ICAI Notes- Components of Business Environment | Business and Commercial Knowledge (Old Scheme) - CA Foundation PDF Download
COMPONENTS OF BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT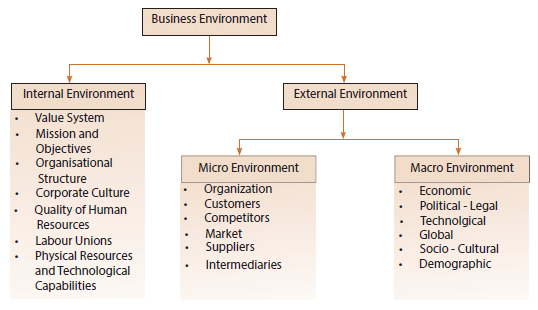
Internal Environment
Internal environment is composed of multiple elements existing within the organization, including management, current employees and corporate culture. Internal environment is the conditions, people, events and factors within an organization that influence its activities and choices, particularly the behaviour of the employees. Factors that are frequently considered part of the internal environment also include the organization’s mission statement, leadership styles and its organizational culture.
External Environment
A business does not operate in a vacuum. It has to act and react to what happens outside the factory and with is the office walls. These factors that happen outside the business are known as external factors or influences. These will affect the internal functions of the business and also the objectives of the business and its strategies.
There are two major types of external environment:
i. Micro Environment
ii. Macro Environment
The environment in which an organization exists can, therefore, be described in terms of the opportunities and threats operating in the external environment apart from the strengths and weaknesses existing in the internal environment. The four environmental influences could be described as follows:
 ⇒ A strength is an inherent capacity which an organization can use to gain strategic advantage over its competitors. An example of strength is superior research and development skills which can be used for new product development so that the company gains competitive advantage. |
 ⇒ A weakness is an inherent limitation or constraint which creates a strategic disadvantage. An example of a weakness is over dependence on a single product line, which is potentially risky for a company in times of crisis. |
 ⇒ An opportunity is a favourable condition in the organization's environment which enables it to consolidate and strengthen its position. An example of an opportunity is growing demand for the products or services that a company provides. |
 ⇒ A threat is an unfavourable condition in the organization's environment which creates a risk for, or causes damage to, the organization. An example of a threat is the emergence of strong new competitors who are likely to offer stiff competition to the existing companies in an industry. |
An understanding of the external environment, in terms of the opportunities and threats, and the internal environment, in terms of the strengths and weaknesses, is crucial for the existence, growth and profitability of any organization.
SWOT Analysis
A systematic approach to understanding the environment is the SWOT analysis. Business firms undertake SWOT analysis to understand the external and internal environment. SWOT, which is the acronym for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats.
Through such an analysis, the strengths and weaknesses existing within an organization can be matched with the opportunities and threats operating in the environment so that an effective strategy can be formulated.
An effective organizational strategy, therefore, is one that capitalises on the opportunities through the use of strengths and neutralises the threats by minimizing the impact of weaknesses.
The process of strategy formulation starts with, and critically depends on, the appraisal of the external and internal environment of an organization. We will learn more about SWOT analysis in the second chapter of strategic Management at Intermediate level.
MICRO AND MACRO ENVIRONMENT
The environment of business can be broadly categorised into two: micro-environment and macroenvironment.
Micro-environment is related to small area or immediate periphery of an organization. Micro-environment influences an organization regularly and directly. Within the micro or the immediate environment in which a firm operates we need to address the following issues:
- The employees of the firm, their characteristics and how they are organised
- The customer base on which the firm relies for business.
- The ways in which the firm can raise its flnance.
- Who are the firm suppliers and how are the links between the two being developed?
- The local community within which the firm operates.
- The direct competition and how they perform.
This last point might act as a convenient linking point as we move towards the macro issues influencing the way a firm reacts in the market place.
Micro environment: consist of suppliers, consumers, marketing intermediaries, etc. These are specific to the said business or firm and affects it’s working on short term basis.
Macro environment has broader dimensions. It mainly consists of economic, technological, political, legal and socio-cultural. The issues concerning an organization are:
- What are its threats in the competitive world in which it operates and why?
- Which areas of technology might pose a threat to its current product range and why?
- The bargaining power of suppliers and customers.
