Concept of Finance - Interdisciplinary Issues in Indian Commerce | Interdisciplinary Issues in Indian Commerce - B Com PDF Download
Introduction to Finance
Finance generally refers to the provision of money when it is needed. More specifically, it involves the procurement of funds and their effective utilization. Financial management is the management of the flow of funds within a firm. Since all business decisions have financial implications, financial management is inherently related to every aspect of business operations.
Evolution of Finance
The evolution of finance can be categorized into three broad phases: the traditional phase, the transitional phase, and the modern phase.
1. The Traditional Phase (Up to 1940)
- During this phase, finance was considered a part of economic activities, and business owners focused more on operational activities.
- The finance function was episodic, meaning it was not a continuous process.
- Funds were primarily arranged from financial institutions or through the issuance of shares and debentures.
- The perspective of outsiders dominated this phase.
2. Transitional Phase (1940 – 1950)
- Although similar to the traditional phase, there was a greater emphasis on day-to-day financial activities.
- Funds analysis and control became more regular, moving away from a casual approach.
3. The Modern Phase (After 1950)
- Beginning in the mid-1950s, this phase was marked by rapid business growth and increased competition, elevating the importance of finance for both episodic and daily activities.
- The finance manager emerged as a professional responsible for raising funds, allocating them to various projects, and measuring the results of these allocations.
- Key characteristics of the modern phase include:
- Greater emphasis on the firm’s (insider’s) perspective.
- Rational matching of funds to their uses to maximize the wealth of current shareholders.
- A more analytical and quantitative approach to financial management.
Financial Decisions in a Firm
Financial decisions in a firm involve raising funds, investing in assets, and distributing returns to shareholders. These decisions are known as:
- Financing Decision: Involves raising funds.
- Investment Decision: Involves investing in assets.
- Dividend Decision: Involves distributing returns to shareholders.
A firm aims to balance cash inflows and outflows while making these decisions. There are three main areas of financial decision-making:
1. Capital Budgeting
Capital budgeting refers to the process of allocating funds to various long-term assets such as:
- Land
- Machinery
- Infrastructure
- Distribution networks
It also encompasses investing in specific projects that the firm intends to undertake.
2. Capital Structure
Capital structure involves determining the optimal mix of debt, equity, and hybrid securities for financing the firm’s activities. Once a firm identifies the investment projects it wants to pursue, it must decide how to finance them. Key considerations in capital structure decisions include:
- Optimal debt-equity ratio: Finding the right balance between debt and equity financing.
- Specific instruments: Choosing the appropriate financial instruments for raising capital.
- Capital markets: Deciding which capital markets to access for financing.
- Timing: Determining when to raise funds.
- Pricing: Setting the price for securities offered to investors.
Additionally, firms must consider the optimal dividend payout ratio, aiming to minimize financing costs while maintaining the ability to raise funds.
3. Working Capital Management
Working capital management, also known as short-term financing decisions, involves managing the firm’s day-to-day financing activities. This includes managing:
- Current Assets: Such as inventories, accounts receivable (debtors), short-term holdings of marketable securities, and cash.
- Current Liabilities: Including short-term debt, trade creditors, accruals, and provisions.
Key issues in working capital management include:
- Optimum inventory level: Determining the ideal level of inventory to maintain.
- Credit policy: Establishing the firm’s credit policy for customers.
- Short-term cash investments: Deciding where to invest short-term cash surpluses.
- Short-term financing sources: Identifying appropriate sources of short-term finance.
Functions of Finance
Finance plays a crucial role in the functioning of a business and involves three main types of decisions:
- Investment Decisions
- Financing Decisions
- Dividend Policy Decisions
Investment Decisions
Investment decisions involve allocating capital to various investment proposals with the expectation of future benefits. Assets can be categorized into:
- Long-term assets: These assets provide returns over an extended period. Examples include machinery, buildings, and land.
- Short-term assets: These assets can be converted into cash without significant loss in value, typically within a year. Examples include inventory, accounts receivable, and marketable securities.
Decisions regarding long-term assets are referred to as capital budgeting, while decisions about short-term assets fall under working capital management.
Financing Decisions
Financing decisions pertain to choosing the right mix of sources to finance the selected investment proposals. This primarily involves decisions related to the capital structure of the company, determining the proportion of debt and equity used to finance the assets.
Dividend Policy Decisions
Dividend policy decisions involve determining how to deal with the profits of the firm. There are two main alternatives:
- Distributing profits to shareholders in the form of dividends.
- Retaining profits within the business for reinvestment.
The final decision on dividend policy depends on the preferences of the shareholders and the availability of attractive investment opportunities for the firm.
Goals and Objectives of Financial Management
The goal of a firm serves as a benchmark for evaluating its operational performance. A clear understanding of this objective is crucial as it provides a framework for making optimal financial decisions. A good objective should possess the following characteristics:
- Clarity: The objective should be clear and unambiguous.
