make mistakes, they are responsible for their conduct. All citizens are made equally responsible, thus enhancing their dignity.
Ques 18: Explain what is meant by "sovereign" and "secular".
Ans: The word 'sovereign' in the context of the Indian Constitution means that the people have the supreme right to make decisions on internal as well as external matters. No external power can dictate to the government. The word 'secular' implies that citizens of India have complete freedom to follow any religion. Government treats all religious beliefs and practices with equal respect. There is no official religion.
Ques 19: List the changes in Palampur due to the advent of electric power in the village.
Ans: The advent of electric power in Palampur has brought about the following changes (i) Irrigation is now done through electric-run tube wells, which reduces the dependence of the farmers upon rainfall, and enables larger areas of land to be irrigated. (ii) Irrigation improvement allowed farmers to grow three different crops in a year. (iii) It enabled Mishrilal to set up a sugarcane crushing machine so that he can sell jiggery manufactured by him to the traders at Shahpur.
Ques 20: Why does unemployment have a detrimental effect on the overall growth of an economy?
Ans: Unemployment tends to increase economic overload, i.e., dependence of the unemployed persons on the people who are working, goes up. This adversely affects the quality of life of people, as they have to live at subsistence level, which leads to poor health and even increase in school dropouts. Ultimately this has a detrimental effect on the growth of the economy if it continues, as it wastes resources who can be gainfully employed.
Ques 21: Three features are shown on the outline map of India. Identify these features and write their names on the lines marked on the map.
1. A state with a large tribal population
2. This state became part of India in 1961
3. A physiographic region where Barchans are found
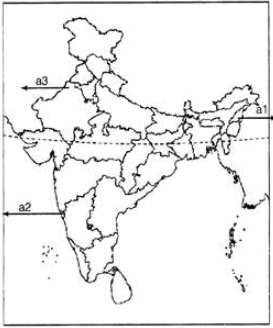
Ans:
1. Nagaland
2. Goa
3. Indian Desert
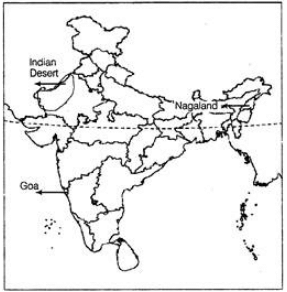
Ques 22: On the map, locate and label the following with appropriate symbols
1. A salt water lake on the border between Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu
2. The only river joining the Ganga from the south in Uttar Pradesh
3. The state in North-East India which has only two nations on its borders
Ans: 1. Pulicat Lake
2. Yamuna River
3. Mizoram (its western end borders Bangladesh and its eastern end borders Myanmar)
Ques 23: What laws were introduced by the revolutionary government in France to improve the status of women?
Ans: The following laws were introduced by the revolutionary government
(i) State schools were established and schooling was made compulsory for all girls.
(ii) Their fathers could no longer force them into marriage against their will. Marriage was made into a contract entered into freely and registered under civil law.
(iii) Divorce was made legal and could be applied for by both women and men.
(iv) Women could now train for jobs, could become artists or run small businesses.
Ques 24: What steps were taken by the Tsar during and after the Revolution of 1905 to protect his authority? OR Explain what role women had in Nazi society.
Ans: Steps taken by the Tsar to protect his authority were
(i) Allowing creation of an elected consultative parliament or Duma. It could not take any final decisions.
(ii) To ensure no questioning of his authority or reduction is his powers, he dismissed the first and second Duma within a time period of 6 months.
(iii) He changed the laws to pack the third Duma with conservative politicians. Liberals and revolutionaries were not included as members
(iv) For a small time during the 1905 Revolution, a number of trade unions and factory committees, all consisting of factory workers, were formed. After the revolution was crushed, all such unions and committees were banned.
(v) He placed severe restrictions on political activities.
OR
In Nazi Germany, young people and children were told that women were radically different from men. They were told that their fighting for equal rights with men was wrong and it would destroy society. While boys were trained for hard jobs, girls were trained to become good mothers and bring up pure blooded Aryan children, look after domestic duties and teach their children Nazi values. Mothers who brought up racially desirable children were awarded and favored by various methods. However, women who married Jews, Poles or Russians and gave birth to children who were undesirable were punished severely and considered to be criminals. Thus all women were not treated equally in Nazi society.