The classification of the relevant environment into components or sectors helps an organization to cope with its complexity, comprehend the different influences operating, and relating the environmental changes to its strategic management process. The business environment can be divided into two major components:
Macro Environment: consists of demographics and economic conditions, socio-cultural factors, political and legal systems, technological developments and global trends, etc. These constitute the general environment, which affects the working of all the firms.

ELEMENTS OF MICRO ENVIRONMENT
This is also known as the task environment and affects business and marketing in the daily operating level. When the changes in the macro environment affect business in the long run, the micro environmental changes are noticed immediately. Organizations have to closely analyse and monitor all the elements of micro environment in order to stay competitive.
Consumers/Customers
According to Peter Drucker the aim of business is to create and retain customer. Customers are the people who pay money to acquire an organization's products. The products may be both in form of goods or services. The organizations cannot survive without customers. Customers may or may not be a consumer. Consumer is the one who ultimately consumes or uses the product or service.
A father may buy a product as a customer for his daughter who will be a consumer. A consumer occupies the central position in the marketing environment. The marketer has to closely monitor and analyze changes in consumer tastes and preferences and their buying habits.
- Who are the customers/consumers?
- What benefits are they looking for?
- What are their buying patterns?
Competitors
Competitors are the other business entities that compete for resources as well as markets. Competition shapes business. A study of the competitive scenario is essential for the marketer, particularly threats from competition. Following are a few of major questions that may be addressed for analyzing competitions:
- Who are the competitors?
- What are their business objectives and strategies?
- Who are the most aggressive and powerful competitors?
Competition may be direct or indirect. Direct competition is between organizations, which are in same business activity. For example, in Indian shampoo sachet market, there are so many competitors who are competing to increase for their market share. At the same time, competition can also be indirect. For example, competition between a holiday resort and a car manufacturing company for available a discretionary income of affuent customers is indirect competition.
India Shampoo Sachet Market Share Split
Organization
Individuals occupying different positions or working in different capacities in organizations consist of individuals coming from outside. They have different and varied interests. In micro environment analysis, nothing is important as self-analysis by the organization itself. Understanding its own strengths and capabilities in a particular business, i.e., understanding a business in depth should be the goal of firm’s
internal analysis. The objectives, goals and resource availabilities of a firm occupy a critical position in the micro environment.
“We have met the enemy and he is us” - Pogo.
An organization has several non-specific elements of the organization's surroundings that may affect its activities. These consist of specific organizations or groups that are likely to influence an organization. These are:
- Owners: They are individuals, shareholders, groups, or organizations who have a major stake in the organization. They have a vested interest in the well-being of the company.
- Board of Directors: Board of directors are found in companies formed under the Companies Act, 1956. The board of directors is elected by the shareholders and is charged with overseeing the general management of the organization to ensure that it is being run in a way that best serves the shareholders' interests.
- Employees: Employees are the people who actually do the work in an organization. They are the major force within an organization. It is important for an organization that employees embrace the same values and goals as the organization. However, they differ in beliefs, education, attitudes, and capabilities. When managers and employees work toward different goals everyone suffers.
Market
The market is larger than customers. The market is to be studied in terms of its actual and potential size, its growth prospect and also its attractiveness. The marketer should study the trends and development and the key success factors of the market he is operating. Important issues are :
- Cost structure of the market.
- The price sensitivity of the market.
- Technological structure of the market.
- The existing distribution system of the market
- Is the market mature?
Suppliers
Suppliers form an important component of the micro environment. They provide raw materials, equipment, services and so on. Large companies rely on hundreds of suppliers to maintain their production. Suppliers with their own bargaining power affect the cost structure of the industry. They constitute a major force, which shapes competition in the industry. Also organizations have to take a major decision on “outsourcing” or “in-house” production depending on this supplier environments.
Reality Bite: Whenever you purchase a packet of biscuit and take a closer look at the pack, you will realise that, the company selling the biscuit and the company actually making the biscuit is actually different, for example, if you take a look at the image below of the biscuit packet . You will see the difference. Here, Parle is marketing the biscuit and others are making on its behalf. This is called outsourcing. |

Intermediaries
Intermediaries exert a considerable influence on the business organizations. They can also be considered as the major determining force in the business. In many cases the consumers are not aware of the manufacturer of the products they buy. They buy product from the local retailers, big departmental stores or online stores that are increasingly becoming popular.
