Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Notes > Science Class 9 > Previous Year Questions Answers - The Fundamental Unit of Life
Class 9 Science Chapter 5 Previous Year Questions - The Fundamental Unit of Life
Short Answer Type Question
Q.1. The grass looks green, papaya appears yellow. Which cell organelle is responsible for this? [2024]
Ans. The cell organelles responsible for the colours seen in plants, such as green grass and yellow papaya, are plastids. Specifically:
- Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll, which gives grass its green colour by absorbing light primarily in the blue and red wavelengths and reflecting green.
- Chromoplasts contain pigments like carotenoids, which are responsible for the yellow, orange, and red colours in fruits and vegetables, such as the yellow colour in papaya.
These plastids store pigments that give plants their characteristic colours.
Q.2. Draw the diagram of a plant cell and label any three parts that make it different from an animal cell. [2024]
Ans.
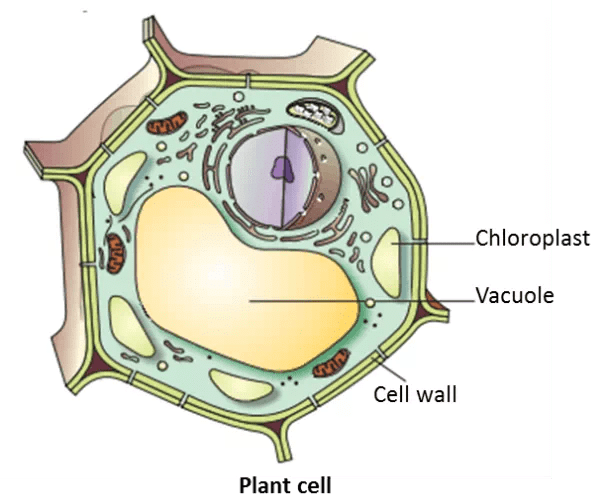
- Cell Wall: A rigid, protective layer that surrounds the cell membrane, giving the plant cell its shape and structural support.
- Chloroplasts: Organelles containing chlorophyll, which enable the process of photosynthesis by absorbing sunlight.
- Large Central Vacuole: A large, water-filled space that maintains cell pressure, stores nutrients, and aids in waste removal.
Q.3. Name the cell organelle which is termed as a powerhouse of the cell. [2024]
Ans. Mitochondria.
Q.4. ‘Every multicellular organism has arisen from a single cell’. Justify this statement. [2023]
Ans. All cells arise from pre-existing cells. Thus, all cells come from preexisting cells, and hence, every multicellular organism has arisen from a single cell.
Q.5. Name the process by which unicellular freshwater organisms and most plant cells fend to gain water. [2023]
Ans. Osmosis.
Q.6. Give two examples of organisms in which a single cell performs all the functions.
OR
Name two unicellular organisms. [2022]
Ans. Amoeba and Paramecium.
Q.7. What is cell theory? Who formulated it? [2021]
Ans: Cell theory states that all living organisms are composed of cells, the cell is the basic unit of life, and all cells arise from pre-existing cells. It was formulated by Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann in 1838–1839, with contributions from Rudolf Virchow.
Q.8. Write the full form of DNA and ATP. [2021]
Ans: DNA: Deoxyribonucleic Acid, ATP: Adenosine Triphosphate
Q.9. What is the importance of the nucleus? [2020]
Ans: The nucleus is the control centre of the cell, containing genetic material (DNA) that regulates cell functions, growth, and reproduction. It directs protein synthesis by controlling RNA production.
Q.10. Why is the plasma membrane selectively permeable? [2019]
Ans: The plasma membrane is selectively permeable because it allows certain substances to pass while restricting others. This is due to its lipid bilayer structure, which has hydrophobic (water-repelling) interior layers and embedded proteins that facilitate the transport of specific molecules.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q.1. Describe the structure of the nucleus. [2021]
OR
Explain in detail what you know about the structure of the nucleus. [2021]
Ans. Robert Brown in 1831 discovered the nucleus in the cell. The nucleus is one of the larger organelles. It is spherical or oval in shape and is a prominent structure. It is usually located in the centre of the cell. Nucleus has the following important parts:
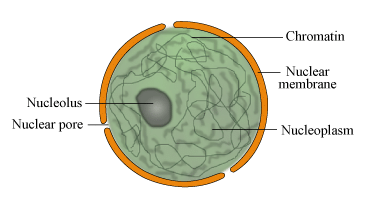 (i) Nuclear membrane: It is a double-layered membrane which separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm.
