Compensation Management | Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce PDF Download
Compensation Management
Compensation management is the process and strategy of determining the appropriate pay and benefits for employees. It's a crucial aspect of talent management and employee retention, using both financial and non-financial rewards to attract talent, reduce turnover, improve performance, and increase engagement.
Typically managed by HR professionals, compensation management involves ensuring that salaries, bonuses, and benefits remain competitive while adapting to the changing needs of the workforce. HR leaders in this role must analyze internal and external salary data, demographics, and economic statistics, while also navigating the complexities of administering employee benefits.
Key Types of Compensation
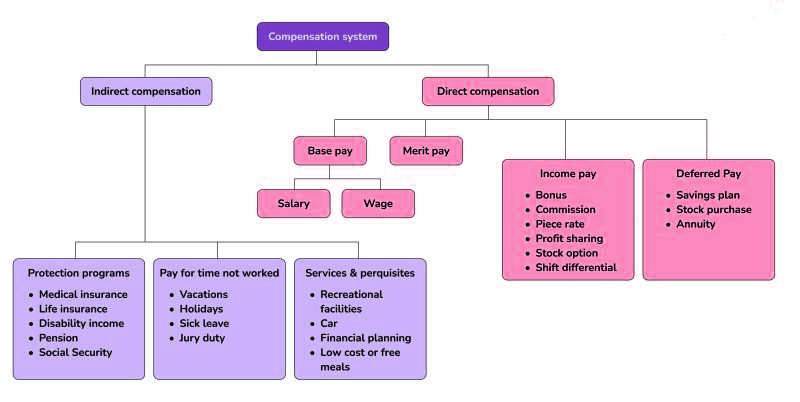
Total employee compensation consists of two primary categories: direct and indirect compensation.
Direct Compensation:
Direct compensation involves monetary payments directly tied to an employee's work and value to the organization. The main forms of direct compensation include:
- Salary: Paid to full-time employees on an annual basis, often in weekly, bi-weekly, or monthly installments. Salaries are typically offered to skilled workers and managers, reflecting a long-term investment in the employee.
- Hourly Wages: Typically paid to unskilled, semiskilled, part-time, or contract workers, as well as gig workers. Hourly employees may qualify for overtime and are often subject to minimum wage laws.
- Bonuses: Awards given for specific accomplishments, such as completing a successful project or achieving a company-wide performance milestone. Bonuses are common across different roles but are frequently part of executive compensation packages.
- Commission: Often used in sales positions, commissions are payments based on meeting sales quotas or revenue targets, and may be structured as commission-only or as a base salary plus commission.
Indirect Compensation:
Indirect compensation refers to additional benefits with financial value that support the overall compensation package. These can be categorized as:
- Monetary Benefits: This includes benefits such as health, dental, vision, life, and disability insurance, retirement plans like 401Ks, pensions, and employee stock options.
- Non-monetary Benefits: Examples include paid leave (e.g., vacation, sick leave, parental leave), childcare, professional development, company-provided resources (e.g., cars, phones, laptops), and meals.
Compensation management plays a critical role in organizations for several reasons:
- Managing Major Expenses: Salaries are often a company’s largest expense, so executives need accurate data to set budgets, create compensation strategies, and make consistent pay decisions.
- Legal Compliance: Employers must adhere to new pay equity laws that require reporting of employee wages along with data on gender, race, ethnicity, and job roles. States like California began enforcing these laws in 2021 to help identify discriminatory wage patterns. Additionally, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission started requiring companies to report human capital metrics, including pay equity, in 2020.
- Focus on Pay Equity: Companies are increasingly prioritizing pay equity as part of their diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) initiatives.
- Adapting to Remote Work: Remote work has led many companies to adjust compensation strategies. For example, employees moving from high-wage areas like Silicon Valley to lower-wage regions might face pay cuts. Crafting competitive compensation packages in a flexible work environment has become more complex.
Steps to Implement a Compensation Management Strategy
Although compensation strategies vary across organizations, certain key steps are generally applicable:
- Vision-Driven Policies: Leadership should develop compensation policies that align with the scope and vision of the roles they are recruiting for.
- Broad Input: Gathering insights from existing plans and external sources helps shape a comprehensive compensation strategy.
- Compliance: The strategy must adhere to local, state, and federal laws regarding compensation and benefits.
- Finalizing the Plan: After careful consideration, leadership must finalize the details of the compensation plan.
- Communication: The finalized plan should be clearly communicated to employees and stakeholders.
- Ongoing Review: Once implemented, the plan should be continually assessed and improved based on feedback and performance.
Compensation Management Software
- Compensation management software is a key component of human capital management (HCM) and talent management systems.
- It equips executives, hiring managers, recruiters, and HR teams with essential data on salary budgets and compensation rates across industries.
- The software centralizes the management of all types of compensation, including bonuses, performance incentives, and non-monetary perks like flexible work hours and wellness programs.
- It also helps organizations calculate and communicate total rewards packages for employees, highlighting the value of benefits such as health insurance and retirement accounts.
- Increasingly, compensation software relies on machine learning to identify data disparities and ensure competitive salaries.