ELEMENTS OF MACRO ENVIRONMENT
Macro environment is that part of external environment which is largely external to the enterprise and thus beyond the direct influence and control of the organization, but which exerts powerful influence over its functioning.
The external environment of the enterprise consists of individuals, groups, agencies, organizations, events, conditions and forces with which the organization comes into frequent contact in the course of its functioning. It establishes interacting and interdependent relations, conducts transactions, designs and administers appropriate strategies and policies to cope with fluctuations therein and otherwise negotiates
its way into the future.
Demographic Environment
The term demographics denotes characteristics of population in a area, district, country or in the world. It includes factors such as race, age, income, educational attainment, asset ownership, home ownership, employment status and location. Data with respect to these factors within a demographic variable, and across households, are of interest, to businessmen in addition to economists. Marketers and other social scientists often group populations into categories based on demographic variables.
Some of the demographic factors have great impact on the business. Factors such as general age profile, sex ratio, education, growth rate affect the business with different magnitude. India has relatively younger population as compared to some other countries. China on the other hand is having an aging population. Many multinationals are interested in India considering its population size. With having approximately sixteen percent of the world’s population, the country holds huge potential for overseas companies.
Business Organizations need to study different demographic factors. Particularly, they need to address following issues:
- What demographic trends will affect the market size of the industry?
- What demographic trends represent opportunities or threats?
The business, as such, is concerned with a population's size, age structure, geographic distribution, ethnic make-up, and distribution of income. While each of the major elements of discussed below, the challenge for strategists is to determine what the changes, that have been identified in the demographic characteristics or elements of a population, imply for the future strategic competitiveness of the company. We will briefly
discuss a few factors that are of interest to a business.
(i) Population Size: While population size itself, large or small, may be important to companies that require a "critical mass" of potential customers, changes in the specific make-up of a population's size may have even more critical implications. Many foreign companies find India lucrative on account of its size. Among the most important changes in a population's size are:
- Changes in a nation's birth rate and/or family size;
- Increases or declines in the total population;
- Effects of rapid population growth on natural resources or food supplies.
Changes in a nation's population growth rate and life expectancy can have important implications for companies.
(ii) Geographic Distribution: Population shifts from one region of a nation to another or from nonmetropolitan to metropolitan areas may have an impact on a company's strategic competitiveness. Issues that should be considered include:
- The attractiveness of a company's location may be influenced by governmental support.
- Companies may have to consider relocation if population shifts have a significant impact on the availability of qualified workforce.
- The concepts of working-at-home and commuting electronically on the information highway have also started in India. These may imply changes in recruiting and managing the workforce.
(iii) Ethnic Mix: This reflects the changes in the ethnic make-up of a population and has implications both for a company's potential customers and for the workforce. Issues that should be addressed include:
- What do changes in the ethnic mix of the population imply for product and service design and delivery?
- Will new products and services be demanded or can existing ones be modified?
- Are the managers prepared to manage a more culturally diverse workforce?
- How can the company position itself to take advantage of increased workforce heterogeneity?
Reality Bite: Shampoo companies sell their product in bottles in residential area/ malls while the same product is sold in sachets in hostel/ rural areas. This is done because in hostels or rural areas the pocket money/disposable income is less as compared to residential areas where people prefer buying in large quantity. |
(iv) Income Distribution: Changes in income distribution are important because changes in the levels of individual and group purchasing power and discretionary income often result in changes in spending (consumption) and savings patterns. Tracking, forecasting, and assessing changes in income patterns may identify new opportunities for companies
Economic Environment
Economic environment refers to the nature and direction of the economy in which a company competes or may compete. It includes general economic situation in the region and the nation, conditions in resource markets (men, money, material, machine, method) which influence the supply of inputs to the enterprise, their costs, quality, availability and reliability of supplies.
Economic environment determines the strength and size of the market. The purchasing power in an economy depends on current income, prices, savings, circulation of money, debt and credit availability. Income distribution pattern determines the marketing possibilities. The important point to consider is to find out the effect of economic prospect and inflation on the operations of the firms.