Ques 25: 'The Indian landmass shows a great physical contrast.' Explain this statement.
Ans: India's landmass has great contrasts as the Peninsular plateau in the South is a very old landmass (65 million years), whereas the Himalayas in the north are fairly new (about 25 million years). Tectonically the Himalayas and the Northern plains are unstable zones, whereas the Peninsular plateau is very stable. Over millions of years, weathering forces have made the contrast sharper. While the Himalayas are composed of sedimentary and metamorphic rocks and the Northern plains are made of deposited alluvium, the Peninsular plateau is made up of igneous and metamorphic rocks. Whereas the Himalayas have lofty peaks and steep sided valleys, the Deccan region has gently rising ranges and wide valleys. Thus the Indian landmass shows a great physical contrast.
Ques 26: Explain the use of salt water lakes in India with particular reference to Chilka and Sambhar lakes.
Ans: Sambhar lake is India's largest saline lake and has made Rajasthan the third largest salt producing state in India. It produces about 2 lakh tonnes of clean salt every year. Salt is produced by evaporation of brine. This lake is also recognized as a wetland of international importance because it is a key wintering area for flamingos and other birds that migrate from northern Asia. Chilka lake in Odisha is the largest brackish water lake in India. It is the wintering ground for migratory birds on the Indian sub-continent. The lake is home to a number of threatened species of plants and animals. It is an ecosystem with large fishery resources sustaining 150,000 fishermen living nearby.
Ques 27: What is a military coup? Why can't Pakistan under General Musharraf be called a true democracy?
Ans: A military coup is an action taken by the military to unseat a legally elected government and put themselves in power. Pakistan under General Musharraf's cannot be called a true democracy because during General Musharraf' rule, the legally elected representatives of the people could not take the final decisions and so were not really the rulers. The power for taking the final decisions rested with the Army headed by Musharraf, and they had not been elected the rulers. After taking power, Musharraf passed a Legal Framework Order, empowering him as President to dismiss the provincial and national assemblies. So even though there was an elected parliament, it had no real powers and thus this cannot be called a democracy.
Ques 28: Which of the following positions can contribute to democracy at the global level? Give reasons for your answer in each case.
(i) My country gives more money to international institutions. Therefore I want to be treated with more respect and exercise more power.
(ii) My country may be small or poor. But my voice must be heard with equal respect, because these decisions will affect my country.
Ans: (i) If any country gives more money to international institutions and its citizens want more respect and more power, it would not contribute to democracy at the global level. Every country and its citizens enjoy equal status whether it is a poor or a rich country. Equality is the basic principle of democracy.
(ii) If any country is small or poor but its citizens are treated equally and their voice is heard with equal respect, it will promote equality and freedom of expression. If this is done at the global level, then this will definitely contribute to democracy at that level. Because of these two facts we can say that this position is nearer to democracy.
Ques 29: In what way are sources of capital required for farming by large farmers different from the capita sources for small farmers?
Ans: Large farmers retain a part of their produce and sell the surplus in the market. This provides them with the required capital for the next season. They may use some of this for giving loans to small farmers at high interest rates, thus increasing their capital further. Thus, medium and large farmers have ready capital with them from one agricultural season to the next. In the small farmer's case, they begin with no working capital and have to take loans at high rates of interest. Due to the small sizes of their farms. Their total production is kept for their needs or for repaying their lenders. Hence they have no savings.
Ques 30: What are the objectives of India's national policy on health? Suggest two ways in which the police objectives can be met.
Ans: The objectives of the National Health Policy (2002) are
(i) Enhancing the contribution of private sector in providing health service for people who can afford to pay.
(ii) Giving primacy for prevention and first line curative initiative.
(iii) Emphasizing rational use of drugs.
(iv) Increasing access to tried systems of Traditional Medicine. Some of the policy objectives can he met through the following methods
(a) Increasing the number of trained nurses or midwives to one per village.
(b) Making available generic medicines (instead of branded medicines) at all government dispensaries. There are many other methods for fulfilling the other policy objectives.
