- Cloud-based data analytics and benchmarking tools allow companies to compare pay rates with industry peers.
- Compensation managers can use these systems to access salary data by factors such as industry, company size, job role, and location.
- Data sources include government statistics, publicly available salary information, and third-party surveys.
- A growing trend is the adoption of on-demand pay, also known as earned-wage access, which allows employees to receive payment for hours worked before payday.
- This service is supported by various niche vendors offering software as a service (SaaS) for earned-wage access.
- However, compensation management software tends to focus on an employee's historical contributions rather than their future potential.
- Compensation analysis often prioritizes past achievements over a person's potential to add future value.
Compensation Management Software Market and Vendors
Major human capital management (HCM) suite providers incorporate compensation management software into their platforms, helping HR professionals and managers streamline compensation processes. According to MarketsandMarkets, notable vendors in this space include ADP, Cegid, Ceridian, Cornerstone, EmployWise, IBM, Infor, Kronos, Microsoft, Oracle, PeopleStrategy, SAP, Sum Total, Ultimate Software, and Workday.
There are also niche vendors that specialize specifically in compensation management. Gartner lists several smaller vendors, including Aeqium, Barley, Beqom, CaptivateIQ, Complete, Complogix, Compport, Dartican, Decusoft, HRSoft, MroganHR, Pave, Payscale, and Salary.com.
Features to Look for in Compensation Management Software
When selecting compensation management software, it’s essential to evaluate the included features and components. Key features to consider include:
- A configurable drag-and-drop dashboard for visualizing compensation trends and expenses.
- Automated, customizable reporting tools.
- Data visualization tools that create charts and graphs suitable for presentations.
- Analytical tools to simplify the analysis of compensation data.
- The ability to compare wages across industries and geographic regions.
- Support for integrating third-party add-on tools.
Benefits of Compensation Management
Effective compensation management provides several key benefits to organizations:
- Competitive Pay: Staying competitive with salary offerings is a major advantage. Market data allows hiring managers to offer appropriate compensation to top talent, as well as set raises and bonuses in line with current trends. This is crucial for attracting and retaining employees who are aware of salary trends.
- Employee Morale: Compensation management tools can help enhance employee motivation, reduce turnover, and boost retention, which in turn lowers operational costs associated with recruiting and training new employees.
- Improved Productivity: A well-designed compensation mix can increase employee productivity, creativity, and performance.
- Profitability: Enhanced productivity and retention directly contribute to increased revenue and profitability for the organization.
Challenges in Compensation Management
Despite the benefits, there are challenges involved in compensation management, including:
- Budget Constraints: Compensation packages can quickly consume a significant portion of a company’s budget, limiting the ability to offer competitive salaries, bonuses, and benefits.
Determining Plan Components: Deciding what to include in compensation plans can be difficult. Although industry data may be available for benchmarking, accessing accurate information can be challenging. As a result, business leaders might need to rely on their own judgment.
Communication: Explaining compensation plans and packages to employees and stakeholders, particularly new hires, can be time-intensive and require careful effort to ensure clarity.
Fairness and Inclusivity: Ensuring that compensation policies are fair and accommodate special needs across the workforce can be time-consuming, requiring a comprehensive approach that fosters equity.
Continuous Monitoring: Continuously tracking the success of compensation plans through various metrics is essential but can be arduous. Many organizations outsource this responsibility to third-party service providers to ensure effectiveness and efficiency.
Compensation Management Specialist: Salary and Career Information
In smaller companies, HR managers may also function as compensation managers. However, compensation management is recognized as a distinct profession. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), compensation and benefits managers earned a median annual salary of $131,280 in 2022. The lowest 10% earned under $77,230, while the top 10% earned over $217,650.
The BLS estimated that in 2022, around 17,500 compensation managers were employed in the U.S., with the role expected to grow by approximately 2% from 2022 to 2032.
The Future of Compensation Management and Benefits
- Compensation management is evolving to keep pace with rapidly shifting workforce priorities.
- HR departments are increasingly using analytical software to support diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) efforts.
- This involves analyzing compensation data for potential wage disparities based on gender and race, from entry-level to senior management roles.
- Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, wellness incentive programs were already a significant part of compensation packages.
- Their importance has only increased, along with financial support for remote workers' home office setups.
- The rise of remote and hybrid work has also led to more complex compliance issues, as employees are often based in multiple states or countries.
- Benefits are an integral part of compensation packages, and compensation management software must be flexible enough to accommodate new and evolving benefit offerings.
- For example, some wellness programs offer employees free activity-tracking smartwatches like the Apple Watch, provided they meet fitness goals.
- If employees fail to meet those goals, they might be required to pay for the device.
- Additionally, some compensation plans include employer-subsidized DNA testing, flexible work options, phased returns to work for new parents, and reimbursements for adoption and eldercare expenses.
|
157 videos|236 docs|166 tests
|
FAQs on Compensation Management - Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce
| 1. What is compensation management? |  |
| 2. Why is compensation management important in organizations? |  |
| 3. What are the key components of compensation management? |  |
| 4. How can organizations ensure a successful compensation management system? |  |
| 5. What are some common challenges in compensation management? |  |





