(i) Nuclear membrane: It is a double-layered membrane which separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm.
(ii) Nucleoplasm: It is a homogeneous and granular dense fluid present inside the nucleus, in which chromatin and nucleolus are suspended.
(iii) Chromatin material: It consists of a long, coiled network of thread-like structures. The chromatin material is made up of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) which is responsible for storing and transmitting hereditary information from one generation to the other. It condenses into compact rod-like bodies called chromosomes at the time of cell division.
(iv) Nucleolus: It is a more or less round structure found inside the nucleus. The nucleolus contains RNA (ribonucleic acid) and proteins.
Ques 2: Explain the following terms: (a) Plasma membrane (b) Cytoplasm (c) Nucleus. [2020]
Ans: (a) Plasma membrane: It is a thin membrane that controls the passage of materials in and out of the cell. It is also called a selectively permeable membrane. It makes the outer boundary of the cell and is made up of lipoprotein,
(b) Cytoplasm: It is a transparent jelly-like thick substance present in the cell. It makes the ground of the cell in which all the cell organelles are suspended.
(c) Nucleus: It is a double-layered membrane structure that contains chromosomes required for the inheritance of characteristics from one generation to the other.
Ques 3: Give five points of differences between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. [2019]
Ans: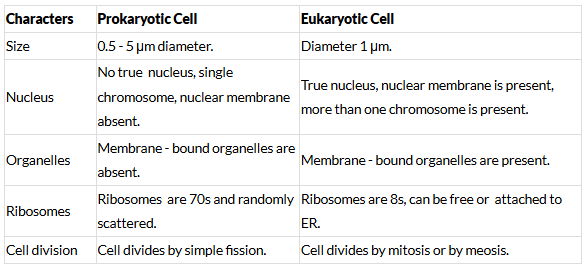
Ques 4: Label the figure and answer the questions: [2019]
(i) A – It is the packaging organelle
(ii) B – Provides energy
(iii) C – helps in the transport of material
(iv) D – Carries the information.
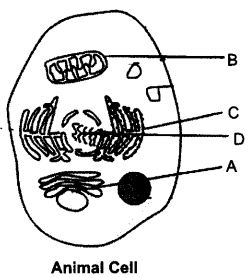 Ans: (i) A – Golgi body
Ans: (i) A – Golgi body
(ii) B – Mitochondria
(iii) C – Endoplasmic reticulum
(iv) D – Nucleus
The document Class 9 Science Chapter 5 Previous Year Questions - The Fundamental Unit of Life is a part of the Class 9 Course Science Class 9.
All you need of Class 9 at this link: Class 9
|
84 videos|541 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Science Chapter 5 Previous Year Questions - The Fundamental Unit of Life
| 1. What is the basic structural and functional unit of life? |  |
Ans. The basic structural and functional unit of life is the cell. Cells are the smallest units that can carry out all life processes, and they are often referred to as the building blocks of living organisms.
| 2. What are the different types of cells found in living organisms? |  |
Ans. There are two main types of cells: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria, do not have a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells, found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists, have a defined nucleus and various organelles.
| 3. What are the main components of a cell? |  |
Ans. The main components of a cell include the cell membrane, cytoplasm, and organelles. The cell membrane surrounds the cell, the cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance within the cell, and organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, and ribosomes perform specific functions.
| 4. How do plant cells differ from animal cells? |  |
Ans. Plant cells differ from animal cells in several ways: plant cells have a rigid cell wall, chloroplasts for photosynthesis, and large central vacuoles for storage, while animal cells have a flexible cell membrane and do not contain chloroplasts or a cell wall.
| 5. Why is the cell membrane important for a cell? |  |
Ans. The cell membrane is important because it acts as a barrier that controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell. It helps maintain the internal environment of the cell, provides protection, and enables communication with other cells.
Related Searches






















