Construction Materials: Structural Steel | Construction Materials & Management - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
Introduction
As far as the carbon content is concerned, steel forms an intermediate stage between cast iron and wrought-iron. In cast iron, carbon content varies between 2–4%. In wroughtiron, carbon content does not exceed 0.15%
- In steel, carbon content varies between 0.25–1.5%.
- If carbon content exceeds 1.5%, it does not combine with iron. It remains as free graphite.
- If there is no free graphite in the composition of material, it is said to be steel. If there is presence of free graphite, then it indicates cast-iron.
Depending upon carbon content, steels can be classified as mild steel, or medium carbon steel, or high carbon steel.
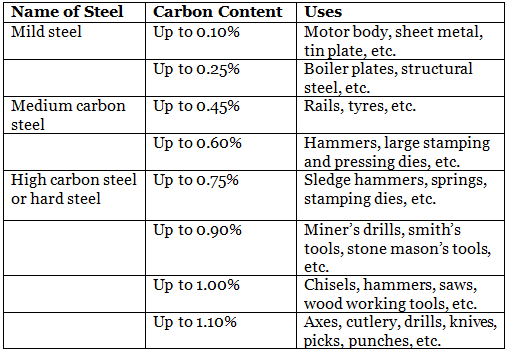
- The carbon content in mild steel varies between 0.10– 0.25%. When carbon content is less than 0.10%, it is known as dead steel or very low carbon steel.
- The carbon content in medium carbon steel varies between 0.25–0.60%.
- In high carbon steel, also known as hard steel, carbon content varies between 0.60–1.10%
Uses of steel
Properties: Mild Steel Vs Hard Steel

Defects in steel
The following four types of defects are found in steel.
- Cavities/blow-holes: Cavities or blow-wholes are formed when gas is confined in the molten mass of metal. This confined gas produces bubbles or blowholes on solidification of metal.
- Cold shortness: Steel with this type of defect cracks when worked in cold state. This defect imparts due to presence of excess amount of phosphorusin the steel.
- Red shortness: Steel having this defect cracks when worked in hot state. This defect happens due to presence of excess amount of sulphur in the steel.
- Segregation: Some constituents of steel solidify at an early stage. Those are separated out from the main mass. This process is known as segregation.
Steel Manufacturing Processes
The following processes are used in manufacturing of steel.
- Bessemer process
- Cementation process
- Crucible steel process
- Duplex process
- Electric process
- LD Process (Linz-Donawitz process)
- Open-hearth process
Mechanical Treatment of Steel
- The purpose of giving mechanical treatment to steel is to give desired shape to the ingots to make steel available in marketable forms.
- Mechanical treatment of steel requires the following types operations.
Drawing
- This operation is carried out to reduce the cross-section and to increase the length proportionately.
- This process is used to prepare wires and rods.
Forging
- This operation is carried out by giving repeated blows under a power hammer or press.
- This increases the density and improves grain size of metal.
- Forging is used for manufacture of bolts, cramps and in riveting, etc.
Pressing
- It is a slow process, carried out using in equipment known as press.
- The main advantage of this process is it does not involve any shock. Pressing is useful in manufacturing large number of uniform type engineering products.
Rolling
- It is carried out in specially prepared rolling mills.
- Using rolling process, various shapes, such as angles, channels, flats, joists, rails, etc., are manufactured.
The physical properties of steel, such as ductility, elasticity, strength, etc., are greatly influenced by the following three factors.
1. Carbon content: Carbon assists in increasing the hardness and strength of steel, but decreases the ductility of steel.
- Mild steel with carbon content of about 0.10– 0.25% is widely used in structural work.
2. Presence of impurities: Silicon, phosphorous and manganese are the common impurities in found in steel.
- If silicon content is raised about 0.3–0.4%, elasticity and strength of steel are considerably increased without serious reduction in its ductility.
- Excess amount of sulphur decreases strength, ductility, malleability and weldability of hot metal.
- Presence of excess phosphorus reduces shock resistance, ductility and strength of steel.
- When manganese content exceeds about 1.5%, steel becomes very brittle, and hence loses its structural value.
Common Impurities and Desirable Limits 3. Heat treatment processes:
3. Heat treatment processes:
- The properties of steel can be altered by heating and cooling under controlled conditions.
- The term ‘heat treatment’ is used to indicate the process in which the heating and cooling of solid steel is involved in changing the structural or physical properties of steel.
- Heat treatment is used for the following purposes:
- To alter magnetic and electrical properties of steel.
- To change the structure of steel
- To increase resistance against heat and corrosion.
- To increase surface hardness.
- To make the steel easily workable.
- To vary the strength and hardness.
- The principal process involved in heat treatment of steel are:
- Annealing
- Case hardening
- Cementing
- Cyaniding
- Hardening
- Nitriding
- Normalizing
- Tempering
Market form of Steel
Various forms of steel available in the market are:
- Angle sections
- Channel sections
- Corrugated sheets
- Expanded metal
- T-sections
- I-sections
- Plates
- Ribbed (HYSD) bars
- Round bars
- Square bars
- Flat bars
- Ribbed mild steel bars
- Thermo-mechanically treated (TMT) bars
- Cold twisted deformed (CTD) bars
- Welded wire fabrics (WWF)
|
5 videos|19 docs|16 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|

