Factors that Affect the Economic Environment
1. Economic Systems
(i) Capitalism: A capitalist economy is an economy where the laws of demand and supply operate freely. The capitalist system is one which is characterized by private ownership of the means of production, individual decision-making, and the use of market mechanisms to carry out the decision of individual
participants and facilitate the flow of goods and services in market.
(ii) Socialism: Socialism is generally understood as an economic system where the means of production are either owned or controlled by the state and where the resources allocation, investment pattern, consumption, income distribution, etc. are directed and regulated by the state.
(iii) Mixed economy: Mixed economy is the outcome of compromise between two diametrically opposing schools of thought. In a mixed economy, private, public and joint sectors and the like all have some say in the major decisions that influence the functioning of the economy. These are followed by the four important economic roles played by the government in a mixed economy viz. regularity role, promotional role, entrepreneurial role and planning role.
2. Economic Conditions or Factors
The economic conditions of a nation refer to a set of economic factors that have great influence on business organizations and their operations. These include gross domestic product, per capita income, markets for goods and services, availability of capital, foreign exchange reserve, growth of foreign trade, strength of capital market, interest rates, disposable income, unemployment, inflation, etc.
3. Economic Policies
All business activities and operations are directly influenced by the economic policies framed by the government from time to time. Some of the important economic policies are:
(i) Industrial policy: The Industrial policy of the government covers all those principles, policies, rules, regulations and procedures, which direct and control the industrial enterprises of the country and
shape the pattern of industrial development.
(ii) Fiscal policy: It includes government policy in respect of public expenditure, taxation and public debt.
(iii) Monetary policy: It includes all those activities and interventions that aim at smooth supply of credit to the business and a boost to trade and industry.
(iv) Foreign investment policy: This policy aims at regulating the inflow of foreign investment in various sectors for speeding up industrial development and take advantage of the modern technology.
(v) Export–Import policy (Exim policy): It aims at increasing exports and bridge the gap between expert and import. Through this policy, the government announces various duties/levies. The focus now-adays lies on removing barriers and controls and lowering the custom duties.
Political-Legal Environment
This is partly general to all similar enterprises and partly specific to an individual enterprise. It includes such factors as the general state of political development, the degree of politicization of business and economic issues, the level of political morality, the law and order situation, political stability, the political ideology and practices of the ruling party, the purposefulness and effciency of governmental agencies, the extent and nature of governmental intervention in the economy and the industry, Government policies (fiscal, monetary, industrial, labour and export-import policies), specific legal enactments and framework in which the enterprise has to function and the degree of effectiveness with which they are implemented, public attitude towards business in general and the enterprise in particular and so on. There are three important elements in political-legal environment.
(i) Government: Business is highly guided and controlled by government policies. Hence the type of government running a country is a powerful influence on business: A business has to consider the changes in the regulatory framework and their impact on the business. Taxes and duties are other critical area that may be levied and affect the business.
For Example: The Indian government is promoting manufacturing sector through campaigns like Make in India.
(ii) Legal: Businesses prefer to operate in a country where there is a sound legal system. However, in any country businesses must have a good working knowledge of the major laws protecting consumers, competitions and organizations. Businesses must understand the relevant laws relating to companies, competition, intellectual property, foreign exchange, labour and so on.
For Example: New GST law will influence most of the businesses.
(iii) Political: Political pressure groups influence and limit organizations. Apart from sporadic movements against certain products, service and organizations, politics has deeply seeped into unions. Also, special interest groups and political action committees put pressure on business organizations to pay more attention to consumers’ rights, minority rights, and so on.
Socio-Cultural Environment
This is too a general factor which influences almost all enterprises in a similar manner. It represents a complex of factors such as social traditions, values and beliefs, level and standards of literacy and education, the ethical standards and state of society,
the extent of social stratification, conflict and cohesiveness and so forth.
Socio-cultural environment consists of factors related to human relationships and the impact of social attitudes and cultural values which has bearing on the operations of the organization. The beliefs, values and norms of a society determine how individuals and organizations should be interrelated. The core beliefs of a particular society tend to be persistent. It is difficult for a business to change these core values, which becomes a
determinant of its functioning.
Some of the important factors and influences operating in the socio-cultural environment are:
- Social concerns, such as the role of business in society, environmental pollution, corruption, use of mass media, and consumerism.
