Constellations | General Knowledge for Young Learners - Class 1 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What are Constellations? |

|
| Uses of Constellations |

|
| Zodiac Constellations |

|
| Big Dipper |

|
| Orion Constellations |

|
| Taurus Constellation |

|
| Gemini Constellation |

|
| Cassiopeia Constellation |

|
What are Constellations?
- Constellations are recognizable patterns of stars in the night sky.
- The term constellation comes from the Latin word constellatus, which means a group of stars.
- A constellation consists of many stars, but these stars are usually not as close together in space as they seem from Earth.
- In the sky, constellations appear to move from west to east. This movement happens because the Earth rotates from west to east.
- Due to the round shape of the Earth, some constellations are not visible from certain locations.
- For example, constellations visible in the Northern Hemisphere cannot be seen in the Southern Hemisphere, and the same is true in reverse.
- However, a person standing at the equator can see nearly all the constellations that are present in our sky.
Currently, there are 88 officially recognized constellations in the night sky, covering both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. These constellations symbolize a variety of figures: 19 land animals, 14 humans, 10 aquatic creatures, 2 insects, 9 birds, 2 centaurs, 1 lock of hair, and 29 inanimate objects. Out of the total, only about 60 constellations can be fully observed at some point during the year.
Uses of Constellations
- Constellations were recognized by common people for various reasons, including:
- They helped in figuring out the seasons for farming even before new calendars were created.
- Explorers and navigators used constellations to make their travels easier by tracking their positions in the sky. This technique, called celestial navigation, has been widely used.
- The celestial objects in the universe can be described using the constellations visible in the sky. Many nebulae, stars, and other cosmic objects are named after the constellations they are found in.
For instance, the Orionids meteor shower, which happens every October, seems to come from the direction of the Orion Constellation, also known as the Hunter.
Zodiac Constellations
- The ecliptic plane is a path in the sky where the sun seems to travel throughout the year.
- There are 12 zodiac constellations recognized in astrology, but astronomically, there are actually 13 zodiac constellations.
The 12 zodiac constellations are:
- Aries (Mesha)
- Taurus (Vrushabha)
- Gemini (Mithuna)
- Cancer/Crab (Karka)
- Leo (Simha)
- Virgo (Kanya)
- Libra (Tula)
- Scorpion (Vruschika)
- Sagittarius (Dhanusha)
- Capricorn (Makara)
- Aquarius (Kumba)
- Pisces (Meena)
The 12 zodiac constellations are primarily aligned along the sun’s path, which is called the ecliptic.
These major constellations were often used to track time through the location of these constellations and by the movement of the sun in ancient times.
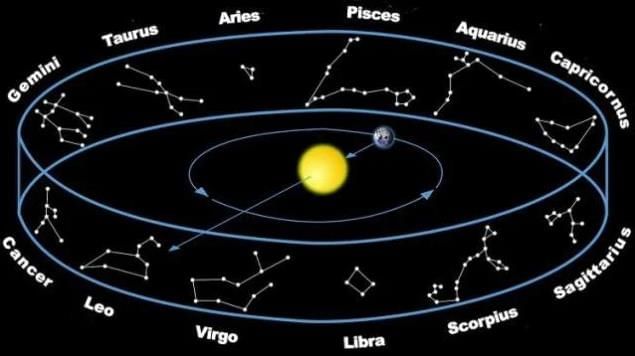 Zodiac Constellations
Zodiac Constellations
The 12 zodiac signs of the horoscope mark the Earth’s journey through the heavens. These constellations outline the path followed by the sun. As the Earth revolves around the sun, it gives the impression that the sun passes through different constellations. Similarly, just as the moon’s position appears to shift each night, the sun also seems to move eastward relative to the distant stars. In reality, the sun itself does not change position; this apparent movement is simply the result of the Earth’s motion around it.
Big Dipper
Saptarishi, also known as the Big Dipper, is a constellation made up of seven stars.- It is visible in the Northern Hemisphere and is part of a larger constellation called Ursa Major, which means The Great Bear.
- This constellation can usually be seen during the early part of summer.
- The shape of the Big Dipper resembles a large ladle, consisting of 7 main stars:
- 3 stars form the handle
- 3 stars make up the bowl
- Its appearance is similar to a wheelbarrow or a big ladle.
- Two stars in the Big Dipper point towards the Pole Star, also known as Dhruva or Polaris.
- The Pole Star is unique because it does not move from East to West in the night sky; it looks fixed.
- This fixed position of the Pole Star is due to its location directly above the Earth's axis.
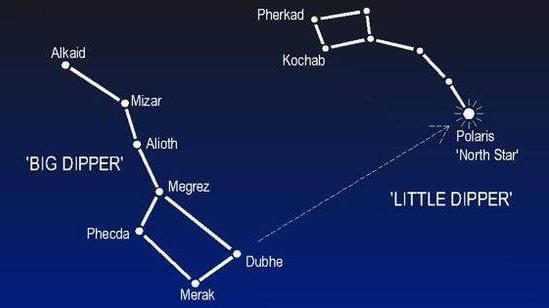
Big Dipper and Little Dipper pointing towards Polaris
Little Dipper: The constellation known as the Little Dipper, or Ursa Minor (“The Little Bear”), can be located in the night sky with the help of the Big Dipper. By focusing on the right side of the cup-shaped part of the constellation and tracing a straight line northward, one can find the North Star, Polaris. Polaris lies at the end of the Little Dipper’s handle, which forms the cup of the bear, while the stars extending from it make up the bear’s tail and part of its side.
Orion Constellations
The constellation Orion, often referred to as “the hunter”, is known in India as Mriga. It is made up of several bright stars, with its distinctive belt formed by three luminous stars arranged in a straight line. This line of stars points directly to Sirius, the brightest star visible in the night sky. Orion is most easily seen during winter evenings.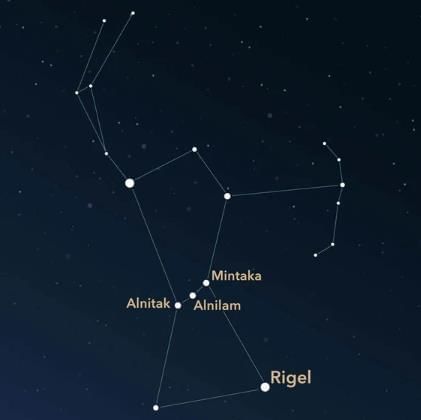
Taurus Constellation
- The Taurus constellation, often called "The Bull", is situated above the Orion constellation in the night sky.
- It is quite easy to find Taurus compared to other constellations.
- You can spot the Taurus constellation by looking for Aldebaran, which is a prominent large red star.
- The bottom of the horn in Taurus is associated with the Crab Nebula.
- This collection of stars can be seen with the naked eye without any telescopes.
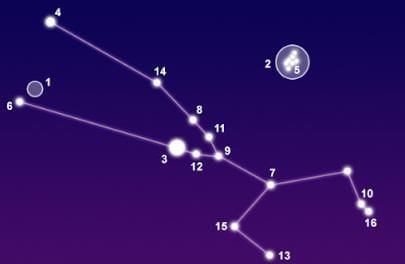 Taurus Constellation
Taurus Constellation
Gemini Constellation
- The Gemini constellation is often referred to as "The Twins."
- This constellation is easy to find by looking for Orion.
- It can be spotted above one side of the raised arm of the hunter in Orion.
- The appearance of the constellation resembles two stick figure twins reaching out with their arms.
- Each twin has recognizable torsos, heads, and legs that can be seen clearly.
- To identify the twins, look for the two brightest stars in the constellation.
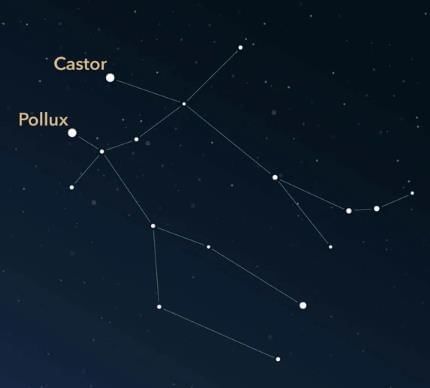 Gemini Constellation
Gemini Constellation
Cassiopeia Constellation
- Cassiopeia is a constellation visible in the winter sky during the early evening.
- The shape of this constellation looks like a W or an M.
- This constellation is bright enough to be seen even in city lights.
- When you look up at the night sky next time, see if you can find the different constellations above you.
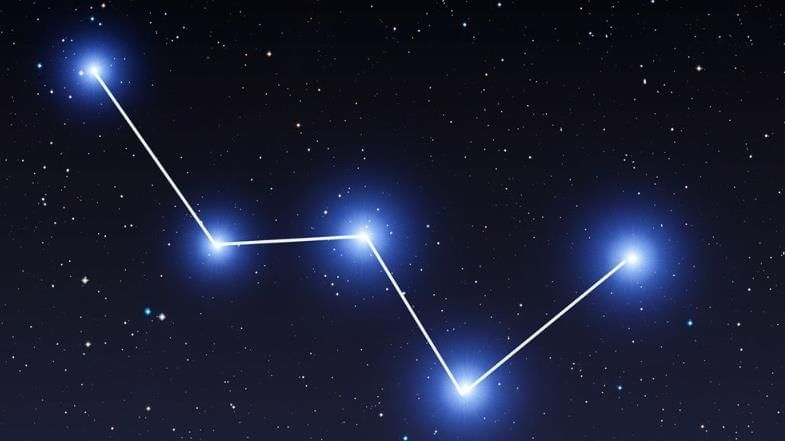 Cassiopeia Constellation
Cassiopeia Constellation
Things to Remember
- Constellations are recognizable patterns formed by groups of stars in the night sky.
- They appear to move from west to east due to the Earth’s rotation from west to east.
- In ancient times, constellations were used to identify seasonal changes in agriculture before modern calendars existed.
- Many celestial objects in the universe are studied and explained with the help of constellations.
- Orion, also called “the hunter”, consists of many bright stars.
- Gemini, known as “the twins”, can be easily located using Orion as a reference point.
|
64 videos|153 docs|40 tests
|
FAQs on Constellations - General Knowledge for Young Learners - Class 1
| 1. What are constellations and how are they defined? |  |
| 2. What are some common uses of constellations in modern times? |  |
| 3. What are zodiac constellations and how do they differ from other constellations? |  |
| 4. Can you describe the Big Dipper and its significance? |  |
| 5. What are some characteristics of the Orion constellation? |  |




