- Time Frame: There should be a timeframe to assess the success or failure of any decision.
- Consistency: The objective should be consistent with the long-term goals of the firm.
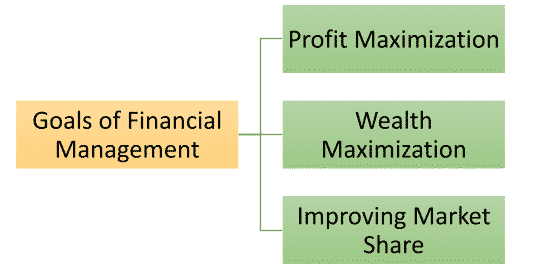
The two most discussed goals of financial management are:
1. Maximization of Profit: This is often considered the implied objective. Financial decisions are made with the aim of maximizing the firm’s profit, which also contributes to societal welfare and efficient resource allocation. However, this objective has limitations:
- It ignores risk.
- It overlooks the time value of money.
- It is vague and ambiguous.
- It may create a gap between management and shareholder perceptions.
Therefore, profit maximization is not a feasible objective for financial management.
2. Maximization of Shareholder’s Wealth: This objective is expressed in terms of maximizing the value of a share. It represents the present value of future cash flows expected by shareholders, discounted at a rate reflecting associated risks. The market price of a share reflects its present value and, therefore, the economic value of shareholders’ wealth. Financial decisions are evaluated based on the firm’s future cash flows, and this objective guides management in resource allocation within risk constraints.
- While this objective is operationally practical, it has limitations:
- It requires an efficient capital market where decision impacts are reflected in share prices.
- Share prices should not be influenced by speculative activities.
Despite these limitations, wealth maximization is considered a superior objective to profit maximization.
Conflicts of Interest between Management and Owners: Agency Issues
- In companies, there is a separation between owners and management.
- The management team is made up of professionals who possess the necessary qualifications and technical expertise to run the business effectively.
- However, because owners (shareholders) and managers have different interests, conflicts can arise.
- To address these agency problems, it is essential to implement effective monitoring and offer appropriate incentives.
Organisation of the Finance Function
Structure and Organisation of Finance Department
A firm should pay careful attention to how it structures and organises its finance department, as this can vary from company to company based on their specific needs.
Titles of Key Finance Officers
The titles used for the key finance officer can differ between companies. Some examples include:
- Vice President (Finance)
- Chief Executive (Finance)
- General Manager (Finance)
- Director (Finance)
- Chief Finance Officer (CFO)
Role of the Chief Finance Officer (CFO)
- The CFO plays a crucial role in supervising the work of the treasurer and controller.
Responsibilities of the Treasurer
The treasurer is responsible for:- Obtaining finance
- Managing banking relationships
- Overseeing cash management
- Administering credit
- Managing corporate bonds
Responsibilities of the Controller
The controller is responsible for:- Financial accounting
- Internal auditing
- Taxation
- Management accounting and control
Other Key Roles in Finance Department
- Cash Manager
- Corporate Bonds Manager
- Portfolio Manager
- Fundraising Manager
- Credit Manager
- Financial Accounting Manager
- Tax Manager
- Cost Accounting Manager
- Data Processing Manager
- Internal Auditor
Relationship of Finance to Other Areas of Management
1. Relationship to Economics:
- Macro Economics: Defines the environment in which a firm operates.
- Micro Economics: Provides tools for financial decision-making.
2. Relationship to Accounting:
- Record-Keeping vs Value Maximizing: Accounting focuses on record-keeping and performance measurement, while finance aims to create shareholder value through positive NPV projects.
- Accrual Method vs Cash Flow Method: Accounting deals with cash-flow, whereas finance considers the magnitude, timing, and risk of cash-flows.
- Certainty vs Uncertainty: Accounting relies on past data, making it more certain, while finance deals with future uncertainties.
3. Relationship to Marketing:
- Finance plays a crucial role in setting product prices, which directly impact a firm's success or failure.
4. Relationship to Production Department:
- Decisions made by the production department have a direct impact on the firm's financial position.
- All production decisions should align with the goal of maximizing shareholder wealth, highlighting the finance manager's important role.
5. Relationship to Personnel Management:
- The personnel department is responsible for recruiting, training, and placing staff, all of which require financial considerations.
- Decisions regarding these aspects cannot be made in isolation from the finance department.
|
52 videos|57 docs|14 tests
|
FAQs on Concept of Finance - Interdisciplinary Issues in Indian Commerce - Interdisciplinary Issues in Indian Commerce - B Com
| 1. What are some of the major interdisciplinary issues in Indian commerce? |  |
| 2. How does globalization affect Indian commerce? |  |
| 3. What role does technology play in Indian commerce? |  |
| 4. How does environmental sustainability impact Indian commerce? |  |
| 5. What are some ethical considerations in Indian commerce? |  |






















