Classification Systems of Plant Kingdom | Biology for Grade 11 PDF Download
In essence, the Biological Classification System is like a roadmap that helps us navigate the vast world of living organisms, allowing us to study and understand the incredible diversity of life that surrounds us. The Biological Classification System involves organizing and categorizing organisms into different hierarchical groups based on their similarities and differences.
Let's study the need of Classification Systems one by one!
Need for Biological Classification System
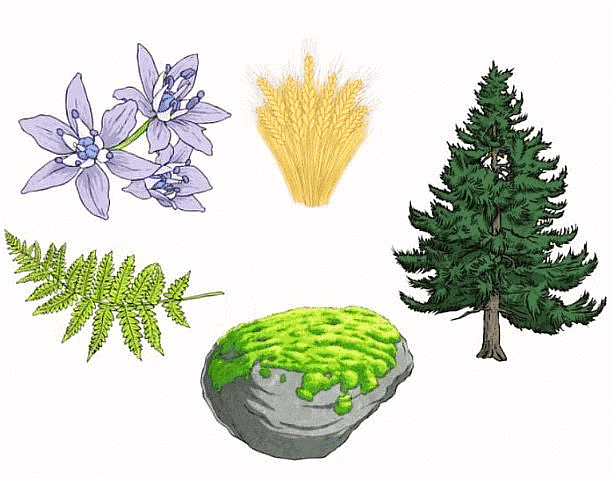 Diversity of Plants Species
Diversity of Plants Species
- It addresses the need to organize and categorize diverse plant species systematically.
- It enables a structured understanding of plant diversity, aiding in effective communication and study of various plant forms and functions.
Mnemonics are like memory tricks that can make it much easier to understand and remember what you're learning in the chapter. To make things easier for you, EduRev offers a document packed with these helpful memory aids.
If you click on the provided link, you'll be taken to the mnemonics document.
Mnemonics-Plant-Kingdom
In 1969, Whittaker proposed a classification system for living organisms, sorting them into Five Kingdoms: Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia.
Whittaker System of Classification was based on cellular and bodily complexity, nutritional methods and more.
 5 Kingdom Classification
5 Kingdom Classification
- Algae: A diverse group of aquatic organisms capable of photosynthesis.
- Bryophytes: Non-vascular plants that include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts.
- Pteridophytes: Vascular plants without seeds, such as ferns and horsetails.
- Gymnosperms: Seed-producing vascular plants with naked seeds, like conifers and cycads.
- Angiosperms: Flowering plants that produce seeds enclosed within a fruit.
But there were many other Classification Systems other than this. Let's study them understanding each one in detail!
Earliest Systems of Classification of Plants
Throughout history, there have been numerous attempts to categorize organisms. One of the earliest known classifications dates back to Aristotle, around 2000 years ago, who categorized plants into groups like herbs, shrubs, and trees.
 Aristotle
Aristotle
 Aristotle's System of Classification
Aristotle's System of Classification
All the classification systems, starting from that of Aristotle to the 20th century, can be divided into three types:
1. Artificial System
In this system, the classification is based on a few morphological characters.
Theophrastus, Pliny and Linnaeus used an artificial system of classification.
Basis of Artificial System of Classification
- The earliest classification systems relied on basic external features like appearance, color, leaf traits, etc.
- These systems primarily focused on vegetative characteristics or the structure of the androecium (as proposed by Linnaeus).
- These early systems were considered artificial because they separated closely related species based on only a few characteristics.
- Artificial systems treated vegetative and sexual traits equally, which is problematic because environmental factors can significantly impact vegetative traits.
Demerits of Artificial System of Classification
- It uses only one or a few traits for comparison.
- Closely related organisms get separated.
- The grouping is done on the basis of external traits.
- It does not bring out natural and phylogenetic relationships
2. Natural System
In this system, the classification is based on all the important related characters: both external and internal.
Bentham and Hooker, Adanson and Candolle used a natural system of classification.
