Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Conservation of Energy
Conservation of Energy | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
Conservation of Energy
- The conservation of energy principle asserts that energy cannot be created nor destroyed; rather, it can only transition between different energy stores.
- In essence, for a closed system, the total energy remains constant over time.
- The total energy inputted into the system equals the total energy outputted from it.
- Consequently, energy cannot vanish; however, it can be transferred to the surroundings.
- Energy dispersion to the surroundings commonly occurs through processes like heating and radiation.
- These dissipated energy transfers are frequently non-utilizable and are thus referred to as wasted energy.
Energy Flow Diagrams
- Energy stores and transfers can be illustrated through a flow diagram.
- Such a diagram visually represents both the various energy stores and the transfers occurring within a system.
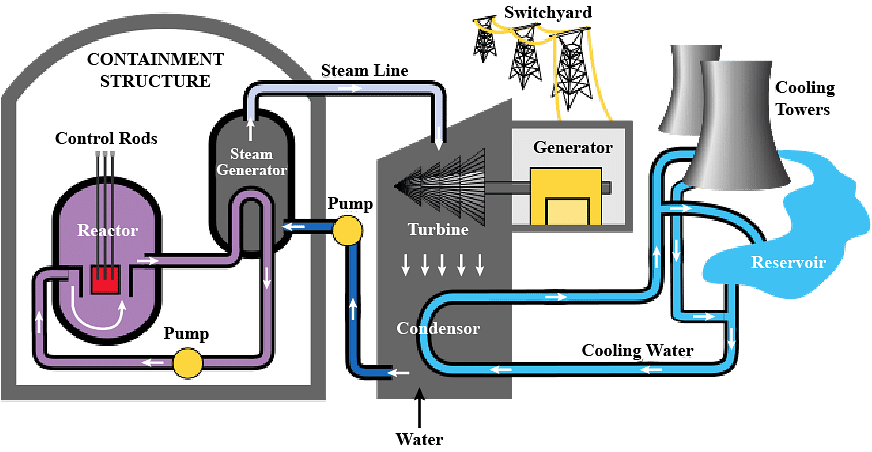 Energy flow diagram showing energy stores and transfers in a nuclear power plant.
Energy flow diagram showing energy stores and transfers in a nuclear power plant.
Question for Conservation of EnergyTry yourself: According to the conservation of energy principle, what happens to energy in a closed system?View Solution
Sankey Diagrams
- Sankey diagrams are a visual tool that illustrates energy transfers. They are characterized by arrows that split to show the proportions of energy moving between different components.
- The different segments of a Sankey diagram represent various energy transfers:
- The left side of the arrow (the flat end) symbolizes the energy entering the system.
- The straight arrow pointing right depicts the energy that is utilized or ends up in the intended destination, which is the useful energy output.
- Arrows bending away signify the energy that is wasted.
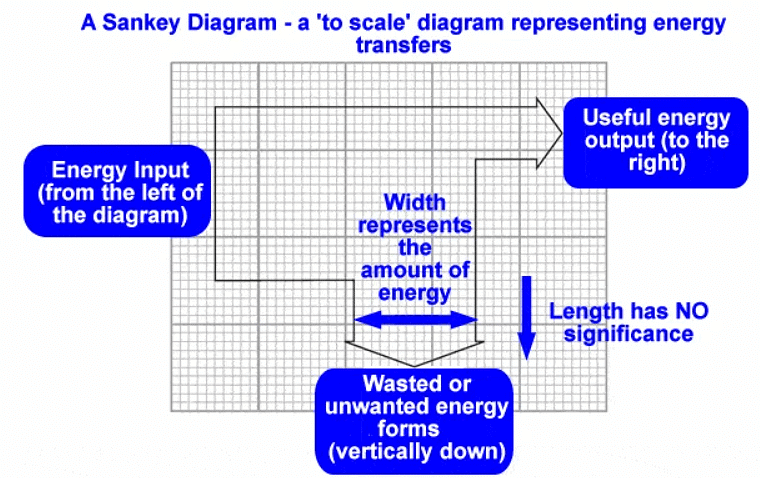
- The width of each arrow in a Sankey diagram corresponds to the amount of energy being transferred.
- Energy conservation principle holds: Total energy in = Useful energy out + Wasted energy
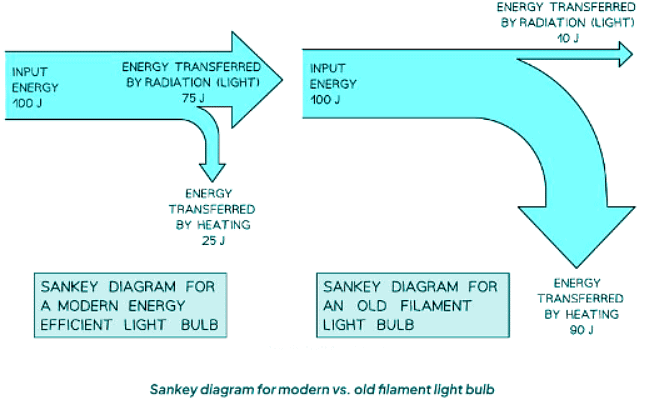
- A Sankey diagram for a modern efficient light bulb differs significantly from that of an old filament bulb.
- A more efficient bulb shows less wasted energy, depicted by a smaller downward arrow representing heat energy.
The document Conservation of Energy | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
127 videos|148 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Conservation of Energy - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What is the principle of conservation of energy? |  |
Ans. The principle of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred or transformed from one form to another.
| 2. How do energy flow diagrams represent the flow of energy in a system? |  |
Ans. Energy flow diagrams use arrows to show the direction and amount of energy transferred between different components of a system, illustrating how energy is transferred and transformed within the system.
| 3. What is the purpose of using Sankey diagrams in energy analysis? |  |
Ans. Sankey diagrams are used to visually represent the flow of energy within a system, making it easier to understand the inputs, outputs, and energy losses within the system, aiding in energy efficiency analysis.
| 4. How can Sankey diagrams help in identifying areas for energy conservation in a system? |  |
Ans. By visually displaying the flow of energy within a system, Sankey diagrams can help identify areas where energy is being wasted or lost, allowing for targeted energy conservation measures to be implemented.
| 5. How are energy flow diagrams and Sankey diagrams useful tools for analyzing energy efficiency in various systems? |  |
Ans. Both energy flow diagrams and Sankey diagrams provide a clear visual representation of how energy is being used within a system, allowing for easy identification of inefficiencies and opportunities for energy conservation and optimization.
Related Searches





