- Social attitudes and values, such as expectations of society from business, social customs, beliefs, rituals and practices, changing lifestyle patterns, and materialism.
- Family structure and changes in it, attitude towards and within the family, and family values.
- Role of women in society, position of children and adolescents in family and society.
- Educational levels, awareness and consciousness of rights, and work ethics of members of society.
The social environment primarily affects the strategic management process within the organization in the areas of mission and objective setting, and decisions related to products and markets.
Reality Bite: The sale pattern in different parts of our country is different. For example, Diwali has a big impact in north, west and central India whereas in eastern India , major sales time is Durga pooja and in south the regional festivals dominate the maximum sales. |
Technological Environment :
The most important factor, which is controlling and changing people’s life, is technology. Man could realise the dream of walking on the moon, traveling in spaceships, and giving to the other side of the globe within a few hours.
Figure: Interface between Business & Technology
Technology has changed the way people communicate with the advent of Internet and telecommunication system. Technology has changed the ways of how business operates now. This is leading to many new business opportunities as well as making obsolete many existing systems. The following factors are to be considered for the technological environment:
The pull of technological change.
- Opportunities arising out of technological innovation.
- Risk and uncertainty of technological development.
- Role of R&D in a country and government’s R&D budget.
Technology can act as both opportunity and threat to a business. It can act as opportunity as business can take advantage of adopting technological innovations to their strategic advantage. However, at the same time technology can act as threat if organisations are not able to adapt it to their advantage. For example, an innovative and modern production system can act as threat if the business is not able to change its production system. New entrants can always use availability of technological improvements in products or
production methods that can be a threat to a business.
The technology and business are highly interrelated and interdependent. The fruits of technological research and development are available to society through business only and this also improves the quality of life of the society. Hence, technology is patronized by business. Then again technology also drives business and makes a total change on how it is carried out.
Using technology many organisations are able to reduce paperwork, schedule payments more efficiently, able to coordinate inventories efficiently and effiectively. This helps to flatten companies, and shrink time and distance, thus capturing a competitive advantage for the company. Because the technological aspects are so important, some of the key questions that can be asked in assessing the technological environment are given below:
- What are the technologies {both production and information technologies} used by the company?
- Which technologies are utilised in the company's business, products, or their parts?
- How critical is each technology to each of these products and businesses?
- Which external technologies might become critical and why? Will they remain available outside the company?
- What has been the investment in the product and in the process side of these technologies? For the company and for its competitors? Design? Production? Implementation and service?
- Which technological investments should be curtailed or eliminated?
- What additional technologies will be required in order to achieve business objectives?
- What are the implications of the technology on business portfolios
Global Environment
Today's competitive landscape requires that companies must analyse global environment as it is also rapidly changing. The concept of global village has changed how individuals and organizations relate to each other.
Further, new migratory habits of the workforce as well as increased offshore operations are changing the dynamics of business operation. Among the global environmental factors that should be assessed are:
- Potential positive and negative impact of significant international events such as a sport meet or a terrorist attack.
- Identification of both important emerging global markets and global markets that are changing. This includes shifts in the newly industrialised countries in Asia that may imply the opening of new markets for products or increased competition from emerging globally competitive companies.
- Differences between cultural and institutional attributes of individual global markets.

Due to economic reforms, the Indian firms are also out to see beyond the physical boundaries of the country. They are acquiring businesses in different countries. The need to think and act from global perspective is universal. For a long time, businesses everywhere believed that home markets were adequate and safe. They never felt the need to explore the overseas markets in a big way. "If they could pick up some extra sales
through exporting, these businesses were more than satisfied. The scenario is different now. The companies are increasingly interested in globalising.
|
21 videos|90 docs|24 tests
|
FAQs on ICAI Notes- Components of Business Environment - Business and Commercial Knowledge (Old Scheme) - CA Foundation
| 1. What are the components of the business environment? |  |
| 2. How does the economic environment affect businesses? |  |
| 3. What role does the social environment play in business? |  |
| 4. How does the technological environment impact businesses? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of the political and legal environment for businesses? |  |
|
21 videos|90 docs|24 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for CA Foundation exam
|

|


