Basis of Natural System of Classification
- These systems considered both external and internal features, such as ultrastructure, anatomy, embryology, and phytochemistry.
- George Bentham and Joseph Dalton Hooker proposed a natural classification for flowering plants.
- Their system accounted for the broader range of characteristics to identify more accurate affinities and relationships among plant species.
The Merits of Natural System of Classification
- It is practically important, as most of the herbaria of the world are based on this system of classification.
- They placed Ranales (most primitive) in the beginning of classification that is phylogenetically true.
- They placed monocots after dicots which is similar to phylogenetic systems.
The Demerits of Natural System of Classification
- They did not use phylogenetic trends in their classification.
- Gymnosperms are placed between dicots and monocots which is not acceptable.
- Monochlamydeae is placed after gamopetalae which does not seem to be natural.
- Some of the associated orders are geographically isolated.
- Groups are not arranged in a consistent manner.
3. Phylogenetic System
In this system, classification is based on the evolutionary relationship of plants.
The use of phylogeny for classification was done by Eichler, Blessy, Whittaker, Engler and Prantl, Hutchinson.
Modern advancements in taxonomy include:
- Numerical Taxonomy: Taxonomy is based on statistical methods with equal importance using computers.
- Cytotaxonomy: Taxonomy that is based on cytology or structure of the cell (chromosome number, shape, behaviour, etc).
- Chemotaxonomy: Taxonomy based on chemical constituents of plants (nature of the protein, DNA sequence, taste, smell, etc).
- Eichler Classification: The classification of Plant kingdom depending on flowering.
It divided the plants into two categories:
a) Cryptogamae: They are non-flowering, seedless plants.
b) Phanerogamae: They are flowering, seed-bearing plants.
 Eichler Classification
Eichler Classification
Note: Cryptogamae and Phanerogamae are further divided into Divisions, each of them are described below:
Cryptogamae
Cryptogamae
"Cryptogams" refers to a group of plants without flowers and seeds, and they hide their reproductive parts. Instead of seeds, they produce tiny particles called spores to reproduce.
Classification of Cryptogamae
It divided into the following divisions:
a) Thallophyta: Plant body is thallus-like (undifferentiated plant body).
b) Bryophyta: Plant body with a root-like structure, stem-like structure (vascular tissues are absent).
c) Pteridophyta: Plant body is differentiated into true root, stem, and leaves (vascular tissues are present in so-called vascular cryptogams).
Thallophytes are further divided into sub-divisions:
- Algae: They are pigmented thallophytes.
- Fungi: They are non-pigmented thallophytes.
Lichens: It is symbiotic association between algae and fungi.
 Lichen
Lichen
Phanerogamae
The plant groups with well-developed reproductive organs, which produce seeds, are known as the phanerogamae.
Classification of Phanerogamae
It divided into the following divisions:
a) Gymnosperms: They are plants with naked seeds.
b) Angiosperms: They are seed-bearing plants.
Angiosperms are further divided into sub-divisions:
- Monocots: They are plants bearing single cotyledon, fibrous root system and parallel venation.
- Dicots: They are plants bearing two cotyledons, taproot system and reticulate venation.
Additional Information
Tracheophytes: They are a plant group characterized by the presence of vascular tissue. It includes Pteridophytes, Gymnosperms and Angiosperms.
Embryophyta: They are plants that have embryos. It includes Bryophytes, Pteridophytes, Gymnosperms and Angiosperms.
|
223 videos|325 docs|294 tests
|
FAQs on Classification Systems of Plant Kingdom - Biology for Grade 11
| 1. What is the need for a biological classification system? |  |
| 2. What are the earliest systems of classification of plants? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between Cryptogamae and Phanerogamae? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of the natural system of plant classification? |  |
| 5. What is the phylogenetic system of plant classification? |  |
|
Explore Courses for Grade 11 exam
|

|


















